The Project 677 Lada Class diesel-electric submarines are being built by Admiralty Shipyard for the Russian Navy. The class is also called the Petersburg Class, after the lead submarine. The Lada Class succeeds the Kilo Class submarines.
The keel for the lead sub in class, Sankt-Petersburg (B-585), was laid down in December 1997 and launched in October 2004. The submarine was delivered to the Russian Navy in April 2010 and commissioned in May 2010.
 B-585 St. Petersburg – kollektsiya.ru
B-585 St. Petersburg – kollektsiya.ru
The keel for the second submarine, Kronshtadt (B-586), was laid in July 2005 and the launching ceremony was held in September 2017. Commissioning of the Kronshtadt submarine is scheduled for 2019.
The keel-laying ceremony of the third submarine, formerly known as Sevastopol (B-587), was held in November 2006. The submarine was renamed as Velikie Luki and re-laid in February 2015 due to a redesign, after continuous delays. The launch of Velikie Luki is expected to take place in 2019, with commissioning slated for 2021.
The Russian Navy plans to procure a total of eight Lada Class submarines.
 B-587 Velikiye Luki – Ruptly
B-587 Velikiye Luki – Ruptly
Project 677 , code “Lada”
Project 677E
Construction
Pr.677 – St. Petersburg, “Admiralty Shipyards” – 1 + 2 units
|
Name
|
Factory
|
Fulfilled
|
Launched on the water
|
Entry into service
|
Note
|
|
B-585 St. Petersburg
|
№01570
|
12/26/1997
|
10/28/2004
|
04/22/2010
|
|
|
B-586 Kronshtadt
|
№01571
|
28.07.2005
|
plan 2018
|
plan 2020
|
in the construction |
|
B-587 Sevastopol
|
№01572
|
10.11.2006
|
–
|
plan 2019
|
in the construction, from 27.01.2012? – B-587 Velikiye Luki |
Pr.677E – St. Petersburg, “Admiralty Shipyards” – 0 + 1 unit
|
Name
|
Factory
|
Fulfilled
|
Launched on the water
|
Entry into service
|
Note
|
|
B-
|
–
|
12/26/1997
|
–
|
–
|
in the construction |
Source russianships.info
 B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале
B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале
B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале
B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале
Planned versions
The engineering office Rubin, in liaison with the Chantiers de l’Admiralty, is proposing, alongside the project 677 for the Russian Navy, an export version called AMUR, and available in several versions. They are all designed to accommodate the KRISTALL-27E anaerobic propulsion system. The engineering firm Rubin announces that it can also equip them with the Siemens AIP system that equips German U-212 / U-214 submarines. The tonnage varies from 550 to 1850t in surface, and the equipment is of course adaptable to the wishes of the customers. No orders seem to have been obtained for the time being.
In addition, there are many variants. We can retain the following principal:
Source soumarsov.eu
Amur 1650
 ckb-rubin.ru
ckb-rubin.ru
Based on many years of experience in operation by the Russian Navy and fleets of other countries in various regions of the World Ocean of diesel-electric submarines of projects 613 (Whiskey), 641 (Foxtrot), 641B (Tango), class Kilo, TsKB MT “Rubin” developed projects of non-nuclear submarines of the fourth generation of the class “Amur” (Amur 1650 and Amur 950).
The submarine “Cupid 1650” has a smaller displacement compared to submarines of the “Kilo” class. Its distinctive features include the possibility of salvo missile fire at sea and ground targets of up to six missiles in a volley, the availability of modern radio-electronic weapons and a hydroacoustic complex with a unique noise-sending antenna that can detect particularly low-noise targets at a great distance.
 Amur 1650 – ckb-rubin.ru
Amur 1650 – ckb-rubin.ru
The level of the acoustic field of the submarine “Amur 1650” is several times lower than that of the “Kilo” class submarines, which are considered to be the lowest noise in the world today. The submarine is equipped with a new generation of electronic weapons, using the achievements of world radio electronics in recent years.

Amur 1650 aoosk.ru
It is possible to equip the submarine with an air-independent power plant with electrochemical generators, which makes it possible to significantly increase the underwater autonomy and range of navigation. Such an installation with reagent stocks is placed in a special compartment-module, which can be built into the submarine both during construction, and during repair or modernization.
The submarine can be operated in any areas of the World Ocean, except areas with a solid ice cover, under any weather conditions, in shallow and deep water areas.
When creating a submarine, equipment and armament of both Russian production and the customer country or equipment of third countries can be used. Amur-1650 data Translated by google – Source ckb-rubin.ru
Amur 950
 ckb-rubin.ru
ckb-rubin.ru
The submarine “Amur 950″ has a smaller displacement compared to the submarines of the class ” Kilo ” and “Amur 1650″. The peculiarity of the submarine is the presence of 10 universal vertical launchers of the ” Club – S ” missile system , which makes it possible to carry out a 10-missile salvo with cruise missiles for maritime and land targets for no more than 2 minutes. For self-defense, there are small-sized hydroacoustic countermeasures devices placed in launchers in the superstructure of submarines.
The integrated combat control system with the latest radio electronic subsystems allows solving all the tactical tasks facing non-nuclear submarines. Due to the relatively small displacement, the submarine “Amur 950” will have an advantage over submarines of similar class by the criterion “efficiency-cost”.
 Amur 950 – ckb-rubin.ru
Amur 950 – ckb-rubin.ru
The level of the acoustic field of the submarine “Amur 950” is several times lower than that of the “Kilo” class submarines, which are considered to be the lowest noise in the world today. The submarine is equipped with a new generation of electronic weapons, using the achievements of world radio electronics in recent years.
Amur 950 aoosk.ru
It is possible to equip the submarine with an air-independent power plant with electrochemical generators, which makes it possible to significantly increase the underwater autonomy and range of navigation. Such an installation with reagent stocks is placed in a special compartment-module, which can be built into the submarine both during construction, and during repair or modernization.
The submarine can be operated in any areas of the World Ocean, except areas with a solid ice cover, under any weather conditions, in shallow and deep water areas.
When creating a submarine, equipment and armament of both Russian production and the customer country or equipment of third countries can be used. Amur-950 data Translated by google – Source ckb-rubin.ru
 B-585 St. Petersburg – kollektsiya.ru
B-585 St. Petersburg – kollektsiya.ru
Lada Class missions capabilities
The Project 677 submarine is an improved version of the Project 636 Kilo Class with much quieter, powerful propulsion and new combat systems. The fourth-generation submarines can be deployed in anti-submarine warfare (ASW) and anti-surface warfare (AsuW) operations, protection of naval bases, reconnaissance and patrol missions.
The export variant of the Lada Class, the Project 1650 Amur Class has been designed for markets such as India and China. Amur Class is offered in various configurations with a displacement of 550t to 1,850t, and different weapon systems.
Performance
The submarine is designed for antisubmarine/antiship/antiaircraft warfare, protection of naval bases, seashore and sea lanes, conducting of reconnaissance. Source rusnavy.com
Lira – Hull Sonar, Active/Passive
| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: Hull Sonar, Active/Passive | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 27.8 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Late 2000s |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| Lira [Hull] – Hull Sonar, Active/Passive Role: Hull Sonar, Active/Passive Search Max Range: 27.8 km |
Source cmano-db.com
MGK-400 Rubikon Suite
The MGK-400EM modernised sonar system is designed for surveillance underwater and surface sea situation to enable actions and weapon application of a submerged submarine.
The MGK-400EM sonar system can be installed on nonnuclear submarines and to perform the following missions:
- search, detection and taking bearing to submarines, surface ships and torpedoes by their noise emission;
- automatic target tracking;
- intercept of sonar signals transmitted from submarines, surface ships and torpedoes;
- detection, localization of the target and distance measuring in active sonar mode;
- mine search and detection of navigation obstacles;
- automatic target classification and targeting to underwater weapons;
- underwater communication in low frequency band, high-frequency band communication, identification “friend-or-foe” and measuring of the distance (MD) to correspondent;
- monitoring of sonar background noise;
- prediction of sonar operation range;
- automatic testing and troubleshooting of sonar system.
MGK-400EM sonar system features advanced antennas with new piezoelectric ceramic compounds and electro acoustic transducers of improved design.
Source roe.ru
 B-585 St. Petersburg – igorrgroup.blogspot.com
B-585 St. Petersburg – igorrgroup.blogspot.com
Squid Head MRP-25 (Bald Head + Rim Hat RWR Element)
| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: ESM | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 222.2 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Early 1980s |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| Squid Head [MRP-25] – (Bald Head + Rim Hat RWR Element) ESM Role: RWR, Radar Warning Receiver Max Range: 222.2 km |
Source cmano-db.com
Quad Loop DF – ESM
| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: ESM | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 926 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Late 1970s |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| Quad Loop DF – ESM Role: HF/DF Max Range: 926 km |
Source cmano-db.com
Lada Class design features
 Amur 1650 – ckb-rubin.ru
Amur 1650 – ckb-rubin.ru
Lada Class diesel-electric submarines are designed by the Russian Rubin Design Bureau. The ship incorporates a mono-hull design. The surface displacement was reduced to 1,765t from 2,300t of the double-hulled Kilo Class submarine.
The full submerged speed has been increased from 19kt to 21kt, and crew complement has been decreased from 52 to 35.
 B-585 St. Petersburg – igorrgroup.blogspot.com
B-585 St. Petersburg – igorrgroup.blogspot.com B-585 St. Petersburg – Vitaly V. Kuzmin
B-585 St. Petersburg – Vitaly V. Kuzmin
 B-585 St. Petersburg – Vitaly V. Kuzmin
B-585 St. Petersburg – Vitaly V. Kuzmin B-585 St. Petersburg – igorrgroup.blogspot.com
B-585 St. Petersburg – igorrgroup.blogspot.com
The submarine has a trimmed profile equipped with sophisticated torpedo and missile systems. The hull is covered with a new anti-sonar coating for low acoustic signature.
Lada Class uses hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells generating electricity for low noise operation. The submarine is fitted with Litiy automated combat control system. The integrated system controls the combat and technical systems of the submarine.
Unique AIP design
 stratpost.com
stratpost.com
The Russian AIP design is unique because hydrogen required for power generation is obtained by means of diesel fuel reforming onboard the submarine. Hydrogen is not stored onboard and is produced as much as needed, which increases the safety of the propulsion plant. Ordinary diesel fuel, which is standard for all diesel-electric submarines, is used for generating hydrogen. It needs no extra component and, hence, extra reservoir for storage. There is also no need for special infrastructure on shore to generate and store hydrogen. To cap it all, the AIP features low noise and high efficiency. Source strategic-culture.org
 oosk.ru
oosk.ru
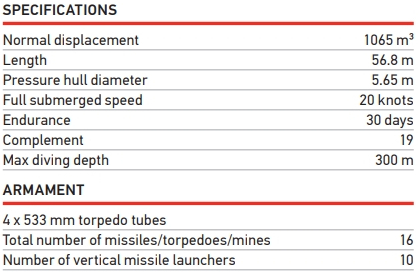
The Lada Class has a surface speed of 10kt and submerged speed of 21kt. The propulsion system provides a submerged cruising range of 7,500nmi at an economical speed of 3kt. The maximum diving depth is 300m. The submerged displacement of the boat is 2,700t.
Russia to Upgrade its First Project 677 Lada-class Submarine St. Petersburg: Here
Weapon systems onboard the Project 677 Lada Class diesel-electric submarines
Lada Class is armed with club-S submarine-launched cruise missiles. The missile can be fired from standard torpedo tubes.
 Closeup of torpedo hatches on the B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале
Closeup of torpedo hatches on the B-586 Kronshtadt – Новости на Первом Канале
Club-S carries up to 400kg warheads and can strike land and naval targets within a range of 300km. The six 533mm torpedo tubes fitted on the ship can launch up to 18 torpedoes, tube-launched anti-submarine and anti-ship missiles.
Club-S Integrated missile systems
Mission
High-performance submarine-based Club-S and ship-based Club-N integrated missile systems are designed to engage surface ships and submarines in conditions of intensive enemy fire and electronic countermeasures. Both systems employ unified combat assets – two types of anti-ship cruise missiles and an anti-submarine ballistic missile. Club-N missile system features standardized launch units and transport-launch containers.
Composition
Integrated missile systems include:
- 3M-54E anti-ship cruise missile (Club-S) comprises a booster, low-altitude subsonic sustainer, and a separable supersonic warhead. 3M-54TE ASM (Club-N) features a TLC to ensure vertical launch;
- 3M-54E1 ASM (Club-S) comprises a booster and a low-altitude subsonic sustainer. 3M-54TE1 ASM (Club-N) differs from 3M-54E1 only by having a TLC;
- 3M-14E land-attack cruise missile (Club-S system) consists of a booster and a low-flying subsonic sustainer. Launched from the Club-N system this missile is designated the 3M-14TE, with the only difference being a TLC;
- 91RE1 anti-submarine ballistic missile (Club-S) performs a controlled flight to the target area. Its separable warhead is a high-speed homing torpedo with a sonar target seeker.
91RTE2 anti-submarine ballistic missile (Club-N) differs from 91RE1 missile in size and booster design Source roe.ru
SS-N-27 “Sizzler”
The SS-N-27 “Sizzler” is a Russian short-range ship-, and submarine-launched anti-ship missile. The Sizzler is part of the Kalibr family of missiles and has several export versions known as the ‘Klub’ missile series.
Originated From: Russia
Possessed By: Russia, Algeria, China, India, Iran, Vietnam
Alternate Names: SS-N-27, SS-N-27A, SS-N-27B, Sizzler, 3M54, 3M54M, 3M54E, 3M-54E1, 3M54TE, 3M54TE1, 3M54AE, 3M54AE1
Class: anti-ship cruise missile
Basing: submarine- ship-launched
Length: 8.22 m for 3M54 (6.2 m for 3M54M1)
Diameter: 0.534-0.645 m
Launch Weight: 1,920 kg for 3M54 (1,570 kg for 3M54M1)
Payload: single conventional warhead
Warhead: 1X200 kg HE for 3M54 (1X450 kg HE for 3M54M1)
Propulsion: solid propellant, turbojet (3M54 is three stage, 3M54M1 is two stage)
Range: 220 km (3M54), 300 km (3M54M1)
Status: Operational
In Service: 1987
Source missilethreat.csis.org
SS-N-30A (3M-14 Kalibr)
The SS-N-30 (3M-14 Kalibr) is a Russian land attack cruise missile (LACM), and improved version of the 3M-14E “Club” LACM. The SS-N-30A has an estimated range of around 1,500 to 2,500 km and has become a mainstay in the Russian Navy’s ground-strike capabilities.
Originated From: Russia
Possessed By: Russia
Alternate Name: 3M-54, Kalibr
Class: Sea-launched Land Attack Cruise Missile
Basing: Ship/Submarine-based
Length: 6.2 m
Payload: 450 kg warhead: High explosive, possibly nuclear capable
Propulsion: Turbojet
Range: 1,500-2,500 km
Status: Operational
In Service: 2015-present
Source missilethreat.csis.org
91RE1 anti-submarine ballistic missile
The 91RE1 Club-N is a submarine-based ballistic missile designed to engage submarines using its warhead which includes a small-size MPT-1UME torpedo fitted with an active homing head. It is suitable for engagements of hostile submarines located at 50 km. It utilizes an Inertial Navigation System (INS) based guidance system to reach the target area. The 91RE1 and 91RTE2 ballistic missiles differ in size and booster design. They are expected to replace the SS-N-15 and SS-N-16 missiles in the Russian Navy.
Dimensions
Diameter: 533 millimeter (21.0 inch)
Length: 8 meter (315 inch)
Performance
Max Range: 50,000 meter (27.0 nautical mile)
Speed
Top Speed: 830 mps (2,989 kph)
Weight
Warhead: 76 kilogram (168 pound)
Weight: 2,050 kilogram (4,519 pound)
Source deagel.com
Futlyar 533mm torpedo (UGST (Fizik-1)?)
 Image: nevskii-bastion.ru
Image: nevskii-bastion.ru
CHARACTERISTICS
Caliber mm 533 – 534.4
Length, mm 7200 (6100)
Weight, kg: 1980 – 2200 (1680)
Weight of explosives, however, kg: 300
Speed, kt:
- 1 mode: 50
- 2-Mode : 30 – 35
Range of stroke, m: 50000 – 60000 (40000)
depth of stroke, m: up to 500
shooting depth with submarines, m: up to 400
Radius response CLO km:
- on submarines: 2.5
- NDT: 1.2
indication time wakefield NK track, from: 350
Length of wire telecontrol km:
- • torpedo coil 25
- • towable coil 5
Range fuse, m:
- on the FL 2
- NDT: 6 – 8
Источник: http://nevskii-bastion.ru/ugst-torpeda/ ВТС «НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН» A.V.Karpenko
USET-80 torpedo
 USET-80 – Dawid Marczyński for large image: Here
USET-80 – Dawid Marczyński for large image: Here
The USET-80 is a multipurpose electric-propelled torpedo with both acoustic wake homing and active/passive acoustic homing. It truly multipurpose as it is launched by both submarines and surface ships against submarines and surface targets.
Specifications:
Source weaponsystems.net
53-56 torpedo
The Type 53-56 is a non homing torpedo that was introduced in 1956 and is fired from surface vessels and submarines. The Type 53-56V and VA that were introduced in 1964 and 1966 respectively are export models that use air instead of oxygen. The V is a non homing torpedo while the VA is an acoustic wake following torpedo.
Specifications:
DM-1 sea mines
In 1957, the Navy received the IGDM-500 small bottom mine, and in 1959 it got the MDT tubular bottom mine and Serpei large bottom mine. In 1961 such unique bottom mines of the UDM family as the UDM large air-dropped mine (1961) and UDM-500 small bottom mine (1965) came into service. In 1979, the UDM-2 mine, featuring fundamentally new performance characteristics, was developed. Later, on the basis of the UDM family of mines, their successors, designated MDM-3, MDM-4 and MDM-5, were developed for export. At the same time, the DM-1 (MDM-1) mine, designed to be laid by submarines, entered service. The latest modification of this mine is the MDM-6.
All of the above mines can be air-dropped, scattered from surface warships and other vessels, and the MDM-1 and MDM-6 types can also be laid from submarines. As regards size and explosive charge, mines can be subdivided into superlarge (UDM-2, DM-1, MDM-5, MDM-1, MDM-6), large (IGDM, AMD-2M, Serpei, UDM, MDM-4) and small (IGDM-500, UDM-500, MDM-3). Source milit.ru
Features
The mines are fitted with local three-channel influence exploders activated by target’s acoustic, electromagnetic and hydrodynamic fields sensed in a hemispherical danger zone. The exploders allow the mines to be deployed in both three- and two-channel configurations, with any combination of the channels possible. The mines possess effective anti-sweeping protection from modern influence sweepers and resistance to natural clutter owing to advanced exploder operating principle and anti-sweep device logic, as well as mine timing and ship counting devices employed. Intricate planting patterns and camouflage painting of the mines hinder their detection by sonars of surface ships and submarines, or by mine-hunting devices of remotely operated underwater vehicles.
MDM-1 Mod. 1 sea bottom mine
The mine can be laid by submarines equipped with 534mm torpedo tubes and ships fitted with mine-laying rails/ramps or mine-scattering systems. Surface ships can lay the mines at speeds of up to 15 knots, and submarines – at speeds of up to 8 knots.
When the assigned service life of the mine expires, it is self-destroyed.
Source roe.ru
9K38 Igla (Needle) Man-Portable Air Defense System (MANPADS)
Intended to defeat approaching and receding jet-engine, turboprop, propeller-driven fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters round the clock when they are visually observed against clutter background and in infrared countermeasure environment.
High counter-countermeasure resistance. Round the clock identification friend-or-foe. Main combat employment – shoulder-firing. Launch options include a 203-OPU Dzhigit support launching unit and 9S846 Strelets set of control equipment and launch modules.
Major features of Igla MANPADS:
- two-colour seeker;
- automatic entry of lead and elevation angles at launch;
- target selection when it deploys IR decoys;
- software-driven target adaptive guidance;
- detonation of sustainer’s remaining propellant together with warhead activation;
- disabling launches at friendly targets.
|
System specifications: |
|
| Target altitude, m | 10…3,500 |
| Target range, m | 5,200 |
| Target speed, m/s: | |
| head-on engagement | Up to 360 |
| tail-chase engagement | Up to 320 |
| Combat equipment weight, kg (in combat position) | 16.8 |
| Major missile specifications: | |
| Missile calibre, mm | 72.2 |
| Missile length, mm | 1,655 |
| Missile launch weight, kg | 10.6 |
| Booster | Solid-propellant |
| Sustainer | Solid-propellant, two-thrust |
| Warhead | Blast fragmentation |
| Aerodynamic configuration | Canard |
| Flight control | Aerodynamic surfaces, powder thruster at initial trajectory |
| Seeker | Optical, two-colour, homing (passive) |
| Control system | Single-channel |
Source kbm.ru
The Lada Class submarines are fitted with modern sonar equipment such as bow, flank arrays and towed array sonars. The Lira sonar system with quasi-conformal (abutting the hull of the submarine) antenna can detect low-noise targets located at long ranges.
The ship has an inertial navigation system for safe navigation and determination of motion parameters. The system ensures the accuracy of on-board weapons by providing guidance during long underwater operations. The countermeasures are provided by the electronic support measures (ESM) system, radar warning receiver and direction finder.
Propulsion and power of the Russian subs
 B-585 St. Petersburg – Russian Marshal YouTube
B-585 St. Petersburg – Russian Marshal YouTube
The submarine’s propulsion system integrates two diesel generators, a main electric propulsion motor, two air independent propulsion (AIP) systems, and a single shaft driving on a skewed seven-bladed propeller.
2 x 28DG Diesel-generator
The diesel engine is located in the fourth compartment. For the generation of electricity, two 28DG generators are used, coupled with rectifiers with a capacity of 1000 kW each. The energy is stored in two groups of storage batteries. In each of them there are 126 elements (they are in the first and third compartments). The total aggregate capacity of the entire plant in the peak state is 10580 kW / h. The working motor is electric, it is excited by permanent magnets. The SED-1 grade, the specific power is 4100 kW. Translated by google – Source kollektsiya.ru
| Parameter | Value |
| Full power, kW | 1335 |
| Engine speed at full power, rpm | 1000 |
| Dimensions, mm, max. | |
| length | 3475 |
| width | 1572 |
| height | 2600 |
| Dry engine weight, kg | 10800 |
| Standard specific fuel consumption (accord. to ISO), g/kW·h | 191 |
| Standard specific burning oil consumption (accord. to ISO), g/kW·h, max | 1,23 |
| Specific burning oil consumption at full power, g/kW·h (g/hp∙h) | 1,47 |
| Oil replacement interval (main М-16DR), h | 2500 |
| Top end overhaul interval, h | 7500 |
| Major overhaul interval, h | 30000 |
| Decommissioning interval, h | 80000 |
Source kolomnadiesel.com
The AIP system based on oxygen / hydrogen fuel cells increases the Lada Class submerged endurance from 15 to 45 days. It also reduces noise by avoiding the need for frequent battery recharge by diesel generators.
 bastion-karpenko.ru
bastion-karpenko.ru
The diesel engine operating short time in the snorkelling mode increases the endurance of the submarine. The submarine also has a storage battery with an increased service life.
KRISTALL-27E anaerobic propulsion system
 forum.keypublishing.com
forum.keypublishing.com
“The Lada project is an unconditional breakthrough and improvement of technologies that exist on traditional diesel submarines. Of course, there will be a certain continuity, all the best that we will get through the Lada, we will invest in a new large non-nuclear submarine, which will be created already within the framework of the formation of the next generation, “he said, answering the question whether Lada VNEU . According to him, now there are two projects of air-independent plants. “One (installation – TASS comment) was carried out by CDB” Malakhit “, the other – TsKB” Rubin “. They use different principles, “Rakhmanov said. “But we hope that in the near future with the help of the Ministry of Industry and Trade we will go to mock testing in water,” he said. According to him, now both installations exist as stands and show good results. TASS. Translated by google – Source bastion-opk.ru
Tactical and technical data
 russianships.info
russianships.info
| Displacement, t: | |
| surface: | 1450 (pr.677E – 1765) |
| underwater: | 2100 (pr.677E – 2650) |
| Dimensions, m: | |
| length: | 58 (pr.677E – 66.8) |
| width: | 7.2 (pr.677E – 7.1) |
| draft on KVL: | 4.8 |
| Full speed, knots: | |
| surface water: | 11 (pr.677E-10) |
| Underwater: | 17 (pr.677E-21) |
| Range of navigation: | |
| above the water | – |
| under the RDP | 4000 miles (7 knots under the RDP) (pr.677E – 4000 miles) |
| under the water | 650 miles (3 knots) (pr.677E – 650 miles (3 knots)) |
| Depth of immersion, m: | |
| working: | 200 (pr.677E-300) |
| limiting: | 250 |
| Autonomy, days: | 30 days (pr.677E – 45 days) |
| GEM, full power: | 1×2700 hp electric motor PG-102M (pr.677E – 1×5575 hp), 2×140 hp electric motor, 1 VFSH, 2 VRK with a vfsh in nozzles |
| Armament: | 6 533 mm NTA – 16 torpedoes 53-56B, SET-53M or 22 mines DM-1 6×1 PU “Igla-1M” missile system (6 missiles) – pr.677E |
| Radiotechnical fire: | SJSC “Lira”, BIUS “Lithium” |
| Crew, person: | 34 (pr.677E-35) |
Tactical and technical data russianships.info
Main material source naval-technology.com
Main image roe.ru
Images are from public domain unless otherwise stated
Revised Oct 08, 2018
Updated Oct 12, 2018







































