The MD 530G is a next-generation light scout attack helicopter being developed by the US-based company MD Helicopters. MD Helicopters has been at the forefront of more than 50-years of scout attack helicopter innovation. Beginning with the 1963 introduction of the OH-6A Cayuse through to the 1985 certification of the MD 530F, the world’s most reliable scout for “hot and high” performance.
MD 530F Cayuse Warrior: Details
 MD 530F
MD 530F
The MD 530G is the next evolution of purpose-built armed scout attack helicopters. Designed to be the lowest cost Gunship in the marketplace, the MD 530G maximizes mission versatility and capability for MD customers. The MD 530G platform enables military customers to meet mission requirements in austere environments more efficiently and effectively than ever before.
The helicopter was officially unveiled at the Helicopter International Association conference and exhibition (Heli-Expo) held in Anaheim, US, in February 2014. It successfully fired .50 calibre and 7.62mm ammunition, and unguided and four Raytheon TALON laser-guided rockets during live fire qualification exercise at Yuma Proving Grounds, Arizona, in August 2014.
Design
The MD 530G is based on the MD530F airframe. The helicopter is 7.76m long and 3m wide and has an overall height of 2.88m. It has five main rotor blades and two tail rotor blades. The main rotor diameter is 8.38m, while the tail rotor diameter is 1.55m. The helicopter has an empty weight of 885kg, maximum internal gross weight of 1,520kg and maximum take-off gross weight of 1,701kg. It can carry an increased useful load of 816kg to operate with additional range and endurance.
MDHI TEAMS UP WITH ELBIT SYSTEMS TO ENHANCE MD 530G BLOCK II
Elbit’s HDTS can be employed in both day and night operations, providing pilots with a hybrid head-tracking capability, which will enhance coordination and improve targeting/cueing. The WMS will give the MD 530G Block II a comprehensive number of suppressive firepower options, including guided and unguided munitions such as the Hellfire air-to-surface missile. Per customer demand, the Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS) can also be integrated onto the helicopter. The WMS also supports M260 rocket pods, RMP digital gun/rocket pods, HMP 400 digital gun pods, and M134D-H miniguns. Elbit’s WMS will add critical weapons management functions to the MD 530G Block II, with weapon activation and HDTS operation being integrated into both pilots’ cyclic grip.
The main addition that will be included in this agreement is the MMS – a digital mapping application which is managed by a touch screen graphical user interface, boosting situational awareness by noting aircraft positions, friendly forces/locations and known threats. The MMS will integrate with the MD 530G Block II’s Electro-Optical/Infrared (EO/IR) system, which will compliment the detection and storing of intelligence, enabling crews to further engage threats. Source key.aero

Propulsion
The MD 530G scout attack helicopter is powered by Rolls-Royce 250-C30 engine, which generates a power output of 485kW. The 250-C30 turboshaft engine is two-shaft modular design featuring a two-stage LP turbine, two-stage HP turbine, and a gearbox with 6,000rpm output. Compressed air is routed to the aft end of the engine for combustion, with exhaust gases exiting from the middle of the engine. The 250-C30 features four to six-stage axial and single-stage centrifugal compressor with a hydromechanical fuel control system. C-30 version turboshaft also features a FADEC (Full Authority Digital Engine Control) system.
Rolls-Royce 250-C30 engine
 Rolls-Royce 250-C30 engine
Rolls-Royce 250-C30 engine
The M250 turboshaft engines are of two-shaft modular design featuring a two-stage LP turbine, two-stage HP turbine, and a gearbox with 6,000rpm output. Compressed air is routed to the aft end of the engine for combustion, with exhaust gases exit from the middle.
The Series II features four to six-stage axial and single-stage centrifugal compressors with a hydromechanical fuel control system. The larger Series IV family is identical in layout, but has a single-stage centrifugal rather than an axial/centrifugal compressor.

Source: rolls-royce.com
The helicopter can fly at a maximum cruise speed of 240km/h at sea level under international standard atmospheric conditions. It has a maximum permitted speed of 282km/h at sea level and can fly to a range of 426km. The MD 530G can endure for two and half hours with an auxiliary fuel tank.
Avionics
The MD 530G helicopter features T-shaped instrument panel installed with two glass multi-function displays (MFDs). On the left is the EO/IR video display, which includes weapon status and targeting overlays. The right side of the panel is the pilot’s Garmin G500H MFD, and below is back up flight/engine instrumentation.
Garmin G500H MFD

Improve Mission Efficiency and Reliability
- Dual 6.5” flight displays that are easy to read
- See clearly in dark VFR night, DVE or inadvertent IMC with HSVT™
- Helicopter Terrain Awareness Warning System (HTAWS) support
- Weather, traffic, and charting all in your primary field of view
- Video input for FLIR or other camera display
Engineered for safety and reliability, the G500H dual-screen electronic flight display provides an affordable flight solution that meets the needs of the most demanding helicopter missions. G500H has received FAA STCs for installation in the Robinson R44, Bell 206 series and Bell 407, as well as the Eurocopter AS350B2, AS350B3 and EC130B4.
Better Situational Awareness
Dual 6.5″ LCD screens, mounted side-by-side in a single bezel, put Primary Flight Display (PFD) and Multi-Function Display (MFD) capabilities right in front of you for easy scanning and interpretation. The PFD screen shows attitude, airspeed, altitude, climb rate and course/heading information, while the left side MFD provides detailed moving-map graphics with the helicopter’s current position in relation to ground features, chart data, navaids and flight plan routings. Both screens are Class B night-vision goggle friendly for use with an array of optics.
Specially adapted to the needs of helicopter operators, our HSVT brings a powerful graphical perspective. Available as an option, HSVT can make a world of difference when visibility is less than ideal.

HSVT gives you a clear depiction of ground and water features, airports, obstacles, traffic and more — all shown in 3-D perspective on the primary flight display. It uses sophisticated computer modeling to recreate a virtual topographic landscape from the system’s terrain alerting database. The HSVT graphics look so real, it’s almost like having a clear-day “out-the-window” view of your flight situation — even in the darkest nighttime VFR or other low-visibility conditions.
Proven AHRS attitude/heading reference delivers high-precision spatial sensing for G500H digital instrumentation, replacing old-style gyros.
G500H can be purchased with the PFD on either the right or left side of the bezel for easy viewing depending on your pilot seat position.
Maintain Maximum Separation
With a GNS 430W or 530W series HTAWS navigator interfaced to G500H, certified “forward looking” terrain avoidance (FLTA) predicts in advance where potential hazards exist. An HTAWS warning received from the GNS 430W- or 530W-series navigator displays as an annunciation to the left and aligned with the top of the Altitude Tape on the G500H PFD.
To monitor location on unfamiliar airports, G500H is preloaded with geo-referenced SafeTaxi® diagrams for either U.S. or Europe airports, as well as a trial version of FliteCharts®. FBO, ground transportation, lodging and other facility information for most U.S. airports are also available through preloaded AOPA Airport Directory Data. When flying internationally, opt for global AC-U-KWIK airport directory data instead. Source: garmin.com
Cockpit For Malaysian Army
 pilotlightmedia.com
pilotlightmedia.com
MD 530G Attack Helicopter for Malaysian Army Aviation As one of six (6) MD 530G helicopters ordered by Malaysia’s Ministry of Defence for delivery to Malaysian Army Aviation, the MD 530G-glass cockpit features: Two (2) Genesys Aerosystems IDU-680 6” x 9” LCD primary displays Tek Fusion Global’s PATHFINDER™ Mission Management System (MMS) and “ARES” Weapons Management System (WMS) on Dual Side-Mounted Mission Displays. Source airsoc.com
IDU-680 Genesys Aerosystems
The Genesys Aerosystems Integrated IDU-680 EFIS/EICAS/MFD system aboard the MD 902 Explorer features:
– Three IDU-680, 6” x 9” High-Resolution LCD displays
– Automatic or Manual Revisionary Modes
– 3D Synthetic Vision
– Highway-In-The-Sky (HITS) Navigation
– Geo-Referenced Hover Vector
– Helicopter Terrain Awareness and Warning System (H-TAWS)
– Night Vision A&B Capabilities
– Weather Radar Integration
– Integrated ADS-B Traffic Display
– Engine Instrument Crew Advisory System (EICAS)
– Data Acquisition Units for Custom Engine Monitoring- Flight Data RecordingGraphicalFMS/VHF FEATURESNavigation- Moving Map
Source helis.com
PATHFINDER™ SYSTEM
INRODUCTION
PATHFINDER™ is a customizable Mission Management System (MMS) that has been meticulously designed by a team of former special operations aviators based on real-world experience. Already fielded on NorthStar Aviation’s highly successful Bell 407GX platform, PATHFINDER™ is proven to maximize utility and ease of use with seamless integration of onboard systems. The architects behind PATHFINDER™ understand the critical needs and challenges of the operator, and are dedicated to delivering the best end-user experience possible.
DESIGN PRINCIPLE
PATHFINDER™ uses an easy to navigate interface to simplify and consolidate mission execution tasks. This provides painless command and control of onboard navigation, communication, and peripheral electronic equipment. Optimizing user tasks directly enhances task efficiency and accuracy, and reduces operator workload. With the defense industry’s most common operationally critical features already implemented, PATHFINDER™ can be rapidly integrated to any existing airframe, ground vehicle, or easily customized to support your unique project. Our modular design approach assures the perfect fit, even for budget-conscious implementations. Source tekfusioninc.com
ARES™ SYSTEM
INRODUCTION
ARES is a weapons management system (WMS) designed from the ground upwith a cutting
edge object-based graphical user interface (GUI) developed by former special operations
aviators based on real-world experience. ARES is a software-based configurable system with
a hardware ARM-SAFE infrastructure. ARES is designed to readily support both legacy and
emerging weapons systems in a tactically optimized manner, while reducing size, weight,
and power.
FEATURES
› Modular
› Lightweight
› Scalable
› Compact
› Rugged
› Adaptable
› NVIS Compatible
› Ease of Use
› Touch & Bezel Interfaces
› Impedence controlled
connections
› Single Source Solution
DESCRIPTION
ARES is designed to use the aircraft’s EO/IR monitor as the WMS interface using a
touchscreen GUI. The system is fully integrated with FLIR and L-3 WESCAM Gen II sensors.
Critical EO/IR functions can be controlled through the user interface. The system provides
aircraft steering commands and targeting overlays to guide the pilot into the proper launch
constraints. This reduces pilot workload, and improves the probability of hitting the target. Source tekfusioninc.com
The MD 530G helicopter is also equipped with Rhode & Schwarz M3AR tactical radio communications solution with a frequency range from 30MHz to 400MHz.With the integration of on-board systems that include a Stores Management System, forward looking infrared sensor, and an advanced communications suite, MD Helicopters has evolved a proven platform to provide comprehensive battlefield command and control coordination for the successful execution of Attack, Reconnaissance and Security missions.
Rhode & Schwarz M3AR tactical radio communications solution
R&S®M3AR Software Defined Radios
VHF/UHF Transceiver Family for Airborne Communications
Key Facts
- Frequency range from 30 MHz to 400 MHz
- Compact and lightweight with high transmit power (up to 20 W in AM mode and up to 30 W in FM mode)
- EPM (ECCM): HAVE QUICK I/II, SATURN, R&S®SECOS
- Approved for jet and propeller aircraft as well as helicopters and unmanned aerial vehicles
- Embedded NATO or R&S®SECOS encryption
- Suitable for communications with military and civil air traffic control (e.g. 8.33 kHz channel spacing or offset carrier receive operation)
Brief Description
The software defined, multiband-capable airborne transceivers of the R&S®M3AR family feature a modular design and state-of-the-art technology. This leads to high MTBF values and a long life. The compact and lightweight transceivers offer high performance, making them suitable for operation in all types of aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles. Different waveforms are available, which can be installed at any time to provide interoperability in a variety of operational scenarios.
The R&S®M3AR family is the product of decades of experience, especially in the design and development of airborne radio equipment and software defined radio technology. The R&S®M3AR multiband, multimode, multirole radio is the solution of choice for the reliable transmission of mission-critical information, whether it’s for jet or propeller aircraft, helicopters or unmanned aerial vehicles.
Rohde & Schwarz satisfies the most demanding requirements of a multitude of airborne platforms. The R&S®M3AR transceivers are in operation around the world and feature high reliability even under extreme environmental conditions. The outstanding MTBF values ensure low maintenance effort and high availability.
A variety of optional EPM (ECCM) methods are available. For instance, the R&S®SECOS frequency hopping method with integrated encryption can be installed in parallel with HAVE QUICK I/II.
The R&S®M3AR family consists of the R&S®MR6000A in an ARINC 600 housing and the R&S®MR6000R/ R&S®MR6000L, both of which are ARC-164 form & fit compatible. The R&S®MR6000L is equipped with a local control panel while the R&S®MR6000R is remote-controlled. All R&S®M3AR radios can be remote-controlled via the MIL‑STD-1553B data bus, as well as by the R&S®GB6500 control unit. The R&S®MR6000R or R&S®MR6000L can serve as a form, fit and function (F3) replacement for legacy AN/ARC-164 radios.
Source: rohde-schwarz.com
The MD 530G is fitted with the Moog Third Generation Weapon Stores Management System (SMS), which provides the aviator with best-in-class weapons management on the MD 530G Armed Scout/Attack platform.
 Moog Third Generation Weapon Stores Management System (SMS)
Moog Third Generation Weapon Stores Management System (SMS)
This scalable SMS includes one Stores Management Computer (SMC), weighing 4 pounds, located in the cargo compartment, one Multi-Function Display (MFD), weighing 6 pounds, mounted in the cockpit instrument panel, one Stores Control Panel (SCP), weighing 1.2 pounds, mounted in the cockpit slant panel, two Stores Interface Unit (SIU), weighing 3.5 pounds/7 pounds total, located in the cargo compartment, and two Rocket Interface Unit (RIU), weighing 3 pounds/6 pounds total, located in the cargo compartment.
Moog Third Generation Weapon Stores Management System (SMS)

The total weight of the SMS is only 24.2 lbs. The Stores Management Computer interfaces with the Multi-function Display and the MX-10D EO/IR sensor and laser designation system via RS-422, MIL-STD-1553, ARINC-429, or Ethernet, depending on customer need. For the MD 530G application, the SMS supports up to 4 weapons stations; including integration of machine guns, unguided and guided munitions.
Accessories
Infused with modern technology and MDHI innovation, the agility and firepower of the MD 530G will provide significant expansion in airborne combat capabilities, enabling military customers to meet mission requirements in austere environments more effectively and efficiently than ever before. With cruise speeds in excess of 110kts, the MD 530G is designed for agile deployment with any rotary wing unit. The aircraft features increased capacity landing gear supporting the 3,750 MGTOW (max gross takeoff weight). This allows the operator to utilize the increased useful load for additional range, endurance and weapons.
Mace Aviation Extended Range Weapons Wing (ER2W)

The MD 530G is equipped with Mace Aviation’s weapons mounting structure. The Mace Aviation Extended Range Weapons Wing (ER2W) is a lightweight, four-station weapons platform constructed of aerospace grade composite materials. The ER2W was specifically designed for MD Helicopters product line and enhances the MD 530G aircraft performance by the wing’s integral 35 gallon auxiliary fuel system.

The Mace ER2W provides four distinct advantages to the MD 530G aircraft that are not provided by other legacy weapons mount structures. The ER2W is lightweight, weighing less than 100 pounds empty and can carry over 1,300 pounds of weapons and ammo to include 235 pounds of fuel. Integral to the ER2W is a crashworthy, self-sealing 35 gallon fuel system, manufactured by Robertson Fuel Systems, increases the MD 530G’s effective range and endurance by approximately one hour. The system is designed for rapid reconfiguration.
A three point attachment scheme and quick disconnects for the wiring harness and fuel line allows the MD 530G to be quickly reconfigured between attack, assault, and/or utility operations in less than 10 minutes by two personnel. The ER2W airfoil design provides increased maneuverability with decreased drag. The ER2W is equipped with four weapons stations that include provisions for the M134D-H for both inboard stations. The two outboard stations are equipped with ALKAN suspension racks with standard 14 inch NATO interfaces and provisions for in-flight store jettison for additional pod guns, rockets or missiles. The ER2W is designed to grow with the capability and operator needs.
Dillon Aero M134D-H Gatling Gun
 Dillon Aero M134D-H Gatling Gun & .50cal FN M3P pod on Malaysian MD 530G – pilotlightmedia.com
Dillon Aero M134D-H Gatling Gun & .50cal FN M3P pod on Malaysian MD 530G – pilotlightmedia.com
M134D-H for both inboard stations the Dillon Aero M134D-H Gatling Gun. The M134D-H (Hybrid) is the latest Gatling Gun design from Dillon Aero. This Hybrid Gatling Gun combines the light-weight attributes of the M134D-T (Titanium) weapon with the long-life durability of the M134D (Steel) variant. The Hybrid Gun is ideal for aircraft applications, weighing a mere two pounds more than the Titanium variant. Service life is extended three-fold, increasing weapon-system longevity from 300,000 to 1,000,000 rounds. The MD 530G offers the M134D-H in multiple arrangement options, including single and dual-weapon configurations, effectively complementing other weapon system capabilities. The M134D-H will come standard with a 3,000 round ammo magazine that will be easily stowed on top of the Mace Extended Range Weapons Wing in the cargo compartment of the MD 530G. The total system weight, including the weapon, feed chute, harness, and ammunition magazine is a mere 93 pounds, excluding ammunition.
Raytheon TALON 2.75-inch (70 mm) Laser-Guided Rocket

Raytheon TALON 2.75-inch (70 mm) Laser-Guided Rocket, co-developed with the United Arab Emirates, leverages Raytheon’s extensive experience in laser seeker technology and builds on its proven track record of precision munitions development and production. TALON is a low cost solution that fills the gap between existing unguided rockets and heavy, expensive anti-tank missiles that are currently deployed on attack helicopters. It is effective against soft and lightly armored point targets while providing precision engagement capability that reduces the potential of collateral damage. TALON’s architecture and ease of employment make it a low-cost, highly precise weapon for missions in urban environments, counter insurgency and swarming boat defense missions.

The TALON LGR consists of a light weight laser guidance kit that attaches to existing 2.75-inch (70 mm) unguided rockets that are used extensively throughout the world. The guidance kit incorporates Raytheon’s digital semi-active laser seeker, guidance electronics, a three-axis control actuation system, and the TALON roll-optimizing tail-fin assembly. The kit is fully compatible with existing airborne and ground laser designators and requires no modifications to the existing 70 mm rocket launchers.
Rocket pod
 Rocket and Rocket pod
Rocket and Rocket pod
.50cal FN M3P pod

 .50cal FN M3P pod & Dillon Aero M134D-H Gatling Gun on Malaysian MD 530G – airsoc.com
.50cal FN M3P pod & Dillon Aero M134D-H Gatling Gun on Malaysian MD 530G – airsoc.com
.50cal FN M3P pod For the heavy machine gun solution, the MD 530G incorporates the FN Herstal Heavy Machine Gun Pod (HMP). This system is an independent unit housing a 12.7 mm (.50 caliber) FN M3P machine gun. Fitted with standard lugs, the pod can be carried by the MD 530G helicopter’s 14-inch NATO standard bomb rack. The weapon is air cooled and operates by short barrel recoil. The gun is accurate up to 1,850 meters and remains effective up to 3,000 meters. Its high rate of fire – up to 1,100 rounds per minute – provides lethal fire concentration. A self-contained ammunition box has a capacity of up to 400 cartridges. Cartridges are fed to the gun by an internal ammunition chute. High ammunition capacity enables a number of attacks to be made without rearming. Belt advance is smooth and without risk of jamming or fouling due to aircraft attitudes and accelerations.
The L-3 Wescam MX-10 series sensor and LASER designator will round out the MD 530G mission and weapons equipment package. The MX-10 and MX-10D deliver MX-series high performance stabilization, high resolution HD Color, Lowlight and Infra-Red imagery, high accuracy Geopoint/Geolocate and precision targeting lasers to the small turret class. The MX-10 and MX-10D are combat proven and serving on U.S Military, International and Special Forces Platforms around the world today.
L-3 Wescam
The MX-10/10D are a single LRU system saving both weight, space and cabling on the MD 530G with a total system weight below 43lbs. The MX10 is self-aligning and bore-sighting requiring input from the aircraft, and permits Geo-point and geo tracking capability. L3’s MX10 features 4-axis stabilization vibration isolation of the payload provide the ability to conduct laser designation beyond 10km, a low Pilot work load as the turret maintains target position without input while maneuvering the aircraft, and a high reliability and low cost of operation with mean time between failure exceeding 1000HRS. The MX-10D is compatible with industry-standard mounting interfaces and also supports platform unique requirements.
The overall diameter of 10.24 inch x 10.6 inch (260 x 270 mm) matches existing small EO/IR systems, making the MX-10D suitable for belly mounting in low ground clearance airframes. The electrical connectors are side mounted to facilitate installations where cable penetration immediately above the turret is not practical. The MX-10 series provide three high definition SMPTE 292M digital video outputs and four analog video outputs, for direct connection to displays, recorders and data links. All internal video paths are digital, excluding the final digital-to-analog conversion step for the analog videos. Each output of the digital video switch matrix can be independently selected to be IR, EO, Fused or Video-In-Control. Symbology on each output from the switch matrix can be individually enabled, disabled and de-cluttered.
MX-10D EO/IR sensor and laser designation system
Ideal for: Low-altitude Tactical Surveillance & Target Acquisition and Designation missions requiring low-weight installation flexibility
Installations: Fixed-wing, Rotary-wing, UAV, Aerostat
Features & Benefits
Compact Solution
- 43 lb./19.5 kg turret
- 15 in. turret height for better ground clearance
Multi-Sensor Imaging/Lasing Payload Options:
- Currently supports up to six sensors simultaneously
- Superior HD imaging resolution from Electro-Optical (EO) camera
- Laser rangefinder, illuminator, designator
Latest Enhancement – 2015
- Picutre-in-Picutre (PiP)
Enhanced Local Area Processing (ELAP):
- Real-time image enhancement for EO day, EO night & Infrared
High-Performance IMU & MX-GEO Software Suite:
- IMU & MX-GEO work to create accurate target location
- MX-GEO automatically aligns to the aircraft
- Robust automatic image focus
Uncompromised Stabilization:
- Four-axis gimbal with internal IMU
- All payloads are fully stabilized
MX-Series Commonality:
- Common operator interfaces and Hand Controller Units (HCUs)
- Simplified interchangeability
- Efficiencies in product support and technology enhancements
Source wescam.com

| Type |
| light scout attack helicopter |
| Country user |
| – (in development) |
| Country Producer |
| United States |
| Crew |
| 2 + 2 |
| Engine |
| Rolls-Royce 250-C30 Engine |
| Speed |
| 282 km/h (max cruise speed: 240 km/h) |
| Range |
| 426 km |
| Weight |
| 885 kg (max payload: 816 kg) |
| Avionics |
| Garmin G500H dual-screen flight display, night-vision-goggle (NVG) devices, dual LH command flight controls, Moog Third Generation Weapon Stores Management System |
| Dimensions |
| Length: 7.76 m; Width: 3 m; Heigth: 2.88 m |

Main material source airrecognition.com
Updated Apr 19, 2018
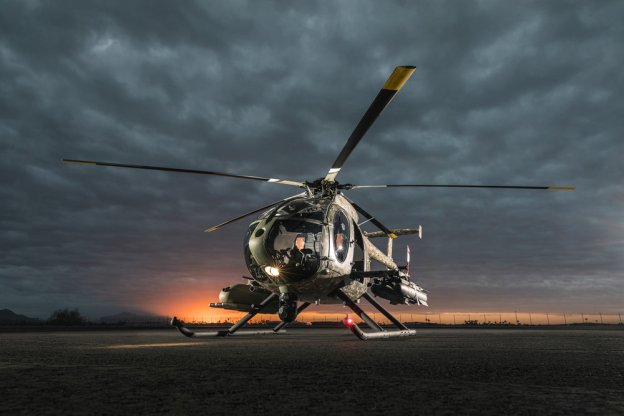

















 Next Gen cockpit
Next Gen cockpit

.jpg)


 Buk-M3 system
Buk-M3 system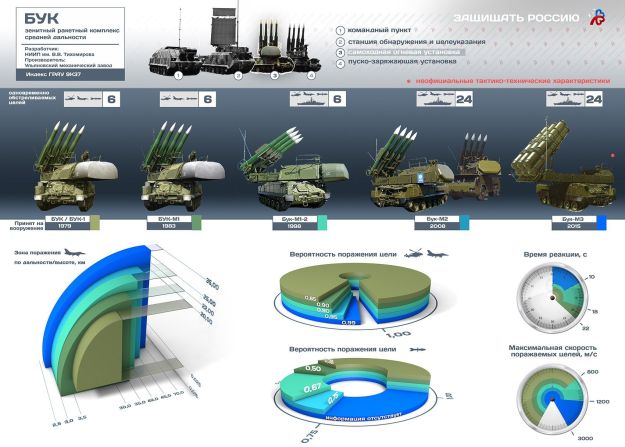



 by 3d_molier International
by 3d_molier International

 TOR-M2U
TOR-M2U TOR-M1
TOR-M1 Tor-M2E
Tor-M2E












 Телеканал Звезда YouTbe
Телеканал Звезда YouTbe

 New BMP-3M-100 Dragun infantry fighting vehicle (right) and New BMP-3 IFV fitted with a gun mount system AU-220m armed with a 57mm automatic cannon (Background)
New BMP-3M-100 Dragun infantry fighting vehicle (right) and New BMP-3 IFV fitted with a gun mount system AU-220m armed with a 57mm automatic cannon (Background).jpg)



 The “Vityaz” fire control system
The “Vityaz” fire control system 2A70 100mm cannon and a 2A72 30 mm automatic cannon
2A70 100mm cannon and a 2A72 30 mm automatic cannon 2A70 100mm cannon and a 2A72 30 mm automatic cannon turret
2A70 100mm cannon and a 2A72 30 mm automatic cannon turret  Dragun RCWS turret closeup
Dragun RCWS turret closeup


 © Alexandr Demyanchuk/TASS
© Alexandr Demyanchuk/TASS








 RAFAEL’s remotely-operated RCWS-30
RAFAEL’s remotely-operated RCWS-30




 Spike LR anti-tank missiles
Spike LR anti-tank missiles

 The S-300 surface-to-air missile systems were first developed by the Soviet Union to defend against enemy aircraft and incoming threats. Photo by
The S-300 surface-to-air missile systems were first developed by the Soviet Union to defend against enemy aircraft and incoming threats. Photo by 








 Телеканал Звезда
Телеканал Звезда Телеканал Звезда
Телеканал Звезда Телеканал Звезда
Телеканал Звезда Телеканал Звезда
Телеканал Звезда
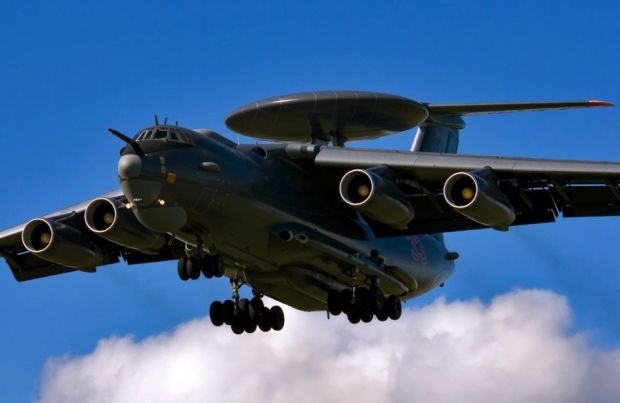
 Russian Air Force A-50 ’37 Red’ prototype
Russian Air Force A-50 ’37 Red’ prototype A-100 Premier flying lab(LL) 52 red – RussianDefence.com
A-100 Premier flying lab(LL) 52 red – RussianDefence.com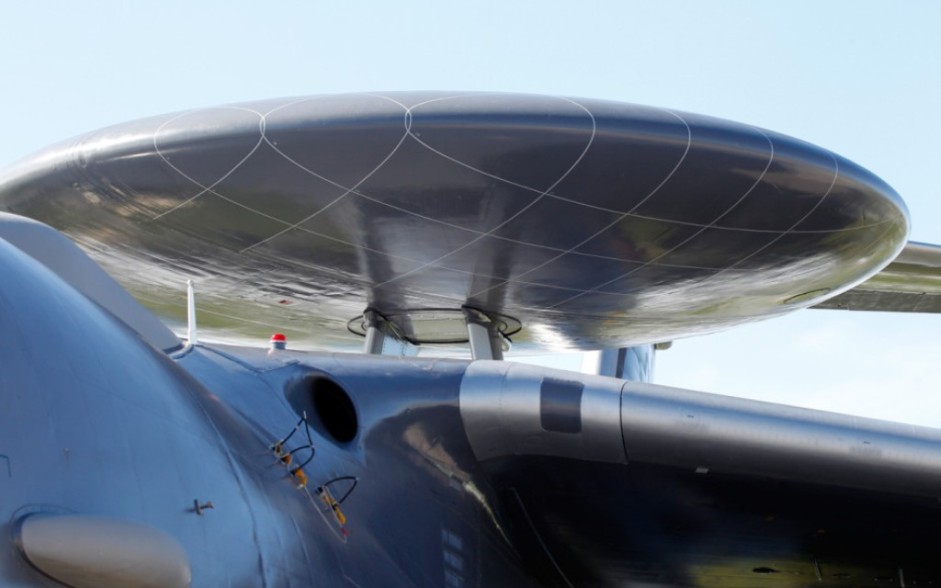 Vega Premier AESA radar
Vega Premier AESA radar
 We are expecting to receive the A-100 AWACS on the Ilyushin Il-476 platform powered by the PS-90 engine for extended flight range – Image: redstar.gr
We are expecting to receive the A-100 AWACS on the Ilyushin Il-476 platform powered by the PS-90 engine for extended flight range – Image: redstar.gr Image: redstar.gr
Image: redstar.gr A-100 AWACs – Image: UAC
A-100 AWACs – Image: UAC_RP63598.jpg)
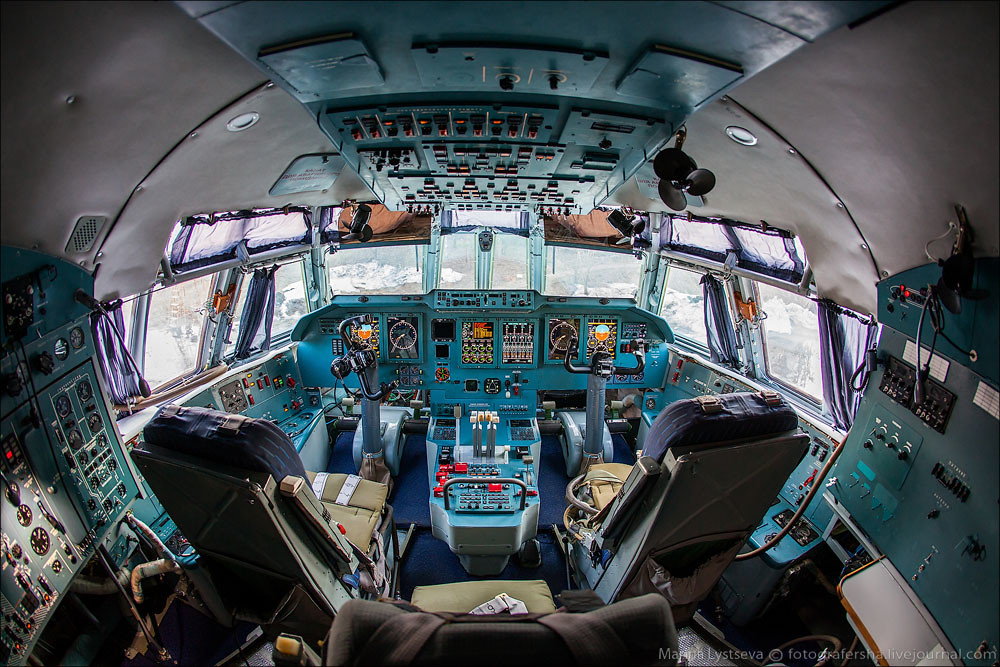
 A-100 cockpit
A-100 cockpit
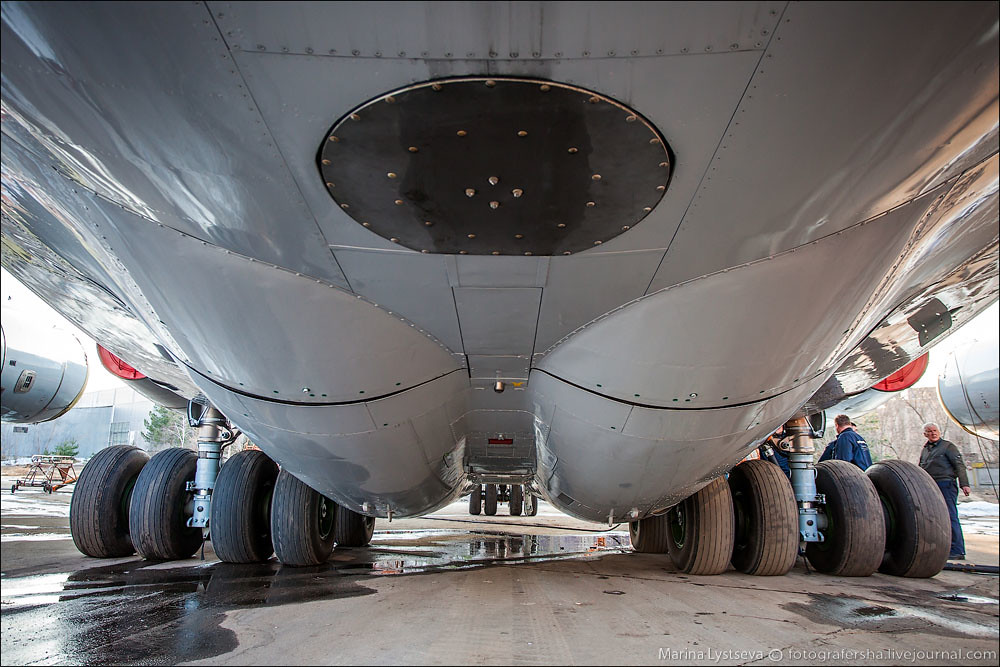


 Izdeliye-976 (SKIP) – englishrussia.com
Izdeliye-976 (SKIP) – englishrussia.com
 A-50E/I Indian Air Force
A-50E/I Indian Air Force iai.co.il
iai.co.il A-50E/I with Aviadvigatel PS-90 A-76 engines Indian Air Force – T24
A-50E/I with Aviadvigatel PS-90 A-76 engines Indian Air Force – T24 Image: hiveminer.com
Image: hiveminer.com

 4 × Soloviev D-30 KP turbofan, 117,68 kN (26,500 lbf) each
4 × Soloviev D-30 KP turbofan, 117,68 kN (26,500 lbf) each