The German Navy’s new F125 frigate will have the capability to be deployed worldwide for up to two years before returning to the home base and can be in operation for up to 5,000h a year, including under tropical conditions. F125 is the project name for the Type 125 Baden-Württemberg class of frigates.
The main mission of the F125 frigate is taking part in joint assignments, including multinational assignments in network-centric operations. The 5,500t displacement frigate has a new and stealthy design of hull and superstructure, which appears to be based on a highly modified Meko-D configuration.
 Type 125 Baden-Württemberg class concept reduced radar, infrared and acoustic signatures stealth technology
Type 125 Baden-Württemberg class concept reduced radar, infrared and acoustic signatures stealth technology
F125 frigate programme
The German Navy started to plan a successor for the F122 Bremen Class frigates in 1997. It operates eight Bremen Class F122 frigates, which entered service between 1982 and 1990.
Type 122 Bremen class Frigate
 FGS Köln (F 211) – Image: seaforces.org
FGS Köln (F 211) – Image: seaforces.org
| Displacement: | 3680 tons (full load) | |||||||
| Length: | 130,5 meters | |||||||
| Beam: | 14,6 meters | |||||||
| Draft: | 6,3 meters | |||||||
| Speed: | 30 knots, max. (56 km/h) | |||||||
| Propulsion: | combined diesel or gas (CODOG)
2 General Electric LM2500 gas turbines / 2 MTU 20V956 TB92 diesel engines 2 shafts / 2 controllable pitch propellers |
|||||||
| Range: | 4000 NM (7400 km) at 18 knots (33 km/h) | |||||||
| Crew: | 220 | |||||||
| Aviation: | flight deck & hangar for 2 Westland Super Lynx Mk.88A helicopters | |||||||
| Armament: | 1 x Oto-Melara 76mm/62-caliber DP gun (3-inches)
2 x Mk-141 missile launcher for 8 RGM-84 Harpoon SSM 1 x Mk-29 launcher for RIM-7 Sea Sparrow SAM (8 missiles + reload) 2 x MLG27 27mm light naval machine gun system (added later) 2 x Mk-49 missile launching system for RIM-116 Rolling Airframe Missiles (RAM) (added later) 2 x Mk-32 12,75-inch (324mm) twin-torpedo tubes for Mk-46 or DM4A1 torpedoes |
|||||||
Type 122 Bremen class Frigate data seaforces.org
The concept of the replacement frigates was originally as a multi-role combatant but by 2005, the requirement for the F125 was based on a capability to counter asymmetric threats and perform stabilisation operations with lethal and non-lethal intervention. The German Navy announced that the F125 would be armed with land attack systems and air warfare point-defence equipment but would not be equipped with sonar.
 Modified photo of Baden-Württemberg class frigate. For a high resolution image click here. – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Modified photo of Baden-Württemberg class frigate. For a high resolution image click here. – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
In June 2007, ThyssenKrupp announced the Arge F125 consortium had been contracted by the German Federal Office for Defence Technology and Procurement (BWB) for four F125 frigates. The Arge F125 consortium comprises the industrial leader, ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (including Blohm + Voss and Nordseewerke) with Lurssen Werft.
 F222 Baden-Württemberg
F222 Baden-Württemberg
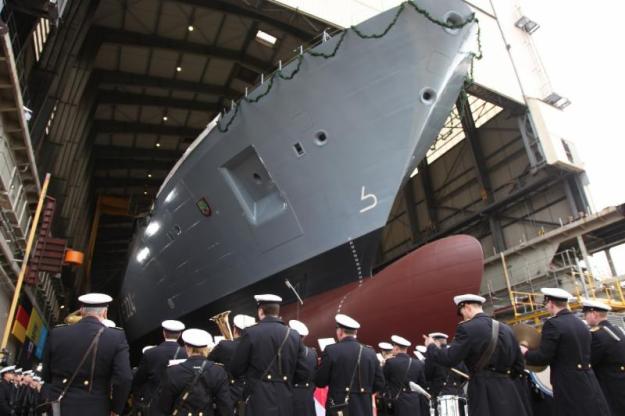
Construction began in May 2011 and the first frigate, Baden-Württemberg, was christened at ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems’ Hamburg site in December 2013. Christening of the second frigate, Nordrhein-Westfalen, took place in April 2015 and keel for the third frigate, Sachsen-Anhalt, was laid at the Hamburg site in June 2014. The keel laying ceremony of the final 125-class frigate, Rheinland-Pfalz, was held in January 2015.
Germany’s new frigates are overweight and float with a persistent list to starboard: Here

Excerpt
Germany’s much-delayed new frigates, built by ThyssenKrupp (TKAG.DE) and Luerssen for at least 650 million euros (£551.4 million) apiece, are overweight and float with a persistent list to starboard, according to a confidential report seen by Reuters.
The ships, designed to need a crew of only 120, less than half their predecessors, are a crucial element in Germany’s plans to beef up its military to face an increasingly uncertain European security landscape and a more assertive Russia.
German Navy’s Third F125 Frigate Christened: Here
Excerpt
The new F125-class frigates replace the German Navy’s eight Bremen-class frigates. The first two frigates of the four vessel series, Baden-Württemberg and Nordrhein-Westfalen, were christened in December 2013 and April 2015, respectively.
Sachsen-Anhalt is scheduled to be handed over to the German defense procurement agency BAAINBw in early 2019. Commissioning and in-port trials of the first F125 frigate, the Baden-Württemberg, have now advanced to the stage where sea trials can commence as planned in spring this year. Handover of the Baden-Württemberg to the BAAINBw is scheduled for mid-2017. The contract for the F125 program is worth around two billion euros in total.
 F224 Sachsen-Anhalt – Photo: ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems
F224 Sachsen-Anhalt – Photo: ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems
German defense procurement agency BAAINBw has reportedly returned FGS Baden-Württemberg F125 frigates to Blohm+Voss shipyard: Here
The German defense procurement agency BAAINBw has reportedly returned FGS Baden-Württemberg, the lead ship of German Navy’s new class of F125 frigates, to the Blohm+Voss shipyard.
According to a report in the German Kieler Nachrichten, BAAINBw has requested Blohm+Voss – which is part of the ARGE F125 consortium responsible for delivering the four frigates – to repair all defects identified on the ship during trials.
F224 Sachsen-Anhalt Begins Sea Trials: Here
Delivery of the first of class F125 is scheduled for 2016. The final vessel is expected to be delivered by 2019.

Ships in the class
| PENNANT NUMBER | NAME | CALL SIGN | SHIPYARD | LAID DOWN | LAUNCHED | DELIVERED | COMMISSIONED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F222 | Baden-Württemberg | ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems | 2 November 2011 | 12 December 2013 | planned for 30 November 2016 | 2017 | |
| F223 | Nordrhein-Westfalen | Lürssen | 24 October 2012 | 16 April 2015 | planned for 15 October 2017 | ||
| F224 | Sachsen-Anhalt | ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems | 4 June 2014 | 4 March 2016 | planned for Spring 2019 | ||
| F225 | Rheinland-Pfalz | Lürssen | 29 January 2015 | planned for February 2016 | planned for 18 August 2019 |
Source wikiwand.com
German Navy’s first F125 frigate reaches new home: Here
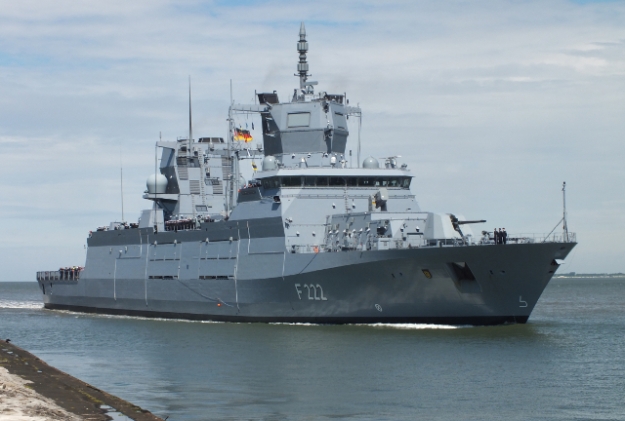 FGS Baden-Württenberg shortly before entering Wilhelmshaven. Photo: Bundeswehr/Dennis Kramer
FGS Baden-Württenberg shortly before entering Wilhelmshaven. Photo: Bundeswehr/Dennis Kramer
F125 frigate crew
 Lead ship of the class, frigate Baden-Württemberg (F222). Photo: Bundeswehr – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Lead ship of the class, frigate Baden-Württemberg (F222). Photo: Bundeswehr – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Each frigate has two crews ranging between 105 and 120 people, who are changed every four months. The number of crew represents an approximately 50% reduction in crew compared with previous generation frigates and is achieved partly through a high level of automation.
The frigate also accommodates 50 special forces soldiers and their equipment. The necessary transport can be two helicopters or four armed boats.
Command and control

In March 2006, EADS was contracted to supply the F125 command and control and weapons deployment system, FuWES (Fuhrungs-und Waffeneinsatzsystem). The contract covered the development and delivery of the system, including the complete software, hardware and infrastructure, and the FuWES testing and performance verification for all four frigates.
The FuWES system has an open and modular structure allowing flexibility to accommodate future additional or modified systems. In order to provide tactical data exchange and a high level of interoperability with other joint and combined military platforms, the communications systems, link 11, link 16 and link 22 are integrated into the F125 command and control system. The combat management system is operated from the Atlas Elektronik OMADA consoles, designed specifically for the F125.
 F125’s enhanced survivability characteristics. By Thyssen Krupp
F125’s enhanced survivability characteristics. By Thyssen Krupp
Integrated bridge and navigation system
 Photo: Alexander Gottschalk – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Photo: Alexander Gottschalk – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Previously Anschutz & Co, a subsidiary of Carl Zeiss, Raytheon Anschutz in Kiel, Germany, was contracted in August 2008 for the supply of the integrated bridge and navigation system for the F125 frigates. The integrated bridge and navigation system consists of six multi-function consoles capable of displaying various functions such as two X/S-band radars, two electronic chart display and information systems (ECDIS) and NautoConning navigation data, which reads and displays in a logically arranged manner and distributes the navigation data.
 The bridge of Baden-Württemberg. Photo: Alexander Gottschalk – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
The bridge of Baden-Württemberg. Photo: Alexander Gottschalk – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com The bridge of Baden-Württemberg. Photo: Alexander Gottschalk – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
The bridge of Baden-Württemberg. Photo: Alexander Gottschalk – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
One of the six consoles is for route planning purposes. The integrated bridge and navigation system encompasses the ship steering and control equipment, a Raytheon ring-laser based dual MINS marine inertial navigation system, two data distribution units and a complete set of navigational sensors and meteorological equipment. A redundant, laid-out ethernet bus configuration interconnects the multi-function consoles and sensors.
Weapons onboard the F125
The ship is equipped for defence against air attack and also for land attack.
The F125 is also armed with non-lethal weapons, such as water cannons and searchlights for non-provocative deterrence and defence.
F125 guns
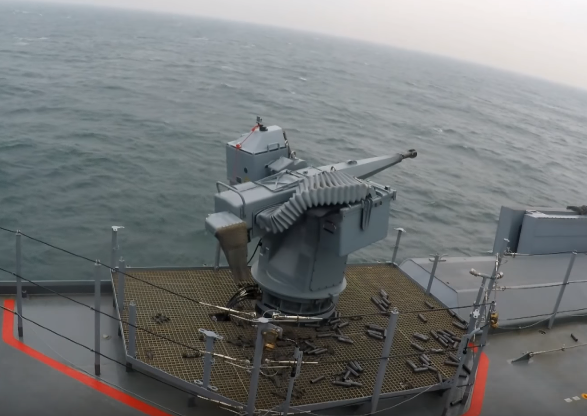
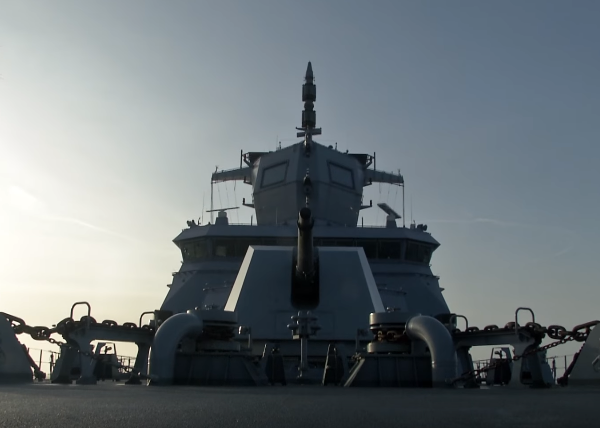 127mm gun of Baden-Württemberg
127mm gun of Baden-Württemberg
The ship is fitted with ten guns, ranging from 12.7mm to 155mm, which allow fast automatic engagement.
The BWB awarded Oto Melara contracts for the supply of five 127/64 LW Alleggerito lightweight naval guns, four for installation on the F125 frigates and the fifth for training.
The gun is installed on the forward gun deck. The turret of the 127/64 Alleggerito has a low radar cross section.
Otobreda 127 mm Vulcano main gun
 Otobreda 127 mm Vulcano main gun F-125 Frigate Baden-Wurttemberg
Otobreda 127 mm Vulcano main gun F-125 Frigate Baden-Wurttemberg
The upcoming Oto-Melara (now OtoBreda) 127/64 Lightweight (LW) naval gun is a rapid fire gun mount suitable for installation on large and medium size ships, intended for surface fire and naval gunfire support as main role and anti-aircraft fire as secondary role. The compactness of the gun feeding system makes possible the installation on narrow section crafts.
The gun can fire all standard 5 inch (127mm) ammunition including the new Vulcano long range guided ammunition.
Modular automatic feeding magazines allow the firing of up to four different and immediately selectable types of ammunition; the magazines (four drums, each with one shell ready to fire) can be reloaded while the mount is in operation.
 F-125 Frigate Baden-Wurttemberg
F-125 Frigate Baden-Wurttemberg
An ammunition manipulator system is available to transport projectiles and propelling charges from the main ammunition store to the feeding magazines, which are automatically reloaded. Ammunition flow is reversible. Rounds can be automatically unloaded from the gun. Digital and Analog interfaces are available for any Combat Management System, also according to Corba protocol. The 127/64 LW Naval Gun Mounts includes a Vulcano module, which acts twofold:
– Programmer for ammunition’s fuse and guidance system.
– Mission Planning and Execution for Naval Fire Support Action (firing solutions, selection of ammunition, definition of trajectories and firing sequences, ballistic computations accounting for ammunition type, etc.), as a standalone or in interaction with ship’s Network Centric System.
 Vulcano unguided projectile. Note how the projectile is carried down in the propelling cartridge. This will allow it to be used in the 54-caliber barrel. Picture courtesy of Ministero della Difesa. – Image: navweaps.com
Vulcano unguided projectile. Note how the projectile is carried down in the propelling cartridge. This will allow it to be used in the 54-caliber barrel. Picture courtesy of Ministero della Difesa. – Image: navweaps.com Future Vulcano Projectile with Inertial and GPS guidance. Picture courtesy of Ministero della Difesa. – Image: navweaps.com
Future Vulcano Projectile with Inertial and GPS guidance. Picture courtesy of Ministero della Difesa. – Image: navweaps.com
Technical data:
Caliber: 5 inches / 127 mm
Barrel lenght: 320 inches / 8,128 meters (= 64 caliber)
Weight: 33000 kg (without ammunition)
Elevation: -12° / +70°
Traverse: +/- 155°
Rate of fire: 32 rounds per minute
Range: 23000 meters, max. / 15000 meters effective / 8600 meters AA / up to 100 km with Vulcano ER/LR ammunition
Ammunition stowage: 56 rounds ready to fire in 4 loader drums / 500-600 in magazine
Ammunition: all standard 5-inch ammunition including the new Vulcano extended range / long range guided ammunition
OTO-Melara 127/64 LW source seaforces.org
 Otobreda 127 mm Vulcano main guns
Otobreda 127 mm Vulcano main guns
The gun has two automatic feeding devices (AFDs), one for the charges and one for the projectiles. The rounds are automatically assembled before entering the turret and can fire long-range Vulcano ammunition. The guns have a 35-rounds-a-minute rate of fire and a range of 23km against surface targets and 8.6km against airborne targets.
The German Navy has also selected the Oto Melara remote-controlled 12.7mm HITROLE naval turret in the naval tilting (NT) option for the F125. The contract covers the supply of 25 systems, five for installation of each of the four frigates and five for installation on land for training.
2 × 27 mm MLG 27 remote-controlled autocannons
 27 mm MLG 27 remote-controlled autocannons
27 mm MLG 27 remote-controlled autocannons
This is the navalized version of the 27 mm BK 27 aircraft gun used on the Tornado and Gripen fighter aircraft. Fire control is provided by a system from STN Atlas Elektronik with target tracking, fire control computation as well as gun control performed from a remote operator console. Sensors include a thermal imager, TV camera, laser range finder and automatic target tracking system with a video tracker.
This weapon was designed by Mauser-Werke Oberndorf Waffensysteme GmbH, a Rheinmetall DeTec subsidiary, to replace older 20 mm and 40 mm guns and the mounting does not require deck penetration. Can be operated remotely or locally with a joystick. 83 of these weapons have been ordered by the German Navy.
This weapon is a gas-operated automatic revolver cannon. Can be assembled for either left- or right-hand feed, and uses linkless ammunition with a case recovery system.
| DESIGNATION | 27 mm MLG 27 Light Naval Gun System |
|---|---|
| SHIP CLASS USED ON | 122, 123 and 124-class frigates, 332 and 333-class minehunters and minesweepers, 352-class mine countermeasures ships, 404-class tenders and 702-class supply ships Planned for K 130 corvette class |
| DATE OF DESIGN | about 1990 (Original aircraft design) |
| DATE IN SERVICE | 2003 (Navalized Version) |
| GUN WEIGHT | 37.5 lbs. (17kg) |
| GUN LENGTH OA | 91 in (2.310 m) |
| BORE LENGTH | N/A |
| RIFLING LENGTH | N/A |
| NUMBER OF GROOVES | N/A |
| LANDS | N/A |
| TWIST | N/A |
| CHAMBER VOLUME | N/A |
| RATE OF FIRE | 1,700 +/-100 rpm cyclic, lower training rates possible |
Source navweaps.com
 Baden-Württemberg Photo: Arne Luetkenhorst
Baden-Württemberg Photo: Arne Luetkenhorst
5 × 12.7 mm Hitrole-NT remote-controlled machine gun turrets
HITROLE® 12.7mm naval turret is a modern system fully controlled from a remote station via an advanced control console that allows the gunner to operate from a protected position within the ship’s structure: any operation, including loading and recocking, can be undertaken with maximum safety for the operator.
Low weight and high level of flexibility make this turret particularly suitable for installation as main armament of any small patrol vessel engaged in border control, maritime traffic interdiction or as a secondary armament on larger ships for self protection in the anti-terrorism role.
The turret is electrically operated and very accurate due to powerful digital servos.
Sighting and tracking actions are performed by means of a high performance day TV camera.
Ballistic Routine is available to provide aid while engaging moving targets.
Additional options include IR sensor for night operation as well as a Laser Range Finder, an Auto Tracker and the sensor suite is protected within a watertight shelter.
HITROLE® 12.7mm turret is a stand alone system with stabilization achieved via built-in Gyros system: no external signal is required by the turret from other ship systems.
Upon request, the HITROLE® 12.7mm turret can also be linked to other Electro-Optical sensors on board the ship and functional interface to ship’s Combat Management System can also be provided.
For special operations the 12,7mm (0.50 cal.) machine gun can be replaced with a 40mm Automatic Grenade Launcher (40mm AGL), capable of shooting also ‘non lethal ammunition’. The weapon replacement can be achieved in a few minutes with no need of special tools.
Belted rounds are available for both the 12,7mm( 0.50 cal) machine gun and the 40mm AGL in standard ammunition boxes, (130 rounds for the 12,7mm (0.50 cal) machine gun and 32 rounds for the 40mm AGL).
An optional ammunition loading system can be installed in a dedicated support in order to increase the available 12,7mm (0.50 cal) rounds up to 400.
Source leonardocompany.com
2 × 12.7 mm heavy machine guns
 12.7 mm heavy machine guns (manually controlled)
12.7 mm heavy machine guns (manually controlled)
Missiles
 Mk141 launchers of the lead ship of the class and one MLG27. Photo: Arne Luetkenhorst – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Mk141 launchers of the lead ship of the class and one MLG27. Photo: Arne Luetkenhorst – Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Two quadruple missile launchers for the Boeing RGM-84 Harpoon anti-ship missile are installed on the missile deck forward of the funnel. The Harpoon missiles are armed with a 227kg warhead and use active radar homing. The missiles have a high subsonic speed (Mach 0.9) and a range of up to 130km.
8 x Boeing RGM-84D Harpoon anti-ship missiles
General characteristics:
Primary function: Air-, surface-, or submarine-launched anti-surface (anti-ship) missile
Contractor: McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing)
Power plant: Teledyne CAE J402 turbojet, 660 lb (300 kg)-force (2.9 kN) thrust, and a solid-propellant booster for surface and submarine launches
Length: Air-launched: 3.8 metres (12 ft) / Surface and submarine-launched: 4.6 metres (15 ft)
Weight: Air-launched: 519 kilograms (1,144 lb) / Submarine or ship launched from box or canister launcher: 628 kilograms (1,385 lb)
Diameter: 340 millimetres (13 in)
Wing span: 914 millimetres (36.0 in)
Maximum altitude: 910 metres (2,990 ft) with booster fins and wings
Range:
Over-the-horizon (approx 50 nautical miles)
AGM-84D (Block 1C): 220 km (120 nmi)
RGM/UGM-84D (Block 1C): 140 km (75 nmi)
AGM-84E (Block 1E): 93 km (50 nmi)
AGM-84F (Block 1D): 315 km (170 nmi)
RGM-84F (Block 1D): 278 km (150 nmi).
RGM/AGM-84L (Block 2): 278 km (150 nmi)
AGM-84H/K (Block 1G / Block 1J): 280 km (150 nmi)
Speed: High subsonic, around 850 km/h (460 knots, 240 m/s, or 530 mph)
Guidance: Sea-skimming cruise monitored by radar altimeter, active radar terminal homing
Warhead: 221 kilograms (487 lb), penetration high-explosive blast
Unit cost: US$1,527,416
Source seaforces.org
Mk141 Harpoon launch tubes
 8 x Mk141 Harpoon launch tubes
8 x Mk141 Harpoon launch tubes
Each frigate carries eight (8) Boeing RGM-84D Harpoon anti-ship missiles in two Mk141 quad launchers amidships. This is an interim solution until the advanced joint sea/land attack missile Saab Bofors Dynamics RBS-15 Mk4 becomes available. The German Navy has chosen the Mk3s and Mk4s to equip its Braunschweig class corvettes and F125-class frigates and also plans to upgrade its Brandenburg-class frigates with Mk3. Source: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
German Navy K130 Corvettes Ready for Saab RBS-15 Mk3 Anti-Ship Missiles: Here
 German Navy Braunschweig class corvettes (K130)
German Navy Braunschweig class corvettes (K130)
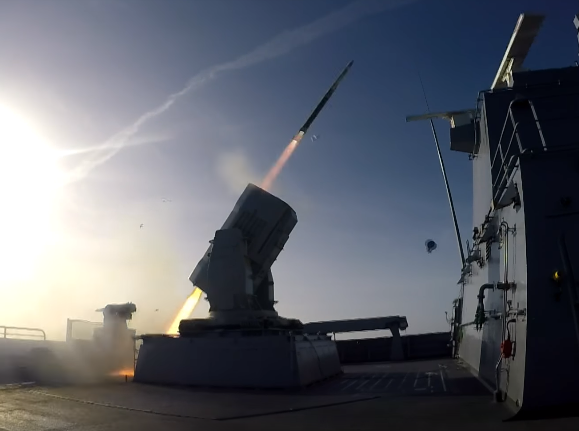
The F125 has two 21-cell MK49 launchers armed with the Raytheon RIM-116 rolling airframe missile (RAM). The RAM point defence missile is a lightweight, infrared-homing, surface-to-air missile for deployment against incoming anti-ship cruise missiles. The forward launcher is installed immediately forward of the bridge and the aft launcher is installed on the roof of the helicopter hangar just forward of the helicopter deck.
2 x 21-cell MK49 launchers
The Rolling Airframe Missiles, together with the Mk 49 Guided Missile Launching System (GMLS) and support equipment, comprise the RAM Mk 31 Guided Missile Weapon System (GMWS). The Mk-144 Guided Missile Launcher (GML) unit weighs 5,777 kilograms (12,736 lb 2 oz) and stores 21 missiles. The original weapon cannot employ its own sensors prior to firing so it must be integrated with a ship’s combat system, which directs the launcher at targets. Source seaforces.org
Raytheon RIM-116 rolling airframe missile (RAM)
RAM Block 2, the latest step in the development of the Rolling Airframe Missile, is a kinematic and Radio Frequency (RF) receiver upgrade of Block 1/1A. A larger, more powerful, composite case rocket motor and advanced Control Section (4 canards vs. current 2) make the missile two and a half times more maneuverable with one and a half times the effective intercept range. This provides the Block 2 missile with the capability to defeat high-maneuvering threats, increasing the survivability of the defended ship. An enhanced RF receiver allows detection of anti-ship missiles that employ low probability of intercept receivers.
The Mk-44 Guided Missile Round Pack (GMRP) and the Mk-49 Guided Missile Launching System (GMLS), which hold 21 missiles, comprise the Mk-31 Guided Missile Weapon System (GMWS). The system is designed for flexibility in ships’ integration, with no dedicated sensors required. A variety of existing ship sensors can readily provide the target and pointing information required to engage the anti-ship threat.
The Mk-44 GMRP is also the missile used in the SeaRAM Anti-Ship Missile Defense System, replacing the M601A1 Gatling gun in the Phalanx Close-In Weapon System (CIWS) with an 11-round launcher. The Phalanx sensor suite serves as the search and track radar designating the threat for RAM missiles to intercept.
General Characteristics
| Primary Function | Ship Self Defense |
| Contractor | Raytheon |
| Missile Capacity (Mk-49 GMLS) | 21 |
| Length | 9.45 feet/2.88 m |
| Diameter | 6.25 inch/15.87 cm |
| Wingspan | 12.65 inch/32.17 cm |
| Weight | 194.4 lbs/88.2 kg |
| Speed | Supersonic |
Source dmitryshulgin.com
Sensors
The frigates have no conventional on-board sonar but instead have a diver and swimmer detection sonar to counter terrorist threats. The frigates are equipped with a 360° infrared surveillance system installed on the front surface of the tower mast at a position just lower than the air and surface search radar.
Radar systems will include an EADS TRS-3D air and surface search radar, navigation and fire control radars. The TRS-3D radar carries out automatic detection, track initiation and tracking of all types of air and sea targets. *Note it is TRS-4D*
The navigation radar is installed on the roof of the bridge.
TRS-4D naval radar
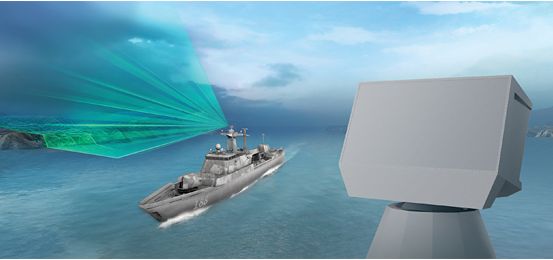
TRS-4D enables ships ranging from patrol vessels to frigates to carry out the various detection tasks required of ship-borne, medium-range radar systems both in the open sea as well as in complex coastal zones with a high target density. Compared to conventional radars, this more accurate, faster system now tackles a wider-than-ever scope of targets, e.g. for protection against asymmetric attacks.
The new radar is based on a unique system concept. In contrast to any other systems available on the market, the TRS-4D is the first surveillance radar to make full use of the advantages of AESA technology (AESA = Active Electronically Scanned Array), which is based on multiple independent emitters. This results in a detection performance that is unprecedented worldwide.
For the F125 frigates the system will be deployed in a version with four fixed arrays. Source: Defense Talk


Source: AIRBUS DEFENSE AND SPACE
 Photo: Hartmut Hoffmann – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Photo: Hartmut Hoffmann – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
The F125 class has the non-rotating multi-function Airbus Group TRS-4D/NR (Non Rotating) Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) C-band radar version with two fixed arrays on the forward radar mast and two on the rear mast. The radar works using the technology of electronic beam scanning (E-Scan), which is deployed for both conventional, mechanically rotating aerials and immovably mounted radar aerial panels. Four aerial panels are distributed between two ship’s masts, each carrying two panels. Due to the real-time electronic control of the beam, this radar can carry out several reconnaissance tasks at the same time. For example, it can do a long-range scan of the sea and airspace while simultaneously concentrating on tracking individual targets. In comparison to conventional radars it thus achieves a significantly higher surveillance and detection efficiency and reliability. The radar’s performance is essentially based on numerous transmitter and receiver modules in the aerial, which are made from materials especially suitable for high frequencies. The radar offers three fundamental modes: Surveillance, Self-Defense and Sector (see table for performances). The maximum range of the radar is up to 250km, up to 14km for small surface targets and up to 100km for maritime patrol aircrafts. It can track up to 1,000 targets.
 Photo: Hartmut Hoffmann – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Photo: Hartmut Hoffmann – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Within a single system, the TRS-4D incorporates:
- 3D air volume surveillance with fast target alert
- High range resolution surface surveillance
- Target designation to combat management system for AAW and ASuW
- Surface gun fire control with splash detection
- Ship-controlled helicopter approach (SCA) support
- Jammer detection, tracking and suppression
- Cued search with enhanced detection performance for a dedicated sector
- Cued track with high-accuracy target tracking for missile guidance
- Sector scanning with non-rotating antenna
- Target classification
- Integrated IFF
Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
MSP 600 – Optronic Modular Sensor Platform
The Modular Sensor Platform MSP 600 is a light-weight four axis stabilized electro-optical system, which can be used in land-based applications (e.g. border or coastal surveillance and air defence), airborne (e.g. helicopters) and shipborne as a stand-alone sensor or as part of a command and fire control system. Always operating in passive mode, the MSP 600 is virtually undetectable and thus complements, or is a substitute for, radar.
The MSP 600 comprises a thermal imager, a daylight camera, a laser range finder and a dual mode tracker. To achieve excellent stabilization values of the line of sight, the sensor package is controlled by a coarse/fine system and is thus independent of environmental influences. The MSP is an excellent data source for tactical and/or nautical navigation as well as for fire control. Source rheinmetall-defence.com
SIMONE (Ship Infrared Monitoring Observation and Navigation Equipment)
In order to close the capability gap in autonomous close-in monitoring and to increase protection against asymmetric threats, Diehl BGT Defence was tasked with the development of an optical surveillance system. Diehl designed SIMONE (Ship Infrared Monitoring Observation and Navigation Equipment) to equip the new German frigates. The system provides complete and permanent monitoring of the vessel´s structure as well as it allows early and reliable detection of small objects, even very small suspicious objects such as inflatable rubber boats or persons swimming, enabling flexible and precise response. SIMONE takes into account the new crew concept envisaging less manpower by provision of autonomous monitoring requiring no additional personnel. Automatic alarm with relevant data for the command and control system is generated in case of detected threats. Uncooled infrared detectors featuring longevity as well as 24/7 high image quality meet the requirement of permanent operational readiness. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
SIMONE consists of a sensor suite either fully integrated into the ship (in case of new constructions) or retrofitted into existing platforms. Figure 1 shows an overview of the system architecture. Modules containing uncooled IR microbolometer sensors are arranged on the ship to continuously cover its surrounding. Using this configuration, the number of ‘dead zones’ caused by shadowing are minimized, and observation is possible from the ship’s hull. Image data is transferred to a central processing cabinet (a computer) for real-time processing over Ethernet. Live video imagery and alarm data can be fed to several clients (computers that possess a network connection to the processing cabinet) simultaneously. All of the system components are connected by fiber-optic links.
 Figure 1. System architecture for automatic surveillance of a ship’s surroundings using sensors.
Figure 1. System architecture for automatic surveillance of a ship’s surroundings using sensors.
 Figure 2. Image enhancement supporting perception of detailed image content. The red rectangle denotes the area where the brightness/contrast adaption is executed in a way that this part of the image can be optimally interpreted by the operator.
Figure 2. Image enhancement supporting perception of detailed image content. The red rectangle denotes the area where the brightness/contrast adaption is executed in a way that this part of the image can be optimally interpreted by the operator.
The homogeneous and simultaneous delivery of the imagery visualization is executed by the human machine interface. This characteristic is particularly important for scenes covering a wide range of temperatures and containing objects with little radiometric contrast compared to their background. Automatic image processing is performed on the full pixel depth. However, the interpretation of the scene content by human operators requires the contrast of the imagery to be improved because the human eye is limited in terms of the range of contrast distinguishable. To improve the contrast, we use a range of algorithms to process the imagery. Figure 2 shows the result of employing these algorithms to enhance the human operator’s ability to capture the full visual content of the image. The top-left image is the raw data. Simple adjustments to brightness and contrast highlight details of the area marked by the red rectangle, whereas information outside this area is lost. Image enhancement algorithms automatically perform a local adjustment of brightness and contrast based on the image content. The result is the detailed image on the bottom right.
By distributing the sensors on the ship, we aim to create a panoramic view of the surroundings, which can be displayed on the human machine interface together with alarm data (see Figure 3). Indeed, our system has been qualified according to military standards for use in harsh naval environments, including electromagnetic compatibility. Source spie.org
Countermeasures
Much of the electronic warfare suite has not been announced but it will include four Rheinmetall multi-ammunition softkill systems (MASS). The MASS decoy and mini mortar dispensers are installed on the port and starboard sides above the bridge and on the helicopter hangar roof.
Rheinmetall multi-ammunition softkill systems (MASS)

The automatic decoy system MASS provides a unique level of protection against modern sensor-guided missiles. MASS can be installed on ships of all types and can be integrated into existing command systems. The new MASS_ISS features built-in sensors for detecting radar and laser threats. Programmable and omni-spectral, the system’s innovative ammunition provides protection in all relevant wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. Source rheinmetall-defence.com
Aircraft
 Fight deck. Photo: Alexander Gottschalk
Fight deck. Photo: Alexander Gottschalk
The frigate has a 490m² aft helicopter deck and a hangar for two NH-90 helicopters. The helicopters have a range of 790km.
NHIndustries NH90: Details
Each ship can accommodate two medium class helicopters and/or UAVs as well as four armed 11-meter FASSMER Special Operations Boats SFB 10.1 Rigid-Hulled Inflatable Boats (RHIB). The four RHIBs are accommodate in equal numbers of bays, two at each side of the ship. These bays are fitted with davits that lower the RHIB on to the water. The FASSMER RHIBs are capable of more than 40 kn (74 km/h); for more information about the boats visit this link. Furthermore, two 6.1-meter containers may be embarked immediately after the fore mast. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
11-meter FASSMER Special Operations Boats
 Photo: Dennis Schneider, Bundeswehr – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Photo: Dennis Schneider, Bundeswehr – Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com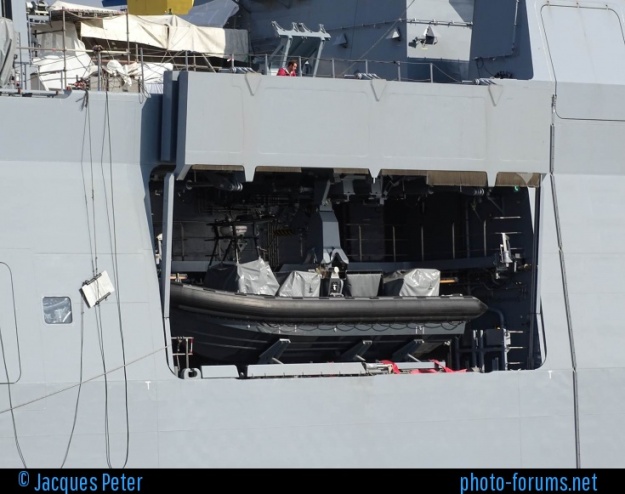
Propulsion
 Image: Thyssen Krupp
Image: Thyssen Krupp
The frigates are fitted with a new combined diesel electric and gas (CODLAG) electrical propulsion system with a 20MW General Electric LM 2500 gas turbine, four MTU 20V 4000 M53B diesel engines providing 3,015kW each (total 12.06MW) and two Siemens electric motors providing 4.5MW each (total 9MW).
1 x General Electric LM2500

The General Electric LM2500 is an industrial and marine gas turbine produced by GE Aviation. The LM2500 is a derivative of the General Electric CF6 aircraft engine.
The LM2500 is available in 3 different versions:
- The LM2500 delivers 33,600 shaft horsepower (shp) (25,060 kW) with a thermal efficiency of 37 percent at ISO conditions. When coupled with an electric generator, it delivers 24 MW of electricity at 60 Hz with a thermal efficiency of 36 percent at ISO conditions.
- The improved, 3rd generation, LM2500+ version of the turbine delivers 40,500 shp (30,200 kW) with a thermal efficiency of 39 percent at ISO conditions. When coupled with an electric generator, it delivers 29 MW of electricity at 60 Hz with a thermal efficiency of 38 percent at ISO conditions.
- The latest, 4th generation, LM2500+G4 version was introduced in November 2005 and delivers 47,370 shp (35,320 kW) with a thermal efficiency of 39.3 percent at ISO conditions.
LM2500 installations place the engine inside a metal container for sound and heat isolation from the rest of the machinery spaces. This container is very near the size of a standard 40-foot (12 m) intermodal shipping container – but not the same, the engine size very slightly exceeds those dimensions. The air intake ducting may be designed and shaped appropriately for easy removal of the LM2500 from their ships. Source wikiwand.com
4 x MTU 20V 4000 M53B diesel engines
 Image: defenceindustrydaily.com
Image: defenceindustrydaily.com
| Engine model | 20V 4000 M53B | |||
| Rated power to DIN ISO 3046 | ICXN | |||
| Rated power max. | kW (bhp) | 3015 (4043) | ||
| Speed max. | rpm | 1800 | ||
| Frequence | hz | 60 | ||
| Exhaust emission | 18 | |||
| Engine main data | ||||
| Bore/Stroke | mm (in) | 170/190 (6,7/7,5) | ||
| Cylinder displacement | l | 4,31 | ||
| Displacement, total | l (cu in) | 86,2 (5263) | ||
| Intake air temparature | °C | 25 | ||
| Sea water temperature | °C | 25 | ||
| Site altitude above sea level | m | 100 | ||
| Barometric pressure | mbar | 1000 | ||
| Power reduction at 45/32 °C | % | 0 | ||
| Fuel consumption | l/h (gal/h) | 738,4 (195,0) | ||
| Fuel consumption | ||||
| at rated power | l/h (gal/h) | 580,9 (153,4) | ||
Source mtu-online.com
Renk main gear unit
The propulsion system provides for the combination of a GE LM2500 gas turbine of 20,000 kW, with two 4,500 kW electric motors in a CODELAG (combined diesel-electric and gas turbine) configuration using a Renk main gear unit on the port side and starboard side, both interconnected by a cross-connect gear. Slow and cruising speeds are achieved using the electric motors, for full speed, additional power is supplied by the gas turbine.
 CODELAG propulsion arrangement for the German F125 Baden Württemberg Class frigate
CODELAG propulsion arrangement for the German F125 Baden Württemberg Class frigate
Image credit: Renk AG – Source: maritimepropulsion.com
The electric motors are positioned forward of the gear unit and drive the propeller shaft directly without a reduction gear via multi-disc clutches. The gas turbine is linked to the cross-connect gear via an over-running clutch. Electrical power for propulsion an hotel use is provided by four MTU 20V4000 M53 gensets each of 3,015kW at 1,800 rpm. Source maritimepropulsion.com
 Baden-Württemberg Photo: Arne Luetkenhorst
Baden-Württemberg Photo: Arne Luetkenhorst
The main machinery will run for 30,000h between major overhauls. The F125 is fitted with bow thrusters for precision dockyard manoeuvring without assistance.
Bow thrusters
 Bow thrusters can be seen – Image: dmitryshulgin.com
Bow thrusters can be seen – Image: dmitryshulgin.com
Technical Data
| MAIN DIMENSIONS | |
| Length overall | 149 m/489 feet |
| Beam maximum | 18.8 m/61.7 feet |
| Draught | 5.0 m/16.4 feet |
| Displacement (approximately) | 7,100 t |
| Speed | 26 knots/30 mph/48 km/h |
| Range | 4,000 NM/4,603 miles/7,408 km at a speed of 18 knots/21 mph/33 km/h |
| PROPULSION PLANT | |
| CODLAG | Combined diesel-electric and gas |
| CPP (Controllable Pitch Propellers) | 2 |
| Diesels MTU 20 V 4000 | 4 × 3,015 kW (total 12.06 MW) |
| Propulsion Electric Motors | 2 × 4.5 MW (total 9 MW) |
| Gas Turbine GE LM 2500 | 1 × 20 MW |
| COMPLEMENT | |
| Crew | 120 |
| Supernumerary (Helicopter/Special Forces) | 70 |
| HELICOPTER | |
| NHIndustries MH-90 | 2 |
| BOATS | |
| RHIBs (11-meter length) | 4 |
Technical data dmitryshulgin.com
Main material source naval-technology.com
Revised May 13, 2017
Updated Feb 08, 2018




















Your article is very interesting. And you have decorated your art beautifully. It inspires people a lot. If the subject is good, then it is also fun to read and this is what people want nowadays, your post is really interesting. Inspired by you, I too think I should write an article on a fun subject.
LikeLike
Thanks
LikeLike
saw this very good post of yours and I liked it very much, I do not know how to praise it, I would just like to say that this post is one of the posts that I like very much and I am very happy to see these posts.
LikeLike
Thank you very much and happy that you like the post.
LikeLike
I really don’t understand the F125 class. It is the biggest war ship the (modern) German Navy ever had, but it has about the same armament as a small corvette. It seems to be the most under-gunned warship I have ever seen. It doesn’t even have vertical launch tubes. What were they thinking? I know, the main “gimmick” and selling point is a new level of mission endurance, but what is the point of having a ship in mission longer when the ship doesn’t carry the tools it needs to get the mission done? So it is “specialized” for littoral warfare, beach head attacks and landing operations, but it can’t even protect the special forces it lands from air attack, because it only has short range anti air capabilities. Maybe I am overlooking something, but to me this ship makes no sense. It seems as if they built a new warship and forgot to put weapons on it. When I first heard about this class, many years ago, there were plans to put a 155mm artillery gun on it, cruise missiles and even a naval version of an MRLS artillery missile launcher. There was even talk about it getting 2 Tiger attack helicopters. It was supposed to be basically a tiny pseudo aircraft carrier, supposed to have a lot of land attack capabilities and built for “cannon boat diplomacy”, to put it bluntly. But none of that was actually done. It seems they exclusively built those ships for those silly pirate hunting missions, which aren’t needed anymore since freight ships and tankers have mercenaries on them now.
LikeLike
That’s why If Thailand or the Philippines want a Cold war era Frigate, they should talk to Germany ASAP on the Bremen class frigates. The Bremen class frigates were designed for AAW and ASUW warfare.
LikeLike
RTN already have ordered the Korean stealth frigate and about to negotiate the second one they also operate the Knox Class which they will decommission when they receive the new frigates
LikeLike
Maybe Thailand can hand over the old Knox to the Philippines.
LikeLike
Take a look https://youtu.be/xdXs4q60Uwk
LikeLiked by 1 person
Here’s a US Navy Training Video on ASROC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vXJQQ5zryik
LikeLike