The US Navy F/A-18 E and F Super Hornet maritime strike attack aircraft, manufactured by Boeing, flew for the first time on November 29 1995. The Super Hornet is about 25% larger than its predecessor, the F/A-18C/D, but contains 42% fewer structural parts. The single-seat F/A-18/E and the two-seat F/A-18/F fly greater ranges with heavier payloads, have more powerful engines and provide greater survivability.

For reference see CF-18 Hornet: Details
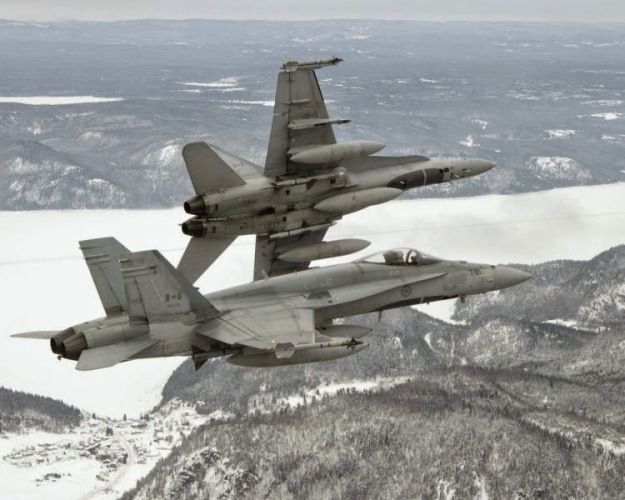 CF-18A
CF-18A
F/A-18 Super Hornet orders and deliveries
The first low-rate initial production aircraft was delivered in December 1998, and all 12 of the first batch were delivered by November 1999.
In February 1999, the US Navy placed an order for 30 Super Hornets, in addition to the 12 already ordered. Following successful completion of operational evaluation, in June 2000 the USN ordered 222 fighters to be produced over five years.

The first full-rate production aircraft was delivered in September 2001.
A second multi-year contract was signed in January 2004 for 42 aircraft to be purchased between 2005 and 2009. Total requirement was for at least 545 aircraft. Over 500 aircraft had been delivered by April 2011.
Super Hornet programme and development
In July 2002, the F/A-18E/F began its maiden operational deployment on board USS Abraham Lincoln (CVN 72). In November 2002, the aircraft made its combat entry, striking air defence sites in Southern Iraq with Joint Direct Attack Munitions (JDAM). The aircraft was also deployed as part of Operation Iraqi Freedom in March 2003.

Improvements scheduled for Block 2 aircraft include a redesigned forward fuselage which has fewer parts and changes to the aircraft’s nose to accommodate the Raytheon APG-79 Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar. The first aircraft was delivered in September 2003.
The aircraft is fitted with new mission computers, fibre-optic network, Raytheon AN/ASQ-228 ATFLIR targeting pod, Boeing joint helmet-mounted cueing system and Raytheon AIM-9X next generation Sidewinder air-to-air missile.
In April 2007, Boeing announced that it had been asked by the US Navy to provide an Infrared Search and Track (IRST) system for the F/A-18E/F. Boeing has selected Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control to supply the system. In November 2011, the US Navy awarded a $135m contract for engineering and manufacturing development of the IRST sensor system. The IRST system is expected to achieve initial operating capability by 2016.
U.S. Navy Purchases F/A-18E/F Infrared Search and Track Systems
The Boeing Co., St. Louis, is being awarded an $82,084,777 fixed-price-incentive-firm contract for the procurement of 12 low-rate initial production infrared search and track (IRST) systems for the F/A-18E/F aircraft. The IRST system is a long-wave infrared detection system that targets airborne vehicles in a radar-denied environment. Work will be performed in Orlando, Florida (50 percent); St. Louis (38 percent); Santa Ana, California (7 percent); and Irvine, California (5 percent). It is expected to be complete in January 2020. Fiscal 2016 aircraft procurement (Navy) funds in the amount of $82,084,777 are being obligated on this award, none of which will expire at the end of the current fiscal year. This contract was not competitively procured pursuant to 10 U.S. Code 2304( c)(1). The Naval Air Systems Command, Patuxent River, Maryland, is the contracting activity (N00019-17-C-0026). Source afcea.org
F/A-18E/F Infrared Search and Track System IRST21 AN/ASG-34
AN/AAS-42 system
 F-14D AAS-42 – Image: sistemasdearmas.com.br
F-14D AAS-42 – Image: sistemasdearmas.com.br
Lockheed Martin’s IRST is a development of the AN/AAS-42 system that was originally carried by Northrop Grumman F-14D Tomcats. However, it has been undergoing development since then, first for the abortive pod-mounted system for the F-15 Eagle, and now further refined for the Super Hornet application. Source ainonline.com
IRST21 AN/ASG-34 IRST Sensor System
 IRST21 Sensor System – Image: lockheedmartin.com
IRST21 Sensor System – Image: lockheedmartin.com
Features
- Long-range infrared scan and detection of airborne threats
- Passive detection and ranging
- Large field of regard
- Immune to electronic deception
- Programmable scan modes
- Low false-alarm rate
- Automatic target detection algorithms
- Multiple mounting options

Source PDF lockheedmartin.com
The F/A-18E/F IRST system is installed in the nose section of the centerline fuel tank on the aircraft. The IRST is the next generation of the F-14D AN/AAS-42 IRST that accumulated over 200,000 flight hours aboard US aircraft carriers. Boeing awarded the technology development contract to Lockheed Martin in May 2009. The US Navy has a requirement for 150 IRST systems with first deliveries due in 2011.
The new IRST technology developed by Lockheed Martin features high resolution providing dramatically improved raid cell count at maximum ranges. Compared to a radar at a maximum range the IRST is 40 times more accurate. The information gathered by the new sensor can stand alone or be fused with other sensor data to enhance situational awareness, ensuring first-to-see, first-to-shoot capability. It also enhances the engagement range of high performance air-to-air missiles such as the AIM-120 AMRAAM. The IRST has been designed to complement the latest generations of tactical radars providing long-range detection of airborne targets with low false alarms under subsonic and supersonic speed and clutter backgrounds such as blue sky to severe mountain and urban terrain. An additional benefit is that the IRST systems are effective against low radar cross section targets while reducing the threat posed by anti-radiation missiles and radar warners. Source deagel.com
 F/A-18E/F IRST system – Image: deagel.com
F/A-18E/F IRST system – Image: deagel.com
The U.S. Navy received Milestone C acquisition approval earlier this month to begin low-rate initial production (LRIP) of an infrared search and track (IRST) sensor pod for the F/A-18 Super Hornet. Manufacturer Lockheed Martin and partner Boeing will deliver six pods in the first LRIP lot.
The AN/ASG-34 IRST sensor gives the F/A-18E/F a long-range, passive search and tracking capability against multiple targets, supplementing the jet’s APG-79 active electronically scanned radar and other sensors. The pod is mounted on the nose section of the Super Hornet’s centerline fuel tank. It completed a first flight aboard an F/A-18F in February.
“Integrating the infrared pod onto the Super Hornet revolutionizes how we fight on a networked battlefield,” said Capt. Frank Morley, Naval Air Systems Command PMA-265 program manager. “IRST advances the Super Hornet’s role in air-to-air combat operations, keeping us ahead of our adversaries in an evolving threat environment.”
The IRST program “was not impervious” to defense budget cuts, said Michele Moran, the PMA-265 electro-optics/infrared integrated product team lead. “Our team was able to completely restructure the program, overcome the budget constraints and press forward with Milestone C.”
Vice Adm. Paul Grosklags, principal military deputy to the assistant secretary of the Navy for research, development and acquisition, made the Milestone C approval on December 2. The six LRIP pods will enable the program to work toward initial operational capability of the system, which the Navy expects in 2017. Source ainonline.com
In February 2007, Australia requested the FMS of 24 F/A-18F Block 2 aircraft. The contract was placed in May 2007. The first five aircraft were delivered in March 2010 and and rest of them were delivered by October 2011. The F/A-18F Block 2 aircraft cover the capability gap between the retirement of the F-111s in December 2010 and the delivery of the first F-35 Joint Strike Fighter to Australia in 2013.
The US Navy has approved System Development & Demonstration (SD&D) for an electronic attack version of the Super Hornet, the EA-18G, to replace the EA-6B Prowler. The EA-18G incorporates the Improved Capability III (ICAP III) suite developed for the Prowler. Two SDD aircraft were delivered. First flight of the EA-18G was in August 2006.
US Navy kicks-off Super Hornet Block 3 effort with IRST contract
 A mock-up of the integrated Block 2 IRST system seen forward of the nosewheel on this Super Hornet that was fitted with the improvements planned under the International Roadmap. This moniker was changed to the Advanced Super Hornet, and has now become the Super Hornet Block 3. (IHS Markit/Gareth Jennings)
A mock-up of the integrated Block 2 IRST system seen forward of the nosewheel on this Super Hornet that was fitted with the improvements planned under the International Roadmap. This moniker was changed to the Advanced Super Hornet, and has now become the Super Hornet Block 3. (IHS Markit/Gareth Jennings)
Gareth Jennings, London – IHS Jane’s International Defence Review
26 May 2017
The US Navy (USN) has begun the process of upgrading its F/A-18E/F Super Hornet to the latest Block 3 standard, with a contract award to Boeing to incorporate the Block 2 Infrared Search and Track System (IRST) onto the combat aircraft.
The cost-plus-incentive-fee contract, which was announced by the Department of Defense (DoD) on 25 May, is valued at USD89 million and covers the initial design and development, procurement of prototyping hardware, technical risk reduction efforts, integrated product support, and technical reviews of the Block 2 IRST with the F/A-18E/F to support the system through the preliminary design review. Work is expected to be completed in April 2020.
The USN’s Super Hornets already field an IRST in the guise of the podded AN/ASG-34. This system, which was developed by Lockheed Martin, with assistance from Boeing and General Electric, is not integrated into the aircraft but is instead housed in a modified centreline drop tank that is carried on the centreline hardpoint. With this system, the Super Hornet is able to identify and track aircraft from their thermal signature (either through the engine or the aerodynamic heating of the airframe). Not being integrated, the AN/ASG-34 is very much an interim solution prior to the navy adopting an internal system.
The Block 2 IRST is one of a number of enhancements for the Super Hornet that the USN is set to incorporate under its Block 3 plan to take the aircraft’s service life out to the end of the 2040s. Block 3, which was previously known by Boeing as the Super Hornet International Roadmap and then as the Advanced Super Hornet, is built around a new more powerful processor than the one currently fitted to the aircraft. Source janes.com
Super Hornet Block III

Super Hornet Block III differs from the earlier proposed Advanced Super Hornet in that Boeing is no longer focused on improving the fighter’s stealth capability relative to the F-35’s, said Dan Gillian, F/A-18 and EA-18 program manager. Rather, it proposes to integrate networking components that along with other improvements would make the Super Hornet an equal partner with the F-35 in future strike formations.
Boeing would enable the Block III fighter by installing a Distributed Targeting Processor-Networked (DTP-N) computer and tactical targeting network technology (TTNT) Internet-protocol-based, high-speed datalink, both program-of-record upgrades for the Super Hornet’s EA-18G Growler electronic warfare variant, Gillian said. It would have an advanced cockpit with a 10-by-19 inch Elbit Systems large area display as the pilot interface, similar to what Boeing has installed in the F-15 and the clean-sheet jet it developed for the U.S. Air Force’s T-X advanced jet trainer requirement. In terms of cost, “the delta between a Block 2 and a Block 3 is a couple million dollars,” Gillian said.
Cockpit
Elbit Systems
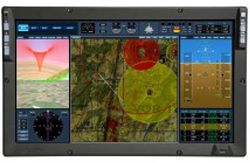
Elbit Systems of America® is a global leader in developing and manufacturing display and mission management systems for air, land, and sea applications. Military forces worldwide rely on our displays to simplify the increasing workload on commanders and crew by presenting information and crisp, sensor video images that enhance communication, navigation, and situational awareness capabilities.
Features and Benefits:
- AMLCD ruggedization to withstand and perform in harsh military environments
- Backlights efficiently deliver high brightness for direct sun viewability while allowing extreme dimmability for night operation in excess of 20,000:1
- ANVIS compatibility with both Class A and Class B requirements, wide-viewing angles, and preservation of the red color
- System
- Powerful real-time and non real-time processors backed with our high-performance and high visual quality graphics accelerators and generators
- Optimized video processing for image clarity and resolution
- Multiple picture-in-picture windowing with a comprehensive interface suite
- System software with powerful applications including: primary flight display, situational awareness, digital real-time moving map, fusion of sensor video with digital maps, digital terrain elevation, threat intervisibility, data sharing, messaging, and EFB.
- Packaged in the smallest volume possible with the lowest power consumption and weight
Source elbitsystems-us.com
The networking system upgrade, matched with the already approved Lockheed Martin AN/ASG-34 long-range infrared search and track (IRST) sensor pod and evolutions of the Raytheon APG-79 active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar and Harris AN/ALQ-214 integrated defensive electronic countermeasures (IDECM) self-protection system, prepare the Super Hornet for the future threat environment, Boeing contends. As with the Advanced Super Hornet, the Block III Super Hornet would come with shoulder-mounted conformal fuel tanks containing 3,500 gallons of fuel, increasing the fighter’s range by about 120 nm and/or time on station by about 20 to 30 minutes depending on its mission payload, Gillian said.
Harris AN/ALQ-214 integrated defensive electronic countermeasures (IDECM) self-protection system

The ALQ-214 is the next generation integrated countermeasures system carried by the U.S. Navy F/A-18 Carrier-based aircraft. It has also been delivered to the Royal Australian Air Force for its F/A-18 aircraft.
Sensitive receivers and active countermeasures form an electronic shield around the F/A-18
The system blends sensitive receivers and active countermeasures to form an electronic shield for the U.S. Navy and RAAF F/A-18 fighter aircraft. The RF countermeasure system responds to threats autonomously with a specific series of measures designed to protect the aircraft from detection and engages any fired threats to the aircraft, to ensure mission success. Source harris.com


Conformal fuel tanks CFT

Tests have shown the CFTs installed on the upper fuselage increase the Super Hornet’s mission radius by up to 130 nm, for a total radius exceeding 700 nm. The CFTs add no drag to the aircraft at subsonic speed; at transonic or supersonic speeds they produce less drag than a centerline fuel tank, Boeing said. Enhancements to the aircraft’s radar cross section, including the EWP, produced a 50-percent improvement in its frontal low-observable (LO) signature. “We have worked very hard to make sure that the CFTs were not a negative contributor to the [radar] signature,” said Paul Summers, Boeing Super Hornet and Growler director.
 Detailed view: RCS improvements – Image: navyrecognition.com
Detailed view: RCS improvements – Image: navyrecognition.com
Radar Cross Section (RCS) improvements – Minor treatments to improve the low RCS levels of the aircraft. The mostly consist in a redesigned muzzle (in the nose of the aircraft) as well as improved angle of attack sensors (located on the sides of the nose). Source navyrecognition.com
CFTs on the Growler would provide equivalent mission performance in terms of range and performance, but with 3,000 pounds less fuel, compared to an EA-18G fitted with two 480-gallon external fuel tanks, three jamming pods and two AGM-88 HARM anti-radiation missiles. Summers said the removal of the external fuel tanks would enable the ALQ-99 tactical jamming pods and their planned replacement system in 2020, the Next Generation Jammer, to have an unobstructed field of regard for jamming. “Historically, the fuel tanks tend to block some of the radiation coming off of the airplane,” he said. Source ainonline.com
The IRST pod is especially a differentiator, he argued. “That’s something Super Hornet brings to the air wing that nobody else has—then you leverage it with things like the conformal fuel tanks and the DTP-N and TTNT and now your networked carrier air wing is much more effective,” Gillian said. The F-35’s integrated electro-optical targeting system (EOTS) infrared search and track sensor represents “medium range air-to-ground versus long range air-to-air” capability, he asserted.
Boeing expects to secure a first contract from the Navy early next year to begin a service life modernization program that will extend the service life of Block II fighters from 6,000 to 9,000 hours. New build Block III Super Hornets would already be 9,000-hour fighters, which Boeing could start delivering in the early 2020s; Block II fighters could be retrofitted through the service life modification “a little later than that,” Gillian said.
With the Navy burning through the service hours it needs to fly Super Hornets into the next two decades, and with President Donald Trump questioning the cost of the F-35 program and hinting at a major new F/A-18 order, Boeing has ramped up promotion of the Super Hornet Block III. Source ainonline.com
Situational awareness Multi-Spectral Fusion
 Detailed view: New satellite link/GPS antenna – Image: navyrecognition.com
Detailed view: New satellite link/GPS antenna – Image: navyrecognition.com
New computers and datalink – They would allow Block III Super Hornet to exchange large quantity of data with Growlers and E-2D Advanced Hawkeyes through the TTNT (Tactical Targeting Network Technology) network and fuze real time information. Source navyrecognition.com
Tactical Targeting Network Technology
Low-latency, ad hoc, IP-based networking for today’s warfighter
Rockwell Collins’ Tactical Targeting Network Technology (TTNT) is a secure and robust IP-based waveform that delivers the fastest ad hoc mesh network to the tactical edge. It’s a proven and mature system that instantly and accurately shares secure voice, video and data across a dynamic battlespace, meeting the rapidly changing networking needs of today’s warfighter.
 Features & benefits
Features & benefits
- Provides low-latency, ad hoc, IP-based networking to more than 200 users at any given time
- Self-forming and self-healing, so platforms automatically enter and leave the network without the advanced planning required with other networking options
- Allows for instant and accurate sharing of vast amounts of secure voice, video and data at speeds up to Mach 8
- Statistical priority-based multiple access (SPMA) protocol ensures critical data is sent and received by holding off the transmission of lower priority data until needed
- Strong anti-jam performance for contested environments that extends far beyond line-of-sight using multi-hop relay and automatic routing
- Platforms simultaneously transmit and receive up to four data streams
Source rockwellcollins.com
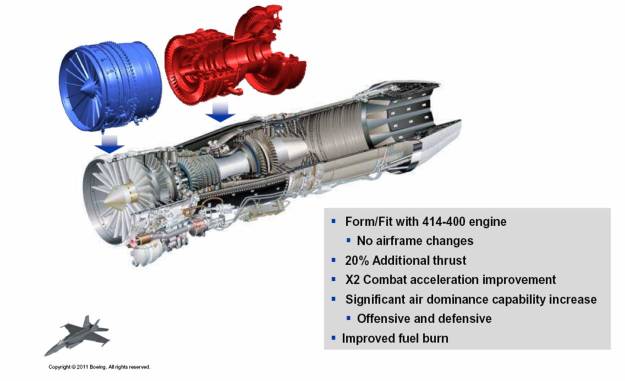
Enhanced version of current GE F414-400 engines
The enhanced powerplant is also more durable and maintainable. Technology changes extend the time between overhaul from 2,000 to 4,000 hours for the hot section, and from 4,000 to 6,000 hours for the turbine fan.
EA-18G Growler: Details
 EA-18G
EA-18G
F-18 Advance Super Hornet: Details

In May 2009, Boeing received a contract worth $48.9m for the development of Distributed Targeting (DT) system for super hornet aircraft.
In November 2011, the US Navy awarded a $48m contract to develop the Type 4 Advanced Mission Computer (AMC) for F/A-18E/F Super Hornet, which will replace the Type 3 AMC currently in use. It is expected to be completed by 2012.
Type 4 Advanced Mission Computer (AMC)

Boeing will collaboratively develop a new mission computer for the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and EA-18G Growler following a contract awarded by the US Navy. According to a company statement issued on 10 November 2011, Boeing received the $48 million contract for the Type 4 Advanced Mission Computer (AMC).
The Type 4 Advanced Mission Computer (AMC) will replace the current Type 3 on the Super Hornet and Growler aircraft, both of which are manufactured by Boeing. The company said that the new hardware will increase aircraft performance, address obsolescence issues, and improve image- and mission-processing functions, ‘increasing warfighter capabilities for both domestic and international customers’.
The system will also better position the aircraft for future Navy Flightplan capability upgrades, which will see the US Navy ensure that the Super Hornet and Growler remain ahead of future threats. Boeing expects a production contract during 2012. Source shephardmedia.com
In September 2011, Boeing and the US Navy proposed to offer F/A-18E Super Hornet Block II version aircraft to the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF).
In September 2011, the US Navy awarded a $5.297bn contract that includes delivery of 66 Super Hornet aircraft between 2012 and 2015.
AN / APX-111 IFF

The AN / APX-111 is a system for friend-to-enemy detection (IFF), which is used on the F / A-18 Hornet . Produced by BAE Systems .
Description

Technical specifications
- Weight: 20,60 kg
- Volume: 0,0134 m³
- Power consumption: 180 watts
- MTBF : 2500 hours
- MTTR : 15 minutes
- Error detection probability: 97%
Transponder system
- Transmission power: 0.5 kW
- Reception: -76 dBm
- IFF modes: 1, 2, 3 / A, C, 4, S (Mode 5 can be retrofitted)
Query system
- Range:> 185 km
- Transmission power: 1.4 kW
- Reception: -83 dBm
- Target sector: 70 ° × 60 ° (forward direction)
- Angular deviation: ± 2 °
- Distance resolution: <152 m
- Maximum targets: 32
- IFF modes: 1, 2, 3 / A, C, 4 (Mode 5 can be retrofitted)
- Waveform: monopulse
Source wikiwand.com
F/A-18 cockpit
The cockpit in the F/A-18E/F is equipped with a touch-sensitive control display, a larger multi-purpose liquid crystal colour display, which shows tactical information, two monochrome displays and a new engine fuel display. The aircraft retains the mission software and a high proportion of the avionics found in the C/D models.
 Pilot seat
Pilot seat  WSO
WSO
Honeywell AMPD 5-by-5-inch display

The AMPD rugged display family consists of 5-by-5-inch forward avionics displays; 5-by-5-inch aft displays, and 8-by-10-inch avionics displays.
The AMPD replaces obsolete cathode ray tube (CRT)-based displays in legacy aircraft, and uses state-of-the-art active matrix liquid crystal display (AMLCD) technology.
The displays are full color, high density, and can be used during the day, at night, and with the night vision imaging system (NVIS). Of the AMPD family, the 5-by-5-inch versions are for the F/A-18E/F/G models, and the 8-by-10-inch versions are for the F/A-18F/G aft cockpit. The 8-by-10-inch model includes a direct digital video input.
The displays provide symbology, raster, and hybrid display formats, and support mono and full-color modes. Source militaryaerospace.com
The cockpit also has a colour digital map and the pilots are equipped with night-vision goggles. The zero/zero ejection seat is the SJU-5/6 from Martin Baker Aircraft Company Ltd in the UK.
Martin Baker SJU-5/6 zero/zero ejection seat
F-18 Hornet Ejection: Here
Super Hornet weapons

The Super Hornet has 11 weapon stations which include two additional wing store stations and will support a full range of armaments including AIM-9 Sidewinder, AIM-7 Sparrow and AIM-120 AMRAAM air-to-air missiles, guided air-to-ground weapons such as Harpoon, SLAM/SLAM-ER, GBU-10, GBU-51, HARM and Maverick; and free-fall air-to-ground bombs, Mk-76, BDU-48, Mk-82LD, Mk-82HD and Mk-84. The aircraft can also carry the GPS- / inertially guided JDAM (Joint Direct Attack Munition), JSOW (joint stand-off weapon) and JASSM (joint air-to-surface stand-off missile).
Weapon pylon
 F-18E – Image: michael_block
F-18E – Image: michael_block
Boeing is the prime contractor for the Joint Helmet-Mounted Cueing System (JHMCS) for the Super Hornet, to be fitted to Block 2 and retrofitted to Block 1 aircraft. Vision Systems International (jointly owned by Kaiser and Elbit) is the major subcontractor. JHMCS is currently in full-rate production. Deliveries of full-rate production systems began in 2005, although the system was deployed operationally during Operation Iraqi Freedom.
Joint Helmet-Mounted Cueing System (JHMCS)

The F/A-18E/F new lightweight gun system is the General Dynamics M61A2 20mm Gatling gun, which has a switchable firing rate of 4,000 or 6,000 shots a minute and a fully integrated linkless ammunition feed system.
Armament/Weapons:
Main Gun: 1x M61A1/A2 Vulcan 20mm gatling gun with 578 rounds;
4x AIM-9 Sidewinder (AIM-9X projected) + 2x AIM-120 AMRAAM; or 6x AIM-120 AMRAAM.
Other Weapons Carried: AGM-65 Maverick; AGM-84 Harpoon, SLAM, SLAM-ER; AGM-88 HARM/AARGM;
AGM-154 JSOW; AGM-158 JASSM; GBU-38 500-pound Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM);
GBU-31 2,000-pound Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM); Mk 82/84 General Purpose Bombs;
CBU-87 1,000-pound Combined Effects Munition; CBU-89 GATOR Mine System; CBU-97 1,000-pound Sensor Fuzed Weapon;
GBU-10 2,000-pound Paveway II; GBU-12 500-pound Paveway II; GBU-16 1,000-pound Paveway II;
GBU-24 2,000-pound Paveway III laser-guided bomb; Mk 62/63 Quickstrike Naval Mines.
Source fi-aeroweb.com
1x M61A1/A2 Vulcan 20mm gatling gun
The M61A1 and M61A2 produced by General Dynamics Ordnance and Tactical Systems are externally powered six-barrel 20mm Gatling gun systems that offer lightweight, highly lethal combat support for a variety of air, land and sea platforms.
The M61A1 and M61A2 increases multiple-hit probabilities when compared to single barrel guns operating at lower rates of fire. The M61A1 and M61A2 weapons are based on the proven Gatling principle of operation and provide reliability up to 10 times greater than single-barrel guns.
The M61A2 shares the same features as the M61A1, but is 20 percent lighter. The M61A2 will meet or exceed the M61A1 gun’s reliability, maintainability and supportability features. It is now available for applications where weapon system weight reduction is critical.
Specifications
| Gun type | Six-barrel, 20mm, externally powered |
| Weight
M61A1 M61A2 |
248 pounds (112.5 kg)
202 pounds (light barrel), 228 pounds |
| Rate of fire | 4,000/6,000 shots per minute |
| Dispersion | 8 milliradians diameter, 80 percent circle |
| Muzzle velocity | 3,380 feet (1,030m) per second |
| Average recoil force
@ 4,000 shots per minute @ 6,000 shots per minute |
Rotary, linkless, closed loop
2,133 pounds (9.4 kN) 3,200 pounds (14.2 kN) |
| Drive system | Hydraulic, electric, pneumatic |
Source gd-ots.com
AIM-9M Sidewinder missile
 Sidewinder AIM-9M
Sidewinder AIM-9M
The Lima was followed in production in 1982 by the AIM-9M, which is essentially an improved AIM-9L. The Mike has improved background rejection, counter-countermeasures capability and a low smoke motor to reduce the visual signature of the inbound weapon. The AIM-9M has the all-aspect capability of the AIM-9L model, but provides all-around higher performance. The M model has infra-red countermeasures, enhanced background discrimination capability, and a reduced-smoke rocket motor. Deliveries of the initial AIM-9M-1 began in 1982. The only changes from the AIM-9L to the AIM-9M were related to the Raytheon Guidance Control Section (GCS). Several models were introduced in pairs with even numbers designating US Navy versions and odd for US Air Force. All AIM-9M GCS are comprised of three major assemblies; a seeker assembly for detecting and tracking the target; an electronics assembly for processing detected target information; and a servo assembly that transforms electrical tracking signals to mechanical movement of the fins. An umbilical cable assembly provides electrical interface between the missile GCS and the aircraft launcher. The umbilical I-3 cable also allows the flow of coolant from the LAU-7 to the missile GCS. AIM-9M GCS versions include the WGU-4A/B used in the AIM-9M-1 and AIM-9M-3, the WGU-4C/B used in the AIM-9M-4, the WGU-4D/B used in the AIM-9M-6, and the WGU-4E/B GCS used in the AIM-9M-8. The WGU-4E/B GCS uses advanced technology that has evolved through the WGU-4D/B development, while expanding the potential of the IRCM detection circuitry and improving the missile’s capability with respect to tactical IRCM deployment. Source scramble.nl
AIM-120 AMRAAM

The AIM-120 AMRAAM (Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile) is one of the most modern, powerful, and widely used air-to-air missiles in the entire world. After it entered limited service in 1991, this missile has been exported to about 35 countries around the world, where it has certainly been proven with over 3 900 test shots and 10 combat victories.
By the 1980s, the US deemed its current stock of air-to-air missiles, particularly the medium-range AIM-7 Sparrow, were obsolete, or at least not as capable as the latest Soviet missiles of the time. While the Sparrow was effective, with about 60 kills, it was not effective enough. In particular, it had one crushing fault—it was not fire-and-forget, meaning that the pilot was forced to remain on the scene and in danger until the missile reached its target. So, development of the AIM-120 AMRAAM began, along with European development of a short-range missile, resulting in the ASRAAM. In 1991, the AMRAAM entered limited service in the US Air Force. Two years later, it was fully operational there as well as the US Navy, while other countries started to show considerable interest.
 Image: defenceindustrydaily.com
Image: defenceindustrydaily.com
| Country of origin | United States |
| Entered service | 1991 |
| Missile | |
| Missile length | 3.66 m |
| Missile diameter | 0.18 m |
| Fin span | 0.53 m |
| Missile launch weight | 150.75 kg |
| Warhead weight | 22.7 kg |
| Warhead type | HE blast-fragmentation |
| Range of fire | up to 75 km |
| Guidance | active radar homing |
Source military-today.com
AGM-65 Maverick

AGM-84 Harpoon, SLAM, SLAM-ER
The Harpoon missile provides the Navy and the Air Force with a common missile for air, ship, and submarine launches. The weapon system uses mid-course guidance with a radar seeker to attack surface ships. Its low-level, sea-skimming cruise trajectory, active radar guidance and warhead design assure high survivability and effectiveness. The Harpoon missile and its launch control equipment provide the warfighter capability to interdict ships at ranges well beyond those of other aircraft.
The Harpoon missile was designed to sink warships in an open-ocean environment. Other weapons (such as the Standard and Tomahawk missiles) can be used against ships, but Harpoon and Penguin are the only missiles used by the United States military with anti-ship warfare as the primary mission. Once targeting information is obtained and sent to the Harpoon missile, it is fired. Once fired, the missile flys to the target location, turns on its seeker, locates the target and strikes it without further action from the firing platform. This allows the firing platform to engage other threats instead of concentrating on one at a time.
An appropriately configured HARPOON can be launched from an AERO-65 bomb rack, AERO-7/A bomb rack, MK 6 canister, MK 7 shock resistant canister, MK 12 thickwall canister, MK 112 ASROC launcher, MK 8 and MK 116 TARTAR launcher, or submarine torpedo tube launcher.
The AGM-84D Harpoon is an all-weather, over-the-horizon, anti-ship missile system produced by Boeing [formerly McDonnell Douglas]. The Harpoon’s active radar guidance, warhead design, and low-level, sea-skimming cruise trajectory assure high survivability and effectiveness. The missile is capable of being launched from surface ships, submarines, or (without the booster) from aircraft. The AGM-84D was first introduced in 1977, and in 1979 an air-launched version was deployed on the Navy’s P-3 Orion aircraft. Originally developed for the Navy to serve as its basic anti-ship missile for fleetwide use, the AGM-84D also has been adapted for use on the Air Force’s B-52G bombers, which can carry from eight to 12 of the missiles.
The AGM-84E Harpoon/SLAM [Stand-Off Land Attack Missile] Block 1E is an intermediate range weapon system designed to provide day, night and adverse weather precision strike capability against high value land targets and ships in port. In the late 1980s, a land-attack missile was needed. Rather than design one from scratch, the US Navy took everything from Harpoon except the guidance and seeker sections, added a Global Positioning System receiver, a Walleye optical guidance system, and a Maverick data-link to create the Stand-off Land Attack Missile (SLAM). The AGM-84E uses an inertial navigation system with GPS, infrared terminal guidance, and is fitted with a Tomahawk warhead for better penetration. SLAM can be launched from land-based or aircraft carrier-based F/A-18 Hornet aircraft. It was employed successfully in Operation Desert Storm and UN relief operations in Bosnia prior to Operation Joint Endeavor.

The SLAM-ER (Expanded Response) Block 1F, a major upgrade to the SLAM missile that is currently in production, provides over twice the missile range, target penetration capability, and control range of SLAM. SLAM-ER has a greater range (150+ miles), a titanium warhead for increased penetration, and software improvements which allow the pilot to retarget the impact point of the missile during the terminal phase of attack (about the last five miles). In addition, many expansions are being made to improve performance, survivability, mission planning, and pilot (man-in-the-loop) interface. The SLAM-ER development contract was awarded to McDonnell Douglas Aerospace (Now BOEING) in February of 1995. SLAM-ER achieved its first flight in March of 1997. All Navy SLAM missiles are currently planned to be retrofitted to SLAM-ER configuration. About 500 SLAM missiles will be converted to the SLAM-ER configuration between FY 1997 and FY 2001.
| Primary Function: | Air-to-surface anti-ship missile | |||
| Mission | Maritime ship attack | |||
| Targets | Maritime surface | |||
| Service | Navy and Air Force | |||
| Contractor: | Boeing [ex McDonnell Douglas] | |||
| Power Plant: | Teledyne Turbojet and solid propellant booster for surface and submarine launch | |||
| Program status | Operational | |||
| sea-launch | air-launch | SLAM | SLAM-ER | |
| First capability | 1977 | 1979 | ||
| Thrust: | 660 pounds | |||
| Length: | 15 feet (4.55 meters) |
12 feet, 7 inches (3.79 meters) |
14 feet, 8 inches (4.49 meters) |
|
| Weight: | 1,470 pounds (661.5 kilograms) |
1,145 pounds (515.25 kilograms) |
1,385 pounds (629.55 kilograms) |
|
| Diameter: | 13.5 inches (34.29 centimeters) | |||
| Wingspan: | 3 feet (91.44 centimeters) | |||
| Range: | Greater than 60 nautical miles | 150+ miles | ||
| Speed: | 855 km/h | |||
| Guidance System: | Sea-skimming cruise with mid-course guidance monitored by radar altimeter, active seeker radar terminal homing | inertial navigation system with GPS, infrared terminal guidance | ||
| Warheads: | Penetration high-explosive blast (488 pounds) | |||
| Explosive | Destex | |||
| Fuze | Contact | |||
| Development cost | $320.7 million | |||
| Production cost | $2,882.3 million | |||
| Total acquisition cost | $3,203.0 million | |||
| Acquisition unit cost | $527,416 | |||
| Production unit cost | $474,609 | |||
| Quantity | Navy: 5,983; Air Force: 90 | |||
| Platforms | A-6, F/A-18, S-3, P-3, B-52H, ships | |||
Source fas.org
Advanced Anti-Radiation Guided Missile (AARGM)
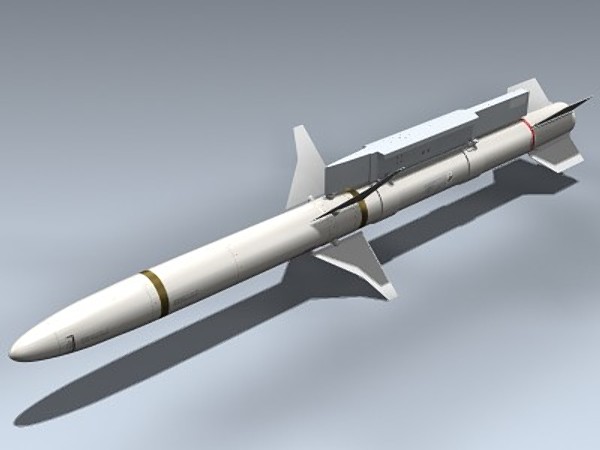

AGM-88 HARM high-speed anti-radiation missiles Range: 150 kilometres; 92 miles (80 nmi) Speed: 2,280 km/h (1,420 mph)
The Advanced Anti-Radiation Guided Missile (AGM-88E) provides the U.S. Navy, U.S. Marine Corps and Italian Air Force the latest and most advanced weapon system for engaging and destroying enemy air defenses and time-critical, mobile targets. AARGM is a supersonic, medium-range, air-launched tactical missile compatible with U.S. and allied strike aircraft, including all variants of the F/A-18, Tornado, EA-18G, F-16, EA-6B, and F-35 (external).
Designed to upgrade the AGM-88 High-Speed, Anti-Radiation Missile system (HARM), AARGM features an advanced, digital, anti-radiation homing sensor, millimeter wave (MMW) radar terminal seeker, precise Global Positioning System/Inertial Navigation System (GPS/INS) guidance, net-centric connectivity, and Weapon Impact Assessment transmit (WIA). Missile Impact Transmitter capability is available for approved customers. The missile offers extended-range engagement, as well as organic, in-cockpit emitter targeting capability and situational awareness.
New capabilities for the warfighter include:
- Anti-radar strike with advanced signal processing and vastly improved frequency coverage, detection range and field of view
- Time-critical, standoff strike with supersonic GPS/INS point-to-point or point-to-MMW-terminal guidance
- Missile-impact zone control to prevent collateral damage through tightly coupled, Digital Terrain Elevation Database-aided GPS/INS
- Counter-emitter shutdown through active MMW-radar terminal guidance
- WIA transmission prior-to-impact for bomb damage assessment
Orbital ATK is teamed with MBDA to provide this advanced, cost-effective weapon system to U.S. and approved allied customers.
AGM-154 JSOW joint stand-off weapon

The AGM-154A (Formerly Advanced Interdiction Weapon System) is intended to provide a low cost, highly lethal glide weapon with a standoff capability. JSOW family of kinematically efficient, air-to-surface glide weapons, in the 1,000-lb class, provides standoff capabilities from 15 nautical miles (low altitude launch) to 40 nautical miles (high altitude launch). The JSOW will be used against a variety of land and sea targets and will operate from ranges outside enemy point defenses. The JSOW is a launch and leave weapon that employs a tightly coupled Global Positioning System (GPS)/Inertial Navigation System (INS), and is capable of day/night and adverse weather operations.
The JSOW uses inertial and global positioning system for midcourse navigation and imaging infra-red and datalink for terminal homing. The JSOW is just over 13 feet in length and weighs between 1000-1500 pounds. Extra flexibility has been engineered into the AGM-154A by its modular design, which allows several different submunitions, unitary warheads, or non-lethal payloads to be carried. The JSOW will be delivered in three variants, each of which uses a common air vehicle, or truck, while substituting various payloads.
AGM-154A (Baseline JSOW) The warhead of the AGM-154A consists of 145 BLU-97/B submunitions. Each bomblet is designed for multi-target in one payload. The bomblets have a shaped charge for armor defeat capability, a fragmenting case for material destruction, and a zirconium ring for incendiary effects.
AGM-154B (Anti-Armor) The warhead for the AGM-154B is the BLU-108/B from the Air Force’s Sensor Fuzed Weapon (SFW) program. The JSOW will carry six BLU-108/B submunitions. Each submunition releases four projectiles (total of 24 per weapons) that use infrared sensors to detect targets. Upon detection, the projectile detonates, creating an explosively formed, shaped charge capable of penetrating reinforced armor targets.
 AGM-154C (Unitary Variant) The AGM-154C will use a combination of an Imaging Infrared (IIR) terminal seeker and a two-way data link to achieve point target accuracy through aimpoint refinement and man-in-the-loop guidance. The AGM-154C will carry the BLU-111/B variant of the MK-82, 500- pound general purpose bomb, equipped with the FMU-152 Joint Programmable Fuze (JPF) and is designed to attack point targets. Source fas.org
AGM-154C (Unitary Variant) The AGM-154C will use a combination of an Imaging Infrared (IIR) terminal seeker and a two-way data link to achieve point target accuracy through aimpoint refinement and man-in-the-loop guidance. The AGM-154C will carry the BLU-111/B variant of the MK-82, 500- pound general purpose bomb, equipped with the FMU-152 Joint Programmable Fuze (JPF) and is designed to attack point targets. Source fas.org
GBU-38 500-pound, GBU-31 2,000-pound Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM)
Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) is a low-cost gravity bomb guidance kit manufactured by Boeing. It converts existing unguided General Purpose Bombs into accurately guided smart weapons. JDAMs can be launched from a distance of more than 17 miles (28 km) from the target and receives updates from U.S. Air Force GPS satellites to help guide the weapon to the target. Boeing builds JDAM weapons at the company’s St. Charles, Missouri facility.
The JDAM guidance kit uses either the 2,000-pound BLU-109/Mk 84 (GBU-31 JDAM), the 1,000-pound BLU-110/Mk 83 (GBU-32 JDAM) or the 500-pound BLU-111/Mk 82 (GBU-38 JDAM) warhead as payload. The Air Force is developing the BLU-137 which is a modernized warhead penetrator to replace the BLU-109. This new warhead uses a modified JDAM tail kit hardback assembly to include an Arming Generator Relocator Adaptor (AGRA). JDAM enables employment of accurate air-to-surface weapons against high priority fixed and relocatable targets from fighter and bomber aircraft. Guidance is facilitated through a tail control system and a GPS-aided Inertial Navigation System (INS). The navigation system is initialized by transfer alignment from the aircraft that provides position and velocity vectors from aircraft systems. Body strakes provide additional stability and lift. Source fi-aeroweb.com
CBU-97 1,000-pound Sensor Fuzed Weapon

GBU-10 2,000-pound, GBU-12 500-pound, GBU-16 1,000-pound Paveway II
GBU-24 2,000-pound Paveway III laser-guided bomb

Mk 62/63 Quickstrike Naval Mines
 Mark 63 “Quickstrike” Mine. USS John C. Stennis (CVN 74) in November 2003. U.S. Navy Photograph 031104-N-1573O-036. – Image: navweaps.com
Mark 63 “Quickstrike” Mine. USS John C. Stennis (CVN 74) in November 2003. U.S. Navy Photograph 031104-N-1573O-036. – Image: navweaps.com
Conversion of Mark 82 [500 lbs. (227 kg)] bomb. Superseded Destructor EX-52. Marks 62, 63 and 64 are known as the “Quickstrike” series and have a variable influence target designation system that can be used against either land or sea targets. Quickstrike was conceived as a new series of ground mines, replacing the ones that had become compromised as a result of the Vietnam War. These new mines use the same design concept as do “smart” bombs, that is, they are simple bolt-on additions to a standard air-dropped bomb. Quickstrike’s design emphasizes ease of maintenance and ease of mine preparation for use. For example, the older mines required refrigeration of their batteries to prolong life, the Quickstrikes do not. Source navweaps.com
AGM-158C LRASM

 Source: navyrecognition.com
Source: navyrecognition.com
JASSM / JASSM ER (AGM-158A/B)

ausairpower.net
The JASSM (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile) is a conventional, stealthy, air-launched ground attack cruise missile designed for the U.S. Air Force and international partners. An extended range version, AGM-158B JASSM-ER, was developed alongside the standard variant, and went into service in 2014.
JASSM At A Glance
Originated From: United States
Possessed By: United States, Australia, Finland, Poland
Class: Cruise Missile
Basing: Air-launched
Length: 4.27 m
Wingspan: 2.4 m
Launch Weight: 1,021 kg
Warhead: 450 kg WDU-42/B penetrator
Propulsion: Turbojet (AGM-158A), Turbofan (AGM-158B)
Range: 370 km (AGM-158A), 1,000 km (AGM-158B)
Status: Operational
In Service: 2009-Present
JASSM utilizes a low-observable airframe designed to defeat various targets, to include enemy air defenses. The missile’s low-profile airframe is particularly important given the proliferation of sophisticated air defenses such as the S-300 (and newer variants). The JASSM-ER will eventually incorporate a weapons data link (WDL) into the missile allowing for course corrections after launch.2This is a critical upgrade for road-mobile and maritime targets.
The missile is fitted to the B-1B Lancer, B-2 Spirit, B-52H Stratofortress, F-15E Strike Eagle, F-16C/D, F/A-18C/D, and possibly the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter. The B-1B is considered the starting point platform, and can carry 24 missiles, and is currently the only one equipped with JASSM-ER. The B-2 can carry up to 16 missiles and the B-52H can carry 12 internally on rotary launchers. Fighter aircraft can carry one or two missiles under each wing. The F-35, if certified to carry the JASSM, would have to carry the weapon externally, because the missile would not fit in the main internal weapon bays the aircraft boasts.
The standard variant has a range of 370 km, whereas the JASSM-ER has a range of approximately 1,000 km. Their airframes are identical, so the weapons cannot be distinguished merely by appearance. The primary differences lie in a larger internal fuel tank, and a more efficient turbofan engine. The airframe itself can be described as angular, similar to the Taurus KEPD 350, although more rounded and fluid. When the missile is carried by aircraft, the fins and wings are folded, and then unfolded by small explosive charges after released. Source missilethreat.csis.org
Raytheon awarded contract for upgrades to Small Diameter Bomb
 An F-15E fighter aircraft, pictured, can carry seven groups of four SDB II bombs, for a total of 28 weapons. Photo courtesy of Raytheon
An F-15E fighter aircraft, pictured, can carry seven groups of four SDB II bombs, for a total of 28 weapons. Photo courtesy of Raytheon
Sept. 28 (UPI) — Raytheon has been awarded a $450 million contract for engineering changes and development of the Small Diameter Bomb II, an update for the U.S. Air Force.
The contract, announced Wednesday by the Department of Defense, is for design, development, integration, test and production engineering for changes to the SDB.
Work will be performed in Tucson, Ariz., and is expected to be finished by Aug. 31, 2024. No funds have been obligated yet for the award, which was the result of a sole-source acquisition.
The SDB II is capable of three modes — a millimeter wave radar that detects and tracks targets through all weather, imaging infrared for improved target discrimination, and a semi-active laser allowing it to track lasers in the air or on the ground.
The bomb can strike targets more than 45 miles away and has a small size, so more of them can be carried by fewer aircraft.
The SDB II is being integrated for use on the F-35 and F/A-18E/F by the U.S. Air Force and Navy, and Raytheon is expected to have it prepared for integration with the F-15E by the end of the year. Source upi.com
SDB II Bomb

Raytheon, the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Navy have begun SDB II™ bomb integration activities on the F-35, F/A-18E/F and F-15E aircraft.
The seeker works in three modes to provide maximum operational flexibility: millimeter wave radar to detect and track targets through weather, imaging infrared for enhanced target discrimination and semi-active laser that enables the weapon to track an airborne laser designator or one on the ground.
This powerful, integrated seeker seamlessly shares targeting information among all three modes, enabling the weapon to engage fixed or moving targets at any time of day and in all-weather conditions. The SDB II bomb’s tri-mode seeker can also peer through battlefield dust and debris, giving the warfighter a capability that’s unaffected by conditions on the ground or in the air.
The weapon can fly more than 45 miles to strike mobile targets, reducing the amount of time that aircrews’ spend in harm’s way. Its small size enables the use of fewer aircraft to take out the same number of targets as previous, larger weapons that required multiple jets. The SDB II bomb’s size has broader implications for the warfighter and taxpayers, as it means fewer attacks with less time spent flying dangerous missions.
The U.S. Air Force and U.S. Navy have begun SDB II bomb integration activities on the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter and the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet aircraft. Raytheon will complete integration on the F-15E Strike Eagle in 2017. Source: raytheon.com
A 100-Drone Swarm, Dropped from Jets, Plans Its Own Moves: Here

Excerpt
What’s small, fast, and is launched from the bottom of a fighter jet? Not missiles, but a swarm of drones.
U.S. military officials have announced that they’ve carried out their largest ever test of a drone swarm released from fighter jets in flight. In the trials, three F/A-18 Super Hornets released 103 Perdix drones, which then communicated with each other and went about performing a series of formation flying exercises that mimic a surveillance mission.
Countermeasures
The AN/ALQ-124 integrated defensive countermeasures system (IDECM) provides a coordinated situation awareness and manages the on-board and off-board deception countermeasures, the expendable decoys, and signal and frequency control of emissions. The system has been jointly developed by BAE Systems information & electronic warfare systems (IEWS – formerly Sanders) and ITT Electronic Systems.
The IDECM system includes the ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser, the ALE-50 towed decoy and the AN/ALR-67(V)3 radar warning receiver. IDECM began operational evaluation in December 2002 and was successfully deployed during Operation Iraqi Freedom.
The BAE Systems Integrated Defense Solutions (formerly Tracor) ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser system is capable of dispensing chaff cartridges, flares, and the POET and GEN-X active expendable decoys.
ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser
 ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser and associated equipments
ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser and associated equipments ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser under F-18E – Image: michael_block
ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser under F-18E – Image: michael_block
The ALE-50 Towed Decoy, from Raytheon E-Systems, provides long-range detection and extremely fast deployment against most radar-guided threats.
ALE-50 Towed Decoy

The AN/ALE-50 towed decoy system was developed by Raytheon to protect multiple US military aircraft from radar-guided missiles. The ALE-50 consists of a launch controller, launcher and towed decoy. It can be used on a variety of platforms without modification. When deployed, the ALE-50’s expendable aerial decoy is towed behind the aircraft. The decoy protects the host aircraft providing a more attractive target and steering the radar-guided missile away from the aircraft and right to the decoy. ALE-50 has countered both surface-to-air and air-to-air missiles. Currently, the ALE-50 is installed on F-16s aircraft and is planned for installation on B-1B bombers and F/A-18 aircraft. The ALE-55 is a derivative of the ALE-50 would be the production decoy installed on B-1B bombers. Source deagel.com
BAE Systems AN/ALE-55 fibre-optic towed decoy

BAE Systems AN/ALE-55 fibre-optic towed decoy has completed development testing and will replace the ALE-50 from December 2009 when it enters service. The Raytheon AN/ALR-67(V)3 radar warning receiver intercepts, identifies and prioritises threat signals, which are characterised in terms of frequency, amplitude, direction and pulse width.
Raytheon AN/ALR-67(V)3 radar warning receiver
 Image: raytheon.com
Image: raytheon.com

The AN/ALR-67(V)3 Advanced Special Receiver is a radar warning receiver (RWR) designed to meet Navy requirements through the year 2020. This is an upgrade to the ALR-67 (V)2 system currently used on F/A-18 Hornet, F-14 Tomcat, and AV-8 Harrier aircraft. It will enable Navy and Marine Corps tactical aircraft to detect threat radar emissions, thus enhancing aircrew situational awareness and aircraft survivability. The program is in the Engineering and Manufacturing Development (EMD) phase, with development work by Hughes, Los Angeles, CA.
The AN/ALR-67(v)3 ASR contributes to full-dimensional protection by improving individual aircraft probability of survival through improved aircrew situational awareness of the radar guided threat environment. Source fas.org
Sensors

The Super Hornet is equipped with the APG-73 radar manufactured by Raytheon. The APG-73 radar has an upgraded processor with increased speed and memory capacity in comparison to the AN/APG-65, which was installed on the earlier builds of the Hornet. The modes of the APG-73 include air-to-ground tracking, air-to-air velocity search mode, range while search and track while scan.
Raytheon’s AN/APG-79 Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) fire control radar will increase the F/A-18’s air-to-air target detection and tracking range and provide higher resolution air-to-ground mapping at longer ranges. The The AN/APG-79 AESA entered Low Rate Initial Production (LRIP) in September 2003 and began Operational Evaluation (OPEVAL) in July 2006. It is being fitted to block 2 aircraft and retrofitted to 135 block 1 aircraft. The radar is planned to begin operational deployment on the USN F/A-18s in 2008.
APG-79 multi-mode radar
 APG-79 multi-mode radar with passive detection mode and active radar suppression
APG-79 multi-mode radar with passive detection mode and active radar suppression
With its active electronic beam scanning — which allows the radar beam to be steered at nearly the speed of light — the APG-79 optimizes situational awareness and provides superior air-to-air and air-to-surface capability. The agile beam enables the multimode radar to interleave in near-real time, so that pilot and crew can use both modes simultaneously.
Now in full rate production for the U.S. Navy and Royal Australian Air Force, the APG-79 demonstrates reliability, image resolution, and targeting and tracking range significantly greater than that of the previous mechanically scanned array F/A-18 radar. With its open systems architecture and compact, commercial-off-the-shelf parts, it delivers dramatically increased capability in a smaller, lighter package. The array is composed of numerous solid-state transmit and receive modules to virtually eliminate mechanical breakdown. Other system components include an advanced receiver/exciter, ruggedized COTS processor, and power supplies.
In addition to the APG-79, Raytheon supplies the F/A-18E/F aircraft with several other systems. Among these are the current APG-73 radar, ATFLIR forward-looking infrared targeting pod, ALR-67(V)3 digital radar warning receiver, ALE-50 towed decoy and a variety of missiles and bombs, including laser-guided weapons such as the Paveway and JSOW. Source raytheon.com
 Image: ausairpower.net
Image: ausairpower.net
The Super Hornet also carries Raytheon’s Miniature Airborne Global Positioning System Receiver (MAGR-2000). Using an open systems architecture, the receiver provides improved position, velocity and time performance reporting, resulting in a more accurate weapon delivery.
MINIATURE AIRBORNE GPS RECEIVER (MAGR) 2000 AND MAGR 2000 SAASM
The MAGR 2000 design is a GPS Receiver Applications Module (GRAM) based open system architecture that is modular in design and incorporates modern electronics. The MAGR 2000 is a form, fit, and function backward compatible replacement of the MAGR, and provides enhancements including improved acquisition and GPS solution performance, all-in-view GPSsatellite tracking and GPS integrity. Source raytheon.com
The aircraft is being fitted with the Raytheon AN/ASQ-228 ATFLIR (Advanced Targeting Forward-Looking Infrared) precision targeting pod. ATFLIR consists of a 3-5 micron staring focal plane array targeting FLIR, BAE Systems Avionics high-powered diode-pumped laser spot tracker, BAE Systems Avionics navigation FLIR and CCD TV camera. Initial Operating Capability (IOC) was achieved in April 2003 and the system is now in full-rate production.
Raytheon AN/ASQ-228 ATFLIR targeting pod
 Advanced Targeting Forward-Looking Infra-Red (ATFLIR)
Advanced Targeting Forward-Looking Infra-Red (ATFLIR)
The AN/ASQ-228 Advanced Targeting Forward-Looking Infrared (ATFLIR) is a multi-sensor, electro-optical targeting pod incorporating thermographic camera, low-light television camera, target laser rangefinder/laser designator, and laser spot tracker developed and manufactured by Raytheon. It is used to provide navigation and targeting for military aircraft in adverse weather and using precision-guided munitions such as laser-guided bombs. It is intended to replace the earlier AN/AAS-38 Nite Hawk pod in US Navy service.
 Image: Avia News
Image: Avia News
ATFLIR is 72 in (183 cm) long, weighs 420 lb (191 kg), and has a slant range of 40 mi (64.3 km), said to be useful at altitude of up to 50,000 ft (15,240 m).[1] It has fewer parts than many previous systems, which is intended to improve serviceability (although early examples, in service with VFA-115 ‘Eagles’ in 2003 experienced problems). Crews indicate that it offers much greater target resolution and image accuracy than previous systems.
ATFLIR presently is used only by the US Navy on the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and the earlier F/A-18C/D and with Marine F/A-18Cs when deployed onboard aircraft carriers. It is normally carried on one of the fuselage hardpoints otherwise used for AIM-120 AMRAAM missiles. 410 pods were delivered to the U.S. Navy. Pods have also been delivered to Switzerland and Australia, and six pods will be delivered to Malaysia. Source revolvy.com
US Marine Corps aircraft are being fitted with the Northrop Grumman Litening AT Advanced Targeting pod, with 540 x 512 pixel FLIR, CCD TV, laser spot tracker, infrared laser marker and infrared laser rangefinder / designator.
Northrop Grumman Litening AT Advanced Targeting pod
Northrop Grumman’s widely fielded LITENING system is a combat proven, self-contained, multi-sensor targeting and surveillance system. LITENING enables aircrews to detect, acquire, auto-track and identify targets at extremely long ranges for weapon delivery or nontraditional intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance missions. LITENING’s 1K FLIR, 1K charged-coupled device (CCD), laser imaging sensors, advanced image processing and digital video output provide superior imagery, allowing aircrews to identify and engage targets under a wide range of battlefield conditions.
LITENING is in operation worldwide
The pod is currently flown by the U.S. Marine Corps, all components of the U.S. Air Force, and international customers. The latest configuration, LITENING G4, is authorized for export to NATO countries, including Canada, the United Kingdom and Korea.
LITENING targeting pods feature:
- Full 1K FLIR and CCD, the highest resolution available in any fielded targeting pod
- Digital, high definition video to the cockpit
- Laser imaging sensors for more accurate identification
- Color symbology for reduced pilot workload and integration with new cockpit displays
- Multiple fields of view for a complete view of the situation
- Advanced two-way plug-and-play datalinks, including NET-T integration, that seamlessly communicate with ground stations
- Flexible upgrade path to bring older pods to the latest configuration affordably.
LITENING by the numbers
- More than two million hours flown, including more than 770,000 combat flight hours
- Greater than 97% availability
- Integrated on the F-16 Block 30, F-16 Block 40/50, A-10C, AV-8B, B-52, EA-6B, F-15E and F/A-18 C/D.
- More than 500 LITENING G4 pods delivered
- More than 800 pods total delivered
Source northropgrumman.com
F/A-18F aircraft also being fitted with the Raytheon SHARP multi-function reconnaissance pod, set to replace USN Tactical Airborne Reconnaissance Pod (TARPS), currently flown on the F-14 Tomcat. SHARP is capable of simultaneous airborne and ground reconnaissance and has sensors manufactured by Recon/Optical Inc. 16 LRIP systems have been ordered and the first was delivered in April 2003. The system is deployed on aircraft operating from USS Nimitz carriers.
Raytheon SHAred Reconnaissance Pod (SHARP)
The U. S. Navy requires an organic, all-weather, day/night, manned, tactical air reconnaissance capability to provide continuous and immediate intelligence support to the Battle Group Commander (BGC) in the prosecution of independent, joint, or combined operations as well as to provide intelligence data for the security of those forces under his/her command. This capability is required to replace the F-14 Tactical Air Reconnaissance Pod (TARPS) capability, scheduled for phase-out in FY03. To meet this requirement, the Department of the Navy will incorporate a SHAred Reconnaissance Pod (SHARP) on the centerline of the F/A-18E/F that will employ a suite of sensors to collect infrared, visible, and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) digital imagery at medium and high altitudes.
SHARP will be a major contributor to the precision strike capability of GPS and digital, image-guided weapons and will IOC with the first FA-18F squadron. The system will utilize COTS/NDI dual-band electro-optic/infrared (EO/IR) sensors and subsystems in a pod for tactical and other aircraft. It will provide all altitude over flight and long range stand-off EO/IR imagery and SAR, capable of near real-time datalink to afloat and shore-based JSIPS stations. The SHARP program is currently funded to meet the Navy’s minimum warfighting requirement of 24 pods. The inventory objective is 50 systems (40 operational and 10 pipeline).
The required capability described herein must be supportable within the capability of the deployed carrier air wing or the F/A-18E/F aircraft forward deployed support posture. The complete airborne reconnaissance system must employ digital technology and be compatible with Common Imagery Ground/Surface System (CIG/SS) compliant ground stations. The reconnaissance system must include overflight and standoff capability in both day and night conditions. The full range of reconnaissance capability may be provided through separate and interchangeable medium and high altitude sensors that can be easily reconfigured into optimum mission suites. However, a single sensor that could meet both medium and high altitude requirements is desirable. To ensure true multi-mission capability of the F/A-18E/F aircraft the SHARP pod must be capable of being installed or removed with full mission turnaround capability of less than one hour. Source fas.org
Sniper pushes its way onto Hornet fleets: Here
 F/A-18E/F Super Hornet with Lockheed Martin’s AN/AAQ-33 Sniper Advanced Targeting Pod – lockheedmartin.com
F/A-18E/F Super Hornet with Lockheed Martin’s AN/AAQ-33 Sniper Advanced Targeting Pod – lockheedmartin.com
Excerpt
In 2015, Sniper flew its first successful flight aboard a US Navy F/A-18F at Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake, California. Lockheed flew the pod on the Super Hornet’s centerline, whereas ATFLIR rides on the aircraft’s cheek station.
Lockheed Martin’ Sniper pod
 Lockheed Martin’s Sniper ATP (Advanced Targeting Pod) Picture: Lockheed Martin – Image: navyrecognition.com
Lockheed Martin’s Sniper ATP (Advanced Targeting Pod) Picture: Lockheed Martin – Image: navyrecognition.com
Mission
Sniper pods provide improved long-range target detection/identification and continuous stabilized surveillance for all missions, including close air support of ground forces. The Sniper pod enables aircrews to detect and identify weapon caches and individuals carrying armaments, all outside jet noise ranges. Superior imagery, a video datalink and J-series-weapons-quality coordinates provided by the Sniper pod enable rapid target decisions and keep aircrews out of threat ranges.
High resolution imagery for non-traditional intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (NTISR) enables the Sniper pod to play a major role in Air Force operations in theater, providing top cover for ground forces, as well as increasing the safety of civilian populations.
The Sniper pod is combat proven on U.S. Air Force and international F-15E, F-16 (all blocks), B-1, A-10C, Harrier GR7/9 and CF-18 aircraft. Lockheed Martin is also in the final stages of integrating the Sniper pod on the B-52. The pod’s plug-and-play capability facilitates moving the pod across platforms without changing software.
Features
Sniper pods include a high definition mid-wave forward looking infrared (FLIR), dual-mode laser, HDTV, laser spot tracker, laser marker, video data link, and a digital data recorder. Advanced image processing algorithms, combined with rock steady stabilization techniques, provide cutting-edge performance. The pod features automatic tracking and laser designation of tactical size targets via real-time imagery presented on cockpit displays. The Sniper pod is fully compatible with the latest J-series munitions for precision weapons delivery against multiple moving and fixed targets.
Advanced Targeting Pod – Sensor Enhancement (ATP-SE) design upgrades include enhanced sensors, advanced processors, and automated NTISR modes.
The Sniper pod’s architecture and modular design permits true two-level maintenance, eliminating costly intermediate-level support. Automated built-in test permits flightline maintainers to isolate and replace an LRU in under 20 minutes. Spares are ordered through a user-friendly website offering in-transit visibility to parts shipment.
The Sniper pod’s modular design also offers an affordable road map for modernizing and enhancing precision targeting capabilities for U.S. Air Force and coalition partner aircraft.
General characteristics
Primary function: positive identification, automatic tracking and laser designation, NTISR
Prime contractor: Lockheed Martin
Length: 98.2 inches (252 centimeters)
Diameter: 11.9 inches (30 centimeters)
Weight: 446 pounds (202 kilograms)
Aircraft: F-15E, F-16 Block 30/40/50, A-10, B-1
Sensors: high resolution FLIR and HDTV, dual mode laser designator, laser spot tracker and laser marker
Source af.mil
Engines
 Image: from the web
Image: from the web
The aircraft’s power is provided by two F414-GE-400 turbofan engines from General Electric. The engines are an advanced derivative of the GE F404 engines installed on the Hornet. The air inlets have been enlarged to provide increased airflow into the engines.
The engines each provide 22,000lb thrust, with afterburn giving a maximum speed in excess of Mach 1.8.
The structural changes to the airframe on the F/E variant of the aircraft increase the internal fuel capacity by 3,600lb, a 33% higher fuel capacity than the F-18C/D variant. This extends the mission radius by up to 40%.
F414-GE-400 turbofan engines
 General Electric F414 turbo-fan engines
General Electric F414 turbo-fan engines
The General Electric F414-GE-400 is a 22,000-pound class afterburning turbofan engine. The engine features an axial compressor with 3 fan stages and 7 high-pressure compressor stages, and 1 high-pressure and 1 low-pressure turbine stage. At a weight of 2,445 pounds, the F414-GE-400 has a thrust-to-weight ratio of 9. The F414 is one of the U.S. Navy’s newest and most advanced aircraft engines. It incorporates advanced technology with the proven design base of its F404 predecessor – for example the F414 features a FADEC (Full Authority Digital Engine Control) system – to provide the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and the EA-18G Growler with a durable, reliable and easy-to-maintain engine.
Manufacturer: General Electric Co.
Thrust: 22,000 pounds
Overall Pressure Ratio at Maximum Power: 30
Thrust-to-Weight Ratio: 9
Compressor: Two-spool, axial flow, three-stage fan
LP-HP Compressor Stages: 0-7
HP-LP Turbine Stages: 1-1
Combustor Type: Annular
Engine Control: FADEC
Length: 154 in (3.91 m)
Diameter: 35 in (88.9 cm)
Dry Weight: 2,445 lbs (1,109 kg)
Platforms: F/A-18E/F Super Hornet; EA-18G Growler
Source fi-powerweb.com
US Navy studying major upgrade of F/A-18E/F & EA-18G engines: Here
Excerpt
The US Navy has revived interest in studying a major upgrade of the engine that powers the Boeing F/A-18E/F, EA-18G and two foreign fighters, including the possible addition of new technologies.
In early February, Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) notified industry that it would ask GE Aviation to submit a proposal for a contract for the company’s engineers to perform a study on an “F414-GE-400 core enhancement evaluation”.
F414 enhanced engine

Main material source airforce-technology.com
Images are from public domain unless otherwise stated
Revised Apr 09, 2017
Updated Jun 06, 2020

Aircraft Specifications:
Primary Function: Multi-role tactical fighter and attack aircraft
Prime Contractor: Airframe: McDonnell Douglas (The Boeing Co.); Engines: General Electric Co.
Power Plant: 2x General Electric F414-GE-400 afterburning turbofan engines
Thrust: 14,000 pounds dry thrust; 22,000 pounds thrust with afterburner (each engine)
Wingspan: 44 ft 9 in (13.68 m)
Length: 60 ft 1 in (18.5 m)
Height: 16 ft (4.87 m)
Weight (Empty): 32,000 lbs (14,520 kg)
Maximum Takeoff Weight (MTOW): 66,000 lbs (29,930 kg)
Payload: Max. 34,000 lbs (15,420 kg)
Speed: Max: Mach 1.8+/1,034 kts/1,190 mph (1,934 km/h)
Service Ceiling: 50,000+ ft (15,240+ m)
Range: 1,275 nm/1,467 miles (2,346 km) – clean plus two AIM-9 Sidewinder missiles
Combat Radius: 390 nm/449 miles (723 km)
Crew: E models: One; F models: Two
Aircraft Inventory (September 2015):
F/A-18A: 95
F/A-18B: 21
F/A-18C: 368
F/A-18D: 129
F/A-18A/B/C/D Hornet Total: 613
F/A-18E: 279
F/A-18F: 261
F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Total: 540
Source fi-aeroweb.com
























Pingback: Super Hornet vs Rafale F3-R pe ultimii metri ai cursei elvetiene Air2030
As I mentioned the F18 is very costly to operate the Philippines is likely to chose the F16 as seen by Indonesia also with many islands as they are cheaper to operate. The US is currently trying to entice the Indonesians to order there latest F16V but I don’t agree as it is a very old platform which is at the end of any further development. However, Indonesia is likely to favor it as they are already operating the F16A/B and recently received 24 F16C/D any change of a new fighter would incur additional cost in training and spare parts. See earlier post https://thaimilitaryandasianregion.wordpress.com/2015/10/09/us-defense-giant-lockheed-martin-is-ready-to-provide-indonesia-with-an-offset-scheme-if-it-decides-to-buy-the-latest-variant-of-the-venerable-f-16-fighting-falcon-light-jet-fighter/
LikeLike
That’s why I am all for the US in giving the Philippines the Legacy Short Hornets the F/A-18 C/D. At least they can take the legacy hornets and the US, Australia and Canada can keep the Super Hornets.
LikeLike
F18 are expensive to operate and maintain so I guess it won’t happen it is more like F16 which is much cheaper to operate and maintain and spare parts are easily available. The US has huge inventory of F16 stored.
LikeLike
For the Philippines, since they are an island nation, they need two engines and I think the legacy F/A-18 C/D is more preferred than the F-16’s. Besides the US is already taking the oldest F-16’s and converting them to QF-16 Drones. They should go for the ones, the USMC & USN are using right now.
LikeLike