The Type 052D destroyer (NATO code name Luyang III class, or Kunming class after the lead ship) is a class of guided missile destroyers being deployed by the Chinese People’s Liberation Army Navy Surface Force. Currently it is being built at two different Chinese ship yards.
After the Type 052C destroyer (NATO code name Luyang II class, or Lanzhou class after the lead ship), two new hulls were spotted under construction at Changxingdao-Jiangnan Shipyard (JNCX) in August 2012. According to imagery, they were armed with a new 130 mm main gun and new AESA radar system. Altogether six vessels of this class are now fitting out or under construction, one vessel is on sea trial and four vessels are active.
Nearing the completion of the first 12 Type 052D ships, the PLAN will shift production to the newer Type 055 destroyer.
Type 055 destroyer compared to Type 052D
 Image @jeffhead.com
Image @jeffhead.com
China launches first stretched Type 052D destroyer
The first stretched variant of China’s Luyang III (Type 052D) destroyer class was launched in early July at the Jiangnan Changxingdao shipyard near Shanghai. The ship, which is the 14th Type 052D to be built overall, is 4 m longer than its predecessors, resulting in a 4 m larger flight deck. The size of the hangar remains unchanged.
Satellite imagery captured on 16 July shows the ship afloat in the fitting-out basin, together with a Type 055 destroyer that was launched in April, three other Type 052D destroyers, and 10 Yuyi (Type 726)-class air-cushioned landing craft (LCAC).
The Type 052D’s increase in size is likely to be in preparation for a navalised version of the Harbin Z-20 helicopter being introduced into service. Source janes.com
Type 052C destroyer: Details
Type 052E destroyer compared to Type 055 and Type 052D
 chinaisgood.com
chinaisgood.com
The PLA Navy Type 052E Destroyer (observation info)
The Type 052E DDG may have dimensions as of 157 meters (L), 18 meters (W), draft of 6 meters, with full-load displacement is estimated to be around 7,500 tons

The main improvements: the Type 364 Radar to be replaced by a Single-sided X-band rotating phased-array radar, the Type 517B VHF air search radar to be replaced by an L-band remote search radar, the single hangar to be enlarged into double, flight deck extension by 2 meters more, powered by two gas turbine generators, Integrated Power System, stealthy chimney, universal VLS (96 cells) and YJ-12 anti-ship missile launchers. Source asiawind.com
Design
 SinoDefence.com
SinoDefence.com
The layout of the Type 052D is similar to the earlier Type 052C, but the superstructure of the Type 052D slopes inward at a greater angle, providing reduced radar cross-section.
**For main radar see bottom of article**
On top of the bridge of the first three 052D hulls is the usual Band Stand over-the-horizon targeting radar radome, along with a Type 344 fire control director and electronic countermeasure (ECM)/jammers on the enclosed mast. Mounting plates outboard the stack may be for 30-millimeter guns, but the 052C had boat davits in that location. Source afcea.org
Type 344 fire control director

Chinese Designation: Type 344
Export Name: MR34
NATO Reporting Name: N/A
Role: Fire-control for the 100mm gun and anti-ship missile targeting
Contractor: Xi’an Research institute of Navigation Technology
Band: I/J
Range: N/A
Description: The Type 344 radar is normally installed on top of the brigade right in front of the main mast. The radar is used as the standard fire-control radar on all post-1990 PRC-built destroyers and frigates for 100mm main gun and anti-ship missile targeting. Source globalmil.com
The helicopter hangar on the Type 052D is moved to the center, as opposed to being on the left like on the Type 052C. A pair of enclosed boat/raft launching systems similar to that of the Type 054A frigate is added, with one on each side of the helicopter hangar. The Type 517HA VHF radar mast is moved toward the stern of the ship.
Type 366 Radar
 Type 366 radar – Chinese internet images
Type 366 radar – Chinese internet images
Type 366 is the Chinese development of Russian MR-331 Mineral-ME naval radar (NATO reporting name: Band Stand], and as late of 2010’s, it is the latest and most advanced surface search radar in Chinese navy.
MR-331 Mineral-ME radar system consists of Mineral-ME1 active radar and Mineral-ME2 passive radar mounted in a back-to-back configuration, and Mineral-ME3 mutual data exchange, navigation and joint combat operation control station, Mineral-ME radar system is designed to detect, track and record (including over-the-horizon) surface targets, provide and receive information to and from other sources. Typical detection range against a destroyer sized target in the active mode in up to 250 km, while that of the passive mode ranges from 80 to 450 km. Active and passive subsystems of MR-331 Mineral-ME can operate in conjunction. MR-331 Mineral-ME is installed on Sovremennyy-class destroyer sold to China, and China also purchased additional sets for its own destroyers.
Sovremennyy-class destroyer: Details
China was thoroughly impressed by the performance of Russian MR-331 Mineral-ME naval radar and proceeded to develop its own version designated as Type 366. The major Chines modification of the Russian system is in the data exchange and operator console, where China has improved mode of operations. Like its Russian predecessor, Type 366 radar operates in five different frequency bands and when working in the active mode, the number of targets can be handled is three times of that of when in passive mode. Type 366 radar is claimed to be superior than its Russian predecessor is when active and passive subsystems work in conjunction. In comparison to the original surface search function of its Russian predecessor, China expanded the functions on Type 366 radar by also using it as a low-altitude 2-D air search radar against sea-skimming anti-shipping missiles. With improved software, Type 366 radar is proven to be effective against sea-skimming target with radar cross section of 0.1 to 1 square meter by detecting such incoming targets at distance of 20 to 35 km range. Source wikipedia.org
Type 517HA VHF radar
 VHF Type 517HA – Image @defencyclopedia.com
VHF Type 517HA – Image @defencyclopedia.com
China Type 517H-1 Knife Rest – (Pea Sticks) Radar
Radar, Air Search, 2D Long-Range
Max Range: 333.4 km
Source cmano-db.com
Further aft, the VHF Type 517HA relic 1950 vintage yagi antenna is retained. The 2D very high frequency radar is moved forward on the 052D to make deck space for an aft vertical launcher. Satellite communication radomes are adjacent to it. Source afcea.org
 VHF Type 517HA forward of VLS & Type 364 is top mast radar within the dome
VHF Type 517HA forward of VLS & Type 364 is top mast radar within the dome
Type 364 Radar
 Type 364 air/surface-search Radar – Image at @apl-chine.com
Type 364 air/surface-search Radar – Image at @apl-chine.com
The Type 364 radar was developed by the Yangzhou Marine Electronic Instruments Research Institute (扬州船用电子仪器研究所) / No. 723 Research Institute. It is typically enclosed in a dome on new PLA-N’s frigates and destroyers.
An improved version of the earlier Type 360, it replaces the Yagi IFF antenna with a planar IFF configuration and moves to higher frequencies in order to achieve better target discrimination. The dome is also expected to improve azimuth resolution.
It is expected to be used primarily for CIWS (Type 730, Type 630) targeting with secondary air search and SSM targeting abilities.
Specifications
- Mast weight: 520 kg
- Scan rate: 10+ RPM
- Other features:
- Full coherent chirp pulse compression
- Adaptive MTD (AMTD)
- Able to track missiles with RCS<0.1m2 between Mach 1-3
Source wikipedia.org
China Type 364 – (SR-64, Seagull-C) Radar
Radar, Target Indicator, 2D Surface-to-Air
Max Range: 129.6 km
Source cmano-db.com
There are several mounting sites for a new single barrel 30 mm stealthy gun mount that is fully automated. The addition of this small caliber weapon is presumably for the need to counter non-conventional threats such as potential terrorist attacks and anti-piracy operations, but as of the end of 2012, no 30 mm gun mounts have been observed to be installed on the hull yet.

Due to the greater angle of superstructure slope, more space was made available for the active phased array radar (APAR), which first appeared in June 2012 onboard PLAN weaponry trial ship Bi Sheng. It is believed that this new APAR is a development of Type 348 Radar mounted on the Type 052C. One of the main differences is that the size of the new array is larger, so presumably there are more transceivers on each array. Another obvious difference is that the curvature resulted in the need for air circulation on earlier APAR on Type 052C is gone, so it is believed that the new APAR on Type 052D must have adopted a pure liquid cooling system instead of the mixed air and liquid cooling system on earlier APAR on board Type 052C.

Vertical Launching System
 Image @errymath.blogspot.com
Image @errymath.blogspot.com
The Type 052D has a brand new vertical launching system (VLS) for surface-to-air missiles, cruise missiles, anti-submarine missiles, and anti-ship missiles, and is capable of quad-packing missiles and cold launch; it is the third type of Chinese VLS system identified, after the circular version of VLS on Type 052C destroyer and the rectangular version on Type 054A frigate. The VLS system on Type 052D differs from that on Type 052C. The circular-shaped VLS system on Type 052C is replaced by the VLS with rectangular cells on Type 052D.
Type 052D VLS model
 Image @errymath.blogspot.com
Image @errymath.blogspot.com
Moreover, this box-like VLS looks different from the VLS system of Type 054A. Photos show that Type 052D’s VLS system does not contain the shared exhaust vents between the rows of launching tubes, which is the common feature of Type 054A’s VLS. Instead, the VLS on Type 052D looks more similar to the American Mk 41 VLS, but without obvious indication of exhausts. The lack of exhaust vents in the leaked photos leads to some Chinese internet forums postulating the cold launch method is adopted on Type 052D, but such claims cannot be confirmed by independent or official sources.
Type 052D VLS
 Forward VLS on Type 052D – Chinese internet images
Forward VLS on Type 052D – Chinese internet images
Other sources on Chinese internet forums state that the difference between the VLS on Type 052D and VLS on Type 054A is simply a rearrangement of exhaust to a different location and Type 052D is still utilizing the hot launch method like Type 054A, but used a more advanced method of concentric canister launch (CCL) system (同心筒式垂直发射系统), first pioneered by USA in the mid-1990 for Mk 41 VLS upgrade.
 Image @defencyclopedia.com
Image @defencyclopedia.com
According to the China Military News, a new destroyer equipped with two sets of vertical launch missiles with 64 cells each to launch anti-aircraft missiles HQ-9B, anti-ship and antisubmarine missiles . Original Type 052C on missile launchers anti-YJ-62, apparently, are not present in the new destroyer. It has been suggested that the Type 052D can be equipped with a marine version of the ground cruise missile long-range DH-10.
HQ-9B SAM
 Image @ausairpower.net
Image @ausairpower.net
The basic airframe configuration and internal layout of the HQ-9/HHQ-9/FD-2000 round appear identical to the Russian Almaz-Antey/Fakel 5V55/48N6 family of SAMs. The only notable difference is the redesign of the TVC vanes, which are situated aft of the nozzle in the Chinese missile.
No details have been disclosed on the seeker employed. Given the design heritage of the missile, the baseline seeker is likely to be a direct derivative of earlier variants of the 48N6E/E1 seeker, employing TVM (SAGG) guidance, and midcourse datalink corrected inertial guidance.
Claims have also emerged of an active radar seeker, but these should be treated with caution as Chinese industry has little experience with such, licencing the Russian Agat 9B-1103M design for the PL-12 AAM. However, in the long term it is likely that an active seeker will find its way into the missile, as this is a strong trend in contemporary long range SAM design.
There are also claims of an alternate HQ-9B configuration, employing a dual mode semi-active radar homing and scanning infrared seeker, claimed by Janes to be an imaging IR seeker1. The latter would not present unusual difficulties as China has designed a range of scanning IR seekers for air to air missiles.

Cutaway of the FT-2000 round from brochure material. Note the additional cruciform strake absent in the 5V55/48N6 family of missile airframes, and the baseline HQ-9 (via R.D. Fisher).
Source ausairpower.net
China Type 346A PAR [HQ-9] – (Kvant/APAR) Radar
Radar, FCR, Surface-to-Air, Long-Range
Max Range: 324.1 km
Source cmano-db.com
DH-10 cruise missile

Many sources claim that the PLA now operates the indigenous HN-1 (320 NMI/600 km), HN-2 (800+ NMI/1,500+ km) and the HN-3 (1,350 NMI/2,500 km). The sole good quality image to emerge suggests these weapons are clones of the BGM-109 Tomahawk, suitable for naval and aerial launch. The CJ-10/DH-10 cruise missile, declared operational, also resembles a Tomahawk.
The missile uses both GLONASS and GPS satellite systems for guidance, with four different types of warheads available; a heavy variant weighing 500kg, and three 350kg variants: high explosive blast, submunition and earth penetrator. Source ausairpower.net
In 2013, the United States credited the missile with a range of more than 1,500 km, and either a conventional or nuclear payload; other sources claim the missile has ranges of 2,000 km (1,200 mi; 1,100 nmi), 2,500 km (1,600 mi; 1,300 nmi), or as much as 4,000 km (2,500 mi; 2,200 nmi). In 2004, the CJ-10 was credited with a CEP of 10 m. Source wikipedia.org
CY-5 (Chiang Ying, Long Tassel) ASROC-type missile
 A PLAN naval drill in July saw the likely first images of an ASROC-type torpedo-carrying missile, fired from the vertical launch system of a Type 054A ‘Jiangkai II’-class frigate. The official designator of this missile is uncertain, although some sources suggest nomenclature of CY-5 (Chiang Ying , Long Tassel). Source: Screengrab from CCTV @janes.com
A PLAN naval drill in July saw the likely first images of an ASROC-type torpedo-carrying missile, fired from the vertical launch system of a Type 054A ‘Jiangkai II’-class frigate. The official designator of this missile is uncertain, although some sources suggest nomenclature of CY-5 (Chiang Ying , Long Tassel). Source: Screengrab from CCTV @janes.com
CY-5 is the vertically launched version of CY-4 with folding control surfaces to fit into VLS. The range is reported to be 30 km. The existence of CY-5 type weapon was first officially revealed in 2012 when Type 054A frigate was opened to public in Hong Kong, when the governmental explanation described the modular VLS at the bow of the ship can launch both air defense missiles and rocket propelled ASW torpedoes armed with various Chinese and western torpedoes. However, the exact designation of the rocket propelled ASW torpedo was not revealed. Because CY series was also first intended for export and armed with torpedoes of western origin, CY-5 is thus also most likely armed with Chinese Y-7, or other western light torpedoes such as A244-S. CY-5 is reportedly also deployed onboard Type 052D destroyer. Source wikipedia.org
Yu-8 anti-submarine missile has successfully tested

Yu-8 is a rocket boosted torpedo that can be launched by the vertical launch system (VLS) in Type 052 destroyers or on-deck launchers on other warships.
The VLS can launch both Yu-8 and HQ-16 air defense missiles while the launchers can launch both Yu-8 and YJ-83 anti-ship missiles. In fact, Yu-8 also has anti-ship capabilities.
As Yu-8 flies quickly in the air before it goes into water to hit its target submarine, it can hit a target further away and quicker than ordinary submerged torpedoes.
As it has similar capabilities to those of Russian SS-N-12 missiles, China has caught up with major world naval powers in anti-submarine capabilities when it has successfully developed its Yu-8 missile.
Some commentators believe that China has surpassed Japan in anti-submarine capabilities due to its successful deployment of Yu-8 People.com.cn says in its report on May 13 that according to Taiwan media, Chinese navy successfully tested Yu-8 anti-submarine missile during its major drill in July, 2015. Source errymath.blogspot.com
Yu-7 torpedo

The Yu-7 is a lightweight torpedo of Chinese origin. Since 1984 China tried to copy and later produce under license the US Mk 46 torpedo. This proved to be difficult and a batch of Italian A.224S torpedoes was ordered and the two designs were mated. An electrically powered Yu-7 offspring called the ET-52 was developed and put into service before the development of the Yu-7 was finished.
| Type |
Anti-submarine torpedo |
|
Platform |
Aircraft, surface ships |
|
Diameter |
324 mm |
|
Length |
2.6 m |
| Weight |
235 kg |
|
Warhead |
45 kg |
|
Guidance |
Active/passive acoustic seeker |
|
Propulsion |
Twin propeller |
| Power supply |
Otto Fuel II |
|
Speed |
43 kt |
|
Range |
10 km |
|
Depth |
6 to 400 m depth |
Source weaponsystems.net

YJ-18 (YingJi-18) Low-Flying Subsonic-to-Supersonic Anti-Ship Cruise Missile (ASCM)

The YJ-18 ASCM first cruises at approximately 600 mph right above the surface of the water, and then accelerates to up to Mach 3 (3X the speed of sound) at about 20 nautical miles out from the target ship, making it “harder to hit with on-board guns”, and a “faster target for radars”, according to one Larry Wortzel of the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission. Even worse, the new missile has an operational/engagement range of roughly 290 nautical miles, or roughly 14 times that of its predecessor, the YJ-82. The commission therefore concluded that the YJ-18 missile “could have serious implications for the ability of U.S. Navy surface ships to operate freely in the Western Pacific” in the event of a naval confrontation. In other words, there’s serious concern right now that the YJ-18 can significantly upset the current balance of naval power, i.e., the US Navy’s firepower advantage in the region, and work as an anti-access/area-denial weapon, presumably alongside the DF-21D ASBM ship killer, to keep US ships off the Chinese coast and outside the First Island Chain–in other words, everything the United States controlled during and after World War II (WWII). Source defensereview.com
YJ-18 is another powerful anti-ship cruise missile that the US has no effective defense. It is but supersonic at its terminal stage but it flies with a zigzag trajectory difficult to intercept. It is mainly launched from the VSL of China’s Type 052D destroyers and 093A/B attack nuclear submarines.
According to mil.sohu.com, Britain’s Jane’s Defense Weekly says that the anti-radiation function of YJ-18 is so powerful that it destroys 60% of an Aegis warship’s electronic system even if it explodes 50 meters away from the warship. Source tiananmenstremendousachievements.wordpress.com
YJ-12a Anti-ship Missile
 Launching a YJ-12A from a Type 052D destroyer – eastpendulum.com
Launching a YJ-12A from a Type 052D destroyer – eastpendulum.com
| TYPE | Anti-ship cruise missile |
|---|---|
| PLACE OF ORIGIN | People’s Republic of China |
| SERVICE HISTORY | |
| IN SERVICE | ~2015-present |
| USED BY | People’s Liberation Army Navy |
| SPECIFICATIONS | |
| WEIGHT | 2,500 kg (5,500 lb)[citation needed] |
| LENGTH | 6.3 m (21 ft)[1] |
| DIAMETER | 0.756 m (2.48 ft)[1] |
| WARHEAD | 205–500 kg (452–1,102 lb)[2][3] |
|
|
|
| ENGINE | integrated ramjet/booster propulsion system[4] |
|
OPERATIONAL
RANGE |
250–400 km (160–250 mi; 130–220 nmi)[4][2] (depending on altitude) |
| SPEED | Mach 2-4[1][2] (depending on altitude) |
|
GUIDANCE
SYSTEM |
Inertial navigation system(INS)/Beidou navigation system[5] Terminal guidance |
|
LAUNCH
PLATFORM |
|
Technical data wikiwand.com
‘World’s best’ anti-ship missile a showstopper: Here
Excerpt
China’s largest missile-maker is promoting what it calls “the world’s best anti-ship missile” for sales in the international market.
China Aerospace Science and Industry Corp, one of the main defense equipment suppliers in the nation, is marketing its CM-302 supersonic anti-ship cruise missile to nation shopping to improve their naval capabilities.
YJ-83 anti-ship missile

The YJ-83 is a long-range anti-ship missile designed to meet the requirements of the PLA Navy (PLAN). The YJ-83 has a range of 150 to 200 kilometers and introduces a data-link to receive target updates from airborne assets such as helicopters or fixed-wing aircraft. The YJ-83 can fly at supersonic speeds (Mach 1.5) during the terminal phase of the flight (approx 15 kilometers). The PLAN is deploying the YJ-83 missile as the standard anti-ship missile onboard frigates and destroyers.
Dimensions
Diameter: 0.36 meter
Length: 6.39 meter (21.0 foot)
Wingspan: 1.22 meter
Performance
Max Range: 200 kilometer (108 nautical mile)
Speed
Cruise Speed: 0.90 mach (1,076 kph)
Top Speed: 1.50 mach (1,793 kph)
Weight
Warhead: 165 kilogram (364 pound)
Source deagel.com
HQ-16 medium range SAM

The Hong Qi 16 or HQ-16 is a Chinese medium-range air defense missile system. It is based on the Soviet Shtil naval air defense system, which in turn is a version of the Buk. So the HQ-16 can be seen as a Chinese improved equivalent of the Buk. Some sources report that is had been adopted in the mid 1990s. Currently the HQ-16 is being widely used by the Chinese armed forces.
Missile of the HQ-16 evolved from the Soviet 9M38 missile, used by the Buk. However the Chinese missile is more capable than its predecessor.
The HQ-16 has a maximum range against aircraft of 40 km. It can engage cruise missiles at a range of 3.5 to 18 km. This air defense system can engage very low flying and high altitude targets. It can reach targets at an altitude of up to 18 km. Claimed hit probability of an aircraft with a single missile is 85%. Hit probability of a cruise missile is 60%.
 Chinese VLS For HQ-16 Air Defence Missiles of Type 054A Frigate – Chinese internet images
Chinese VLS For HQ-16 Air Defence Missiles of Type 054A Frigate – Chinese internet images
|
Entered service |
? |
|
Missile |
|
|
Missile length |
5 m |
|
Missile diameter |
0.34 m |
|
Missile weight |
615 kg |
|
Warhead weight |
? |
|
Warhead type |
HE-FRAG |
|
Maximum range of fire |
40 km |
|
Maximum altitude of fire |
18 km |
|
Number of targets engaged simultaneously |
? |
Source military-today.com
DK-10A SAM

First concrete proof of the existence of the Chinese SD-10A Sky Dragon Medium-Range Surface To Air Missile System program. Surface Launched SD-10A is also known as DK-10 Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) which also forms medium range part of Chinese Lie Shou LS-II (Hunter II) Surface To Air Missile System.
Range: 3 km to 50 km
Altitude: 30 m to 20 km
Guidance system: ≤ 13 m
Launch mode: canister-launched missile
Single Shot Kill Probability: ≥ 0.80 (fighter like targets)
Range of Search radar: ≥ 130 km
12 Missiles Can Be Fired Simultaneously To Engaging 12 Targets
System reaction time (normal): ≤ 20 sec
System reaction time (emergency): ≤ 16 sec
Deployment time: 15 min
Withdrawal time: 6 min
Continuous operating time: ≥ 12 hrs
Operating temperature: -20°C to +55°C
HHQ-10 (FL-3000N) short-range Air Defense System
 FLN 3000 missile – Image @scmp.com
FLN 3000 missile – Image @scmp.com
FL-3000N missile utilizes a combined guidance system that incorporates both passive radio frequency (RF) guidance and imaging infrared (ImIR) guidance. There are a pair of horn like protrusions mounted on the ImIR seeker at the tip of the missile, and these two protrusions are the passive RF seeker. An optional ImIR only guidance is also available and the missile is a fire and forget weapon.
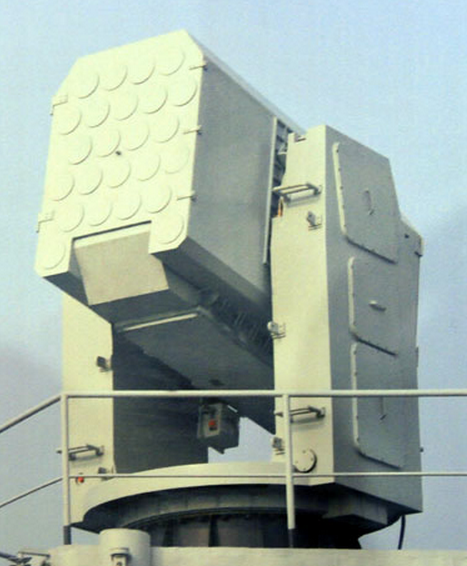

The fire control system (FCS) of FL-3000N can simultaneously control two launchers, and can be integrated into other FCS on board ships. Alternatively, FL-3000N is also capable being directly controlled by other FCS on board ships. The system is usually fully automatic without human intervention, but manual operation can be inserted when needed.
Specifications:
- Length: 2 meters
- Diameter: 0.12 meter
- Minimum range: < 500 meters
- Maximum range: > 9 km for subsonic targets, > 6 km for supersonic targets
- Guidance: passive RF + ImIR or ImIR only.
Chinese military standard GJB-5860-2006
In accordance with the requirements of the CIP are intended for simultaneous planning and implementation of the four classes of missiles, including anti-aircraft missiles, anti-ship missiles, anti-submarine rockets and missiles to bombard land targets. OHR should independently provide missile launch according to the ship’s fire control system.
CIP must ensure the storage and use of rockets three standard sizes:
– “big” – up to 9.9 m;
– “medium” – up to 7 m
– “small” – a length of 3.3 m.
Source army-news.ru
Type 054A VLS
 Image @forummarine.forumactif.com
Image @forummarine.forumactif.com
This second claim appears more probable than the cold launch claims, because official Chinese sources have confirmed the existence of CCL VLS developmental program headed by the School of Mechatronics Engineering of Beijing Institute of Technology, and various research papers have been publicized, such as the effect of the flow mechanism and annular size of CCL and others. It is reported that chief designers of Chinese CCL VLS included Professor Yuan Zenfeng (袁曾凤), Professor Miao Peiyun (苗佩云) and professor Liang Shijie (梁世杰). When using CCL method, the flame produced in hot launch is diverted through the space between the inner and outer canisters within each individual VLS cell, so no specially dedicated exhaust shared by several cells are needed, thus similar to how British vertical launched (VL) Sea Wolf missile operates, and this is why CCL VLS can be mistaken for cold launch due to the lack of dedicated exhaust sandwiched between two rolls of cells in traditional VLS, while in reality, the exhaust of CCL VLS is within each individual cell.
 Image @deagel.com
Image @deagel.com
Another improvement of the Type 052D is that the Type H/PJ87 100mm gun on the Type 052C is replaced by a new single barrel 130 mm gun, designated as the Type H/PJ38 CIWS.
Type H/PJ38 130 mm naval gun

The H/PJ38 is a new single barrel 130 mm gun of the Chinese Navy introduced on the Type 052D destroyer. Designed by the Zhengzhou Mechanical-Electrical Engineering Research Institute (郑州机电工程研究所, also known as the 713th Research Institute of the 7th Academy) and manufactured by Inner Mongolia 2nd Machinery Manufacturing Factory (内蒙第二机械制造厂), the H/PJ-38 130 mm naval gun was developed from reverse engineering of Soviet AK-130 twin 130 mm naval gun, which was carried out by the same two establishments.
The general designer of the H/PJ-38, Chen Dingfeng (陈汀峰), was also the general designer of all models of Type 79 100 mm naval gun, all models of Type 210 100 mm naval gun, and the H/PJ26 76 mm naval gun. Chen was recalled from retirement to complete the H/PJ38 single barrel 130 mm naval gun. When the Soviet AK-130 was first successfully copied by Chinese developers, the Chinese navy was unsatisfied and decided not to let the AK-130 into production, despite all performance parameters being met. Because the AK-130 was judged out-of-date by the Chinese Navy, the H/PJ38 program was created in 2005. The H/PJ38 130 mm single barrel naval gun is considered more powerful and more reliable than other smaller caliber naval guns currently in Chinese service, and as with naval guns on most warships, it is installed in front of the VLS.
Research led to the development of a single barreled 70 caliber, 130 mm system which took more than four years to complete, and the H/PJ38 went to series production soon after completion. The primary improvement of the H/PJ38 over the AK-130 is its adaptability: H/PJ38 can fire both separate loading rounds and semi-fixed rounds, which is crucial in firing gun-launched missiles and PGMs. The H/PJ38 can also fire a variety of sub-caliber rounds, but more importantly, a variety of PGMs were developed for H/PJ38 to increase its effectiveness. Source wikipedia.org
China Type 349A – (GFCR, 130mm) Radar
Radar, FCR, Weapon Director
Max Range: 37 km
Source cmano-db.com
H/PJ-11 CIWS
 Main gun and H / PJ11 CIWS – Image @apl-chine.com
Main gun and H / PJ11 CIWS – Image @apl-chine.com
H / PJ11 model (estimate) 11 30mm near Artillery, 730 1130 the latest developments in the turret change is particularly evident. Since the increase in the volume of the turret. Radar cabin shift. Turret to make room for the installation playing the drums, so that 1130 becomes about playing the drums structure, increase the amount of shells to accommodate the need for a substantial increase in the rate of fire of 1130. Double the amount of deposit is estimated at 730 bombs basis. More than 1,000 rounds of level 730B. 9000-10000 rate of fire rounds / min or so, other performance is unknown. Translated by Google – Source haijun360.com
**Information confirmed by navyrecognition.com
 PLAN Type 052D Destroyer firing with the H/PJ-12 30mm CIWS – Chinese internet images
PLAN Type 052D Destroyer firing with the H/PJ-12 30mm CIWS – Chinese internet images
Sources on the Chinese Internet have stated that Type 052D is equipped with a newest Chinese data link which has just completed national certification in Jun 2012 and publicized by the end of year. Designated as JSIDLS (Joint Service Integrated Data Link System, 全军综合数据链系统), this is the Chinese equivalent of Link 16, a significant improvement of earlier HN-900 which is the Chinese equivalent of Link 11/TADIL-A installed on Type 052C. The general designer of JSIDLS is Major General Wang Jianxi (王建新), who was the also head of the research institute of the People’s Liberation Army General Staff Department assigned as primary contractor of JSIDLS. More than 300 establishments and 8000 people were involved in the development of JSIDLS, and it won State Science and Technology Prizes after completion.
Ships interior
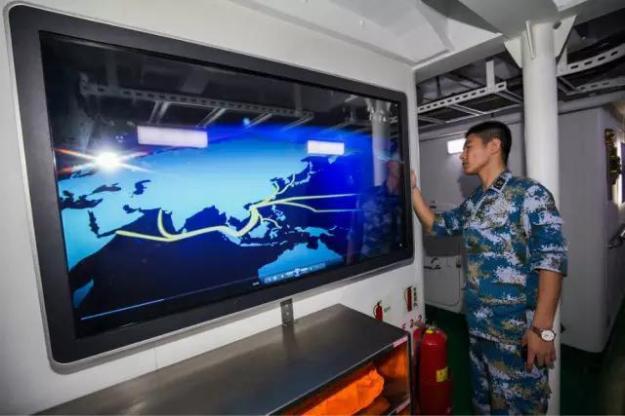





China’s Aegis
China’s state-run media informally designate the Type 052D as Zhonghuashendun / 中华神盾 which means “of and referring to China” and God-Shield. The new destroyer is equipped with a flat-array AESA radar, a 64-cell VLS and modern long-range anti-air missiles. The destroyer is expected to have capabilities similar to those of U.S. Arleigh Burke-class destroyers.
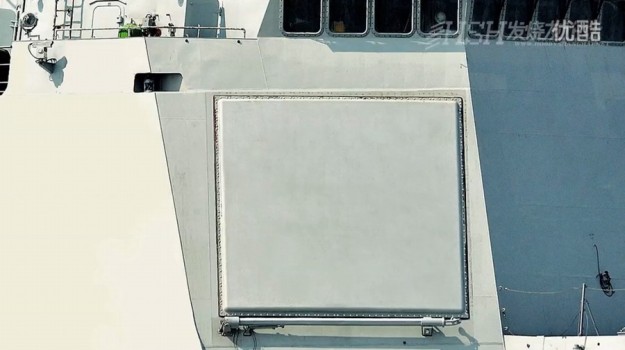 Type 052D flat-array AESA radar – Image apl-chine.com
Type 052D flat-array AESA radar – Image apl-chine.com
There is speculation that the radar systems on Type 052D destroyers are able to detect stealth fighter aircraft, particularly the American F-35 Lightning II, especially if the Type 346 radar is an S-band radar like the American SPY-1 radar. Tactical stealth fighters are optimized to be undetectable from higher-frequency radar bands such the C, X, and Ku, but features like the tail-fin may make it susceptible to lower S or L-band frequencies.
 Type 052D flat-array AESA radar – Image apl-chine.com
Type 052D flat-array AESA radar – Image apl-chine.com
Depending on the distance between the ship and aircraft and the strength of the return of the omni-directional signal, a target may not be picked up at a tactically significant distance since L-band and most S-bands have resolution cells that cannot generate quality targets for weapons tracking. However, the SPY-1 and Air and Missile Defense Radar operate in higher frequency portions of the S-band and are able to generate weapons quality tracks, so Chinese systems could be similar. China is also speculated to be reducing the size of the large radar resolution cells by connecting multiple low-frequency radars through high-speed data-networks, which can refine resolution enough for tracking a missile to the target.

Type 346 S-band multi-function active phased-array radar with four antenna arrays, each of which has a maximum range of 150km, a maximum resolution of 0.5 metres, and can scan a 0-120-degree arc in azimuth and 0-90 degrees in elevation, with a peak power output of 1mWe. Source trishul-trident.blogspot.com
Propulsion:
Two QC-280 gas turbine engines
 Image @china.com
Image @china.com Image apl-chine.com
Image apl-chine.com
The Chinese QC280 is a high performance gas turbine developed and assembled by the China Shipbuilding Industry. The QC280 relates to the Ukranian GT-25000 gas turbine technology delivered to China in 1993 but with key components manufactured in Ukraine. In the early 2000s, China was able to get all the technology of the GT-25000 allowing it to manufacture all its components locally thus receiving the designation of UGT-25000. In the early 2010s, after solving a series of defects and shortfalls China re-designated this gas turbine as the QC-280. As of 2014 the QC280 is in production and is expected to be provided to large displacement ships such as the 12,000-ton class Type 055 destroyer and the new conventionally-powered Type 011 aircraft carrier. Source deagel.com
Two MTU 20V 956TB92 diesel engine

| Series 956 | ||||||
| Engine type | ||||||
| 956 | 956 | 956 | ||||
| No. of cylinders | ||||||
| 12V | 16V | 20V | ||||
| Cylinder configuration | ||||||
| 60°V | 60°V | 60°V | ||||
| Bore/Stroke mm | ||||||
| 230/230 | 230/230 | 230/230 | ||||
| Rated power max. kW | ||||||
| 3750 | 5000 | 6250 | ||||
| Speed max. 1/min. | ||||||
| 1500 | 1500 | 1500 | ||||
Source mtu-online.com
Ships of class
| # | Pennant number | Name | Builder | Launched | Commissioned | Fleet | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DDG-172 | 昆明 / Kunming | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 28 August 2012 | 21 March 2014 | South Sea Fleet | Active[27] |
| 2 | DDG-173 | 长沙 / Changsha | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 28 December 2012 | 12 August 2015 | South Sea Fleet | Active[28] |
| 3 | DDG-174 | 合肥 / Hefei | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 1 July 2013 | 12 December 2015 | South Sea Fleet | Active[29] |
| 4 | DDG-175 | 银川 / Yinchuan | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 30 March 2014 | 12 July 2016 | South Sea Fleet | Active[30] |
| 5 | DDG-117 | 西宁 / Xining | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 26 August 2014 | 22 January 2017 | North Sea Fleet | Active[31] |
| 6 | DDG-154 | 厦门 / Xiamen | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 30 December 2014 | 10 June 2017 | East Sea Fleet | Active[32] |
| 7 | DDG-118 | 乌鲁木齐 / Ürümqi | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 7 July 2015 | January 2018 | North Sea Fleet | Active[33] |
| 8 | DDG-155 | 南京 / Nanjing | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 28 December 2015 | April 2018 | East Sea Fleet | Active[34] |
| 9 | DDG-119 | 贵阳 / Guiyang | Dalian Shipbuilding Industry Company | 28 November 2015 | Sea trials | ||
| 10 | DDG-131 | 太原 / Taiyuan | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 28 July 2016 | Sea trials | ||
| 11 | DDG-120 | 成都 / Chengdu | Dalian Shipbuilding Industry Company | 3 August 2016 | Sea trials | ||
| 12 | DDG-161 | 呼和浩特 / Hohhot | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 26 December 2016 | Fitting out | ||
| 13 | DDG-121 | 齐齐哈尔 / Qiqihar | Dalian Shipbuilding Industry Company | 26 June 2017 | Fitting out | ||
| 14 | DDG-132 | 淄博 / Zibo | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | 29 June 2018 | Fitting out | ||
| 15 | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | Under Construction | |||||
| 16 | Dalian Shipbuilding Industry Company | Under Construction | |||||
| 17 | Dalian Shipbuilding Industry Company | Under Construction | |||||
| 18 | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | Under Construction | |||||
| 19 | Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Co. Ltd. | Under Construction |
| General characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Type: | Destroyer |
| Displacement: | 7,500 tons (full load)[2] |
| Length: | 157 m (515 ft)[2] |
| Beam: | 17 m (56 ft)[2] |
| Draught: | 6 m (20 ft)[2] |
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 31 knots (57 km/h; 36 mph) |
| Complement: | 280 |
| Sensors and processing systems: |
|
| Armament: |
|
| Aircraft carried: | 1 helicopter |
| Aviation facilities: |
|
Main material source wikipedia.org
Updated Sep 12, 2018



