Naresuan Class guided-missile frigates were built by the China State Shipbuilding Corporation, Shanghai, for the Royal Thai Navy. Naresuan is a modified variation of the Chinese-built Type 053 frigate.
The keel for the lead ship in class, Naresuan (421), was laid down in July 1991. The ship was launched in December 1993 and commissioned in January 1995. Taksin (422) was laid in May 1991, launched in September 1994 and commissioned in to the Royal Thai Navy in October 1995.
 Naresuan (421) and Taksin (422) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
Naresuan (421) and Taksin (422) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
| Name | Number | Builder | Launched | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
| HTMS Naresuan | 421 | China State Shipbuilding Corporation | July 1993 | 15 December 1994 | Active | |
| HTMS Taksin | 422 | China State Shipbuilding Corporation | 1994 | 28 September 1995 | Active |
Source wikiwand.com
Naresuan Class vessel specifications and Saab command and control system
 Photo by Tyrone
Photo by Tyrone Photo by Tyrone
Photo by Tyrone Photo by Tyrone
Photo by Tyrone Photo by Tyrone
Photo by Tyrone
Naresuan ClaPhoto by Tyroness was jointly designed by the Royal Thai Navy and China State Shipbuilding Corporation. The ships are considered to be more modern than the Type 053 class frigates.
The frigate has an overall length of 120m, beam of 13m and a draft of 3.8m. The full load displacement of the ship is 2,900t. Each ship can complement a crew of 150.
In June 2011, Saab was awarded two contracts by the Royal Thai Navy for the upgrade of combat management and fire control systems on two Naresuan Class frigates. The total value of the contracts is SEK454m ($72.8m).
Under the contract, Saab will supply a 9LV Mk4 combat management system (CMS), CEROS 200 fire control system and data-link equipment. Deliveries are expected to be completed by 2014.
Upgrade
On 3 June 2011, Saab announced that it was awarded a contract for the upgrading of the two Naresuan class frigates with new electronics and new weapons. The extensive midlife upgrade program (MLU) included a Vertical Launching System (VLS), new secondary guns, Saab’s 9LV MK4 combat management system, Sea Giraffe AMB 3D long range air surveillance radar, CEROS 200 fire control systems, EOS 500 electro-optical system, Tactical Data Links (TDL’s) for communications with the newly acquired Royal Thai Air Force Erieye surveillance aircraft, a new sonar system, a new ESM system and other improvements The upgrade programme was finally concluded in 2016, after five years of work, and delivered almost complete new warships to the Royal Thai Navy. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
 Modified photo of Naresuan class frigate of the Royal Thai Navy. For a high resolution image click here. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Modified photo of Naresuan class frigate of the Royal Thai Navy. For a high resolution image click here. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
The 9LV Mk4 CMS consists of multi function console (MFC) providing input and display facilities to control the system and integrated sensors and weapons. The CMS is integrated with smart sensor system EOS 500, navigation radar, surveillance radar, small or medium calibre gun, data link processor (DLP), AIS-transponder, GPS and wind sensor. The system will perform command and control, identification and tracking, as well as weapons engagement.
9LV Mk4 CMS
 Image: Thai internet
Image: Thai internet
The frigates Naresuan and Taksin are equipped with the latest generation Combat Management (CMS) of Saab, and one of the most advanced in the world today, the Saab 9LV Mk4. The Saab 9LV system integrates sensors, weapons and data links enabling the frigates to engage a variety of modern threats including sea-skimming missiles and small surface threats. The 9LV Mk4 CMS comprises a set of Multi-Function Consoles (MFC) providing display and input facilities for control of the system and the integrated sensors and weapons. The CMS is the core of the frigates CS and performs command and control, identification, tracking and weapon engagements. In addition to the modernization of the CMS the frigates are also equipped with Tactical Data Links (TDL’s) to enable them to share their tactical picture between them and to share information with the Royal Thai Air Force Gripen fighters and Airborne Early Warning radar aircraft which dramatically improves the effectiveness of both the naval and air force assets. In September of 2015, HTMS Naresuan frigate successfully tested a datalink with the Saab Gripen fighter and Saab 340 Airborne Early Warning aircraft. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
 Saab CMS of Naresuan – Image: air-defense.net
Saab CMS of Naresuan – Image: air-defense.net
The full suite of Saab’s Combat Management System (CMS) and integrated fire control solutions in configurations for every type of Coast Guard and naval vessel, is on offer for the Royal Thai Navy
The latest generation of Saab 9LV solutions is built on operationally proven modules and fielded in the major combatants of navies such as the Royal Australian Navy, the Swedish Navy and many others. Building on the experience in over 230 warship installations, the CMS offering from Saab is the open architecture, flexible and extensible, 9LV family.
This offer is applicable to all types of vessels from patrol vessels, corvettes, frigates and aircraft carriers. Source saab.com
 Saab CMS of Naresuan – Image: air-defense.net
Saab CMS of Naresuan – Image: air-defense.net
SURFACE COMBATANTS
9LV technology is able to interface many subsystems, and its architecture readily scales to corvettes and large frigate or destroyer-type vessels. These solutions will typically support a high number of MFCs. They meet the demanding needs of battle resilience through extensive redundancy and physical separation of critical assets.
Medium-sized configurations often focus on one type of mission, such as anti-submarine warfare (ASW) or surface warfare (SuW) using surface-to-surface missiles (SSM). Larger configurations provide a wide range of capabilities and typically include multiple tactical data links and highly automated tactical responses to a range of simultaneous threats, above and below the surface. They also integrate with command support systems to provide the ship with complete C4I capability. Source saab.com
 Naresuan (421) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
Naresuan (421) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
EOS 500 integrated with CMS
 Image: saab.com
Image: saab.com
Saab EOS-500 is a lightweight stabilized electro-optical fire control director with high quality stabilization and advanced TV- and IR-cameras and Laser Range Finder for observation, gun fire, missile laser guidance and target identification. The new sensor replaced the Chinese-built Type 347G I-band fire-control radar (Rice Bowl) above hangar, for the 37mm guns. The inherent video tracker provides automatic detection of up to four concurrent threats, enabling the operator to change target within fractions of a second. EOS-500 is capable of high accuracy 3-D tracking all types of threats, including sea skimming missiles. The advanced Saab video tracker uses simultaneous input from the TV- and the IR- cameras in a data fusion process. The two (2) Saab CEROS 200 radar and optronic tracking systems and the EOS 500 optronic tracking system are the core of the frigates fire control capability and are fully integrated with the small and large calibre guns as well as the Surface to Surface (SSM) and Surface to Air (SAM) Missile systems providing unprecedented self defence capabilities against all modern symmetric and asymmetric threats. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
 Image: saab.com
Image: saab.com
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
| Pedestal | |
| Type | 2-axis, elevation over azimuth |
| Angular speed | < 2 rad/s |
| Angular acceleration | < 2 rad/s2 |
| Weight | < 112 kg including all sensors |
| IR Thermal imager | |
| Type | Third generation |
| Wavelength | 3-5 um or 8-12 um |
| Laser range finder | |
| Type | OPO-shifted Nd YAG |
| Wavelength | 1.57 um (eye-safe) |
| PRF | 3 Hz continuous (8 Hz during 30-sec burst) |
| Power | 115 V 50-60 Hz, 3kVA |
| Communication interface | |
| Ethernet TCP/IP | |
| Environmental conditions |
Source saab.com
 Naresuan (421) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
Naresuan (421) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
The CEROS 200 radar and optronic tracking system can be interfaced with the 9LV Mk4 CMS Gun Fire Control and SAM modules to deliver self-defence capabilities against advanced sea-skimming missiles or asymmetric surface threats. The shipboard data-link equipment from Saab will allow communication between the frigates and Gripen and Saab 340 aircraft of the Royal Thai Air Force.
Data-link
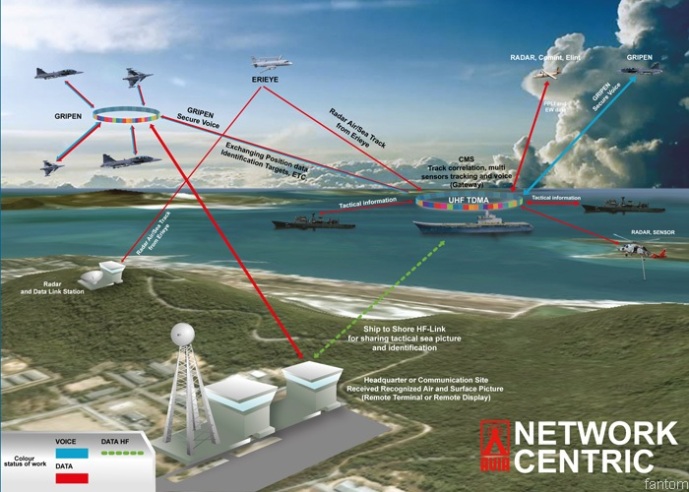 Thales Network centric to integrate with RTN developed by Avia Satcom/Rohde & Schwar
Thales Network centric to integrate with RTN developed by Avia Satcom/Rohde & Schwar Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.grI
Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.grI
Saab upgraded RTN aircraft carrier H.T.M.S. Chakri Naruebet: Here

Weapon systems on the Chinese-built Thai Navy frigates
Naresuan Class is armed with eight RGM-84 Harpoon anti-ship missiles launched from two quad launchers. The Mk 41 vertical launch system fitted on the ship can launch Sea Sparrow and Evolved Sea Sparrow Missiles (ESSMs).
RGM-84 Harpoon anti-ship missile
The Harpoon is an all weather, subsonic, over the horizon, anti-ship missile which can be launch from surface ships, submarines and aircraft. Its guidance system consists of a 3-axis integrated digital computer/ radar altimeter for midcourse guidance, and an active radar seeker for the terminal phase of the flight.
The Harpoon flies at subsonic speeds, with a sea-skimming flight trajectory for improved survivability through reduced probability of detection by enemy defenses. It was designed to strike enemy ships in an open ocean environment.
The ship launched RGM-84 Harpoon was introduced in 1977, as well as the encapsulated submarine launched UGM-84.
Dimensions
Diameter: 340 millimeter
Length: 4.63 meter (15.2 foot)
Wingspan: 910 millimeter
Performance
Max Range: 124 kilometer (67 nautical mile)
Speed
Top Speed: 237 mps (853 kph)
Weight
Thrust: 660 pound
Warhead: 224 kilogram (494 pound)
Weight: 691 kilogram
Source deagel.com
2 x 4 Mk141 Harpoon quad launchers
 2 x 4 Harpoon launchers
2 x 4 Harpoon launchers
Mk 41 vertical launch system

The MK 41 Vertical Launching System (VLS) is the worldwide standard in shipborne missile launching systems. Under the guidance of the US Navy, Martin Marietta performs the design, development, production, and field support that make the battle-proven VLS the most advanced shipborne missile launching system in the world. The Mk 41 VLS simultaneously supports multiple warfighting capabilities, including antiair warfare, antisubmarine warfare, ship self-defense, strike warfare, and antisurface warfare.
The Vertical Launching System (VLS) Mk 41 is a canister launching system which provides a rapid-fire launch capability against hostile threats. The missile launcher consists of a single eight-cell missile module, capable of launching SEASPARROW missiles used against hostile aircraft, missiles and surface units. Primary units of the VLS are two Launch Control Units, one 8-Cell Module, one 8-Cell System Module, a Remote Launch Enable Panel and a Status Panel.
“quad pack” launcher (Mk-41 VLS)
 HTMS Naresuan (421) “quad pack” launcher being loaded – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
HTMS Naresuan (421) “quad pack” launcher being loaded – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
The Launch Control Units receive launch orders from the Multi-Function Computer Plant (MFCP). In response to the orders, the Launch Control Units select and issue prelaunch and launch commands to the selected missile in the VLS launcher. During normal VLS operations, each Launch Control Unit controls half of the Launch Sequencers in the launcher. Either Launch Control Unit can be ordered by the MFCP where one Launch Control Unit is offline and the other Launch Control Unit assumes control of all Launch Sequencers in the launcher.
 HTMS Naresuan (421) 8-Cell Module – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
HTMS Naresuan (421) 8-Cell Module – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
The 8-Cell Module consists of an upright structure that provides vertical storage space for eight missile canisters. A deck and hatch assembly at the top of the module protects the missile canisters during storage and the hatches open to permit missile launches. The plenum and uptake structure capture and vent missile exhaust gases vertically up through the module to the atmosphere through the uptake hatch. Electronic equipment mounted on the 8-Cell Module monitors the stored missile canisters and the module components and assists in launching the missiles.

Sea Sparrow and Evolved Sea Sparrow Missiles (ESSMs)
RIM-162 ESSM was developed by the U.S. Navy in cooperation with an international consortium of other NATO partners plus Australia. ESSM is a short-range, semi-active homing missile that makes flight corrections via radar and midcourse data uplinks. The missile provides reliable ship self-defense capability against agile, high-speed, low-altitude anti-ship cruise missiles (ASCMs), low velocity air threats (LVATs), such as helicopters, and high-speed, maneuverable surface threats. ESSM is integrated with a variety of U.S. and international launchers and combat systems across more than 10 different navies.
 HTMS Naresuan (421) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
HTMS Naresuan (421) – Image: thaidefense-news.blogspot.gr
ESSM has an 8-inch diameter forebody that tapers to a 10-inch diameter rocket motor. The forebody includes a guidance section uses a radome-protected antenna for semi-active homing and attaches to an improved warhead section. A high-thrust, solid-propellant 10-inch diameter rocket motor provides high thrust for maneuverability with tail control via a Thrust Vector Controller (TVC).
ESSM’s effective tracking performance and agile kinematics result from S- and X-band midcourse uplinks, high average velocity and tail control, increased firepower through a vertical “quad pack” launcher (Mk-41 VLS), and greater lethality with a warhead designed for defeating hardened ASCMs.
Background:
ESSM is a cooperative effort among 10 of 12 NATO Sea Sparrow nations governed by a Production Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) and multinational work-share arrangement. In addition to the United States, ESSM Consortium Members include Australia, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Greece, The Netherlands, Norway, Spain, and Turkey.
The first production ESSM was delivered in late 2002 to the U.S. Navy by Raytheon Missile Systems (RMS) and has been in full operational use in the U.S. since 2004. ESSM is fired from the Mk-29 trainable launcher, Mk-41 Vertical Launch System (VLS), Mk-57 VLS (DDG 1000), Mk-48 Guided Missile VLS (Canadian, Greece, Japan), and Mk-56 Dual Pack ESSM Launching System (Danish Navy) configurations by the U.S. Navy, NATO, and other Foreign Military Sales (FMS) customers. ESSM interfaces with the Aegis (DDG 51 and CG 47 classes), NSSMS (LHD and CVN classes), Ship Self-Defense System (LHA-6 and future CVN classes), Total Ship Computing Environment (DDG 1000), ANZAC (Royal Australian Navy), Dutch Configuration (various European Navies), FLEXFIRE (Danish Navy), and APAR (various European Navies) combat systems.
 HTMS Naresuan (421) – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
HTMS Naresuan (421) – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
General Characteristics:
Primary Function: Surface-To-Air and Surface-To-Surface radar-guided missile.
Contractor: Raytheon Missile Systems, Tuscson, Ariz.
Date Deployed: 2004
Unit Cost: $787000 – $972000 depending on configuration
Propulsion: NAMMO-Raufoss, Alliant (solid fuel rocket)
Length: 12 feet (3,64 meters)
Diameter: 8 inches (20,3 cm) – 10 inches (25,4 cm)
Weight: 622 pounds (280 kilograms)
Speed: Mach 4+
Range: more than 27 nmi (more than 50 km)
Guidance System: Raytheon semi-active on continuous wave or interrupted continuous wave illumination
Warhead: Annular blast fragmentation warhead, 90 pounds (40,5 kg)
RIM-162 ESSM data Source seaforces.org
ESSM is a medium range surface-to-air missile with a range of more than 27km. It can counter supersonic manoeuvring anti-ship missiles, while travelling at a speed of Mach 4.
The main gun fitted on the bow deck is an Mk-45 Mod 2 127mm naval artillery gun. The gun can fire at a rate of 16 to 20 rounds a minute for a maximum range of 24km.
Mk-45 Mod 2 127mm naval artillery gun

The 127mm Mk 45 is a naval gun turret of US origin. It was developed in the 1960’s by United Defense as a lighter alternative to the earlier Mk 42 turret. The Mk 45 is the smallest 127mm gun turret in the world and can be considered a direct competitor to the Italian 127mm Compatto. The Mk 45 is a lighter and easier to install design while the Compatto has a higher rate of fire and has more ammunition ready to fire. Both guns use the same US standard 127mm ammunition.
The Mk 45 is a single gun turret which is armed with the 127mm Mk 19 gun which was derived from the earlier Mk 18 that was used in the older Mk 42 turret. The Mk 45 is an unmanned turret with an automatic loader and a 20 round magazine below deck. Additional rounds are stored elsewhere in the ship and fed into the magazine using a feed chute. The gun is controlled using consoles below deck or in the command center. The latest development are a longer barrel and extended range guided munition (ERGM), the latter program was cancelled while the new barrel is in production.
The Mk 45 fires 127mm shells for use against shore targets, naval vessels and aircraft. The gun has a rate of fire of 16 to 20 rounds per minute. The maximum range is 23 km versus surface targets and the anti-aircraft range is quoted as 15 km. The latest Mk 45 design with longer barrel has a longer range and higher rate of fire. The ERGM round has a range of 117 km but was never fielded. Depending on the ship design the total ammunition load ranges between 475 and 680 rounds

The Mk 45 turret can be easily distinguished from the earlier Mk 42 turret by its shape and longer ordnance. The Mk 45 is one of the smallest 127mm gun turrets. The Mk 45 guns with original 54-caliber barrel can be identified by their round turret shapes since the Mod 4 uses an angled one.
Mk 45 Mod 0: Original production model with mechanical fuze setter and two piece barrel.
Mk 45 Mod 1: Improved Mod 0 with automatic fuze setter and unitary barrel.
Mk 45 Mod 2: Export version of US Navy Mod 1.
HTMS Naresuan (421) – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
| Type | Naval gun turret |
| Armament | 127mm 54-caliber, 808 m/s muzzle velocity, 8.000 round barrel life |
| Rate of fire | 16 to 20 rpm |
| Ammunition | 20 rounds in loading system, single feed chute |
| Range | 23 km vs surface targets, 15 km vs aircraft |
| Traverse | -170 to +170°, 30°/s |
| Elevation | -15 to +65°, 20°/s |
| Dimensions | ? |
| Weight | 24.1 t empty |
| Crew | 3 or 6 |
| Fire control | ? |
127mm mk45 mod 2 gun data weaponsystems.net
HiFrag
| Targets: Aircraft, Helicopter, Missile, Surface Vessel, Land Structure – Soft, Mobile Target – Soft |
| Weapons: |
|---|
| 127mm/54 HE-CVT [HiFrag] – (USN) Gun Air Max: 2.8 km. Surface Max: 20.4 km. Land Max: 20.4 km. |
HiCap
| Targets: Aircraft, Helicopter, Surface Vessel, Land Structure – Soft, Land Structure – Hardened, Mobile Target – Soft, Mobile Target – Hardened |
| Weapons: |
|---|
| 127mm/54 HE-PD [HiCap] – (USN) Gun Air Max: 2.8 km. Surface Max: 20.4 km. Land Max: 20.4 km. |
Source cmano-db.com
Two Type 76 twin 37mm naval guns onboard defend the ship from anti-aircraft and anti-surface threats. (New MSI guns replaced the old Type 76s naval guns)
MSI Defense Systems 30mm DS30M Mark 2 (Seahawk A2) gun systems
 MSI Defense Systems 30mm gun – Photo by Tyrone
MSI Defense Systems 30mm gun – Photo by Tyrone
The two secondary Chinese-built Type 76 twin 37mm dual-purpose gun systems that were equipping originally the ships, were removed and replaced by the MSI Defense Systems 30mm DS30M Mark 2 (Seahawk A2) gun systems consisting of a 30mm Mark 44 Bushmaster II cannon on a fully automated mount with an off-mount electro-optical director (EOD) and with below deck control console. The gun has a rate of fire of approximately 650 rounds per minute in a maximum range of less than 3km in anti-aircraft role. Except the main naval gun, the ships are equipped with 2-4 MH2B heavy machine guns. The M2 has a maximum (effective) range of around 1,830m and a cyclical rate of fire of approximately 600 rounds per minute. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
2-4 MH2B heavy machine guns

| Calibre | 12.7x99mm NATO (.50 cal) |
| Operating principle | Short recoil of the barrel |
| Overall length | 1,656mm (65.2″) |
| Weapon weight | 38.150 kg (84 lb) |
| Barrel type | Quick Change Barrel |
| Barrel weight | 13 kg (28.63 lb) |
| Barrel length | 1,143 mm (45″) |
| Buttstock type | N/A |
| Cyclic rate of fire | 485 to 635 RPM |
| Effective range | 2,000m (2,187 yds) |
| Feed | Disintegrating link belt (M2 or M9 link) |
| Firing mode | Single shot, full automatic |
| Handguard type | N/A |
| Role | Heavy Machine Gun |
FN® M2HB-QCB data fnherstal.com
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capability is provided by the Mark 32 anti-submarine torpedo launching system. Two 324mm Mk-32 Mod.5 torpedo tubes can launch Mk 46 or Mk 50 torpedoes against submarines.
324mm mk32 torpedo tube
 HTMS Naresuan (421) Mk32 torpedo launcher – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
HTMS Naresuan (421) Mk32 torpedo launcher – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
12.75 inch (324mm) Mark 32 Surface Vessel Torpedo Tubes (Mk 32 SVTT):
Models:
Mk-32 / Mod. 5, 7, 14, 15 (3 tubes) – for Mk-44, Mk-46 torpedoes
Mk-32 / Mod. 17, 19 (3 tubes) – for Mk-46, Mk-50, Mk-54 LHT torpedoes
Mk-32 / Mod. 9 (2 tubes) – for Mk-44, Mk-46 torpedoes
Mk-32 / Mod. 11 (1 tube) – for Mk-44, Mk-46 torpedoes
Mk-32 SVTT can be modified to use other 12.75″ torpedoes (such as EuroTorp MU90 / Eurotorp A244S LWT / BAE Systems Stingray)
Source seaforces.org
MK 54 Mod 0 Lightweight Torpedo
 An exercise MK 54 Mod 0 Torpedo is launched from the Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyer USS Roosevelt (DDG 80) in 2014. Photo: US Navy – Source navaltoday.com
An exercise MK 54 Mod 0 Torpedo is launched from the Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyer USS Roosevelt (DDG 80) in 2014. Photo: US Navy – Source navaltoday.com
The Mk 54 is carried mainly by aircraft but also by many American and foreign surface ships and has replaced depth charges as the main weapon against submarines. The Mk 54 is particularly effective when used by aircraft equipped to seek out submarines. Patrol aircraft can carry up to eight lightweight torpedoes, while helicopters can carry up to three (but often just one). The Mk 54 is a 324mm (12.75 inch) weapon, weighing about 340 kg (750 pounds), and with a warhead containing 45 kg (100 pounds) of explosives. Its guidance system has been deliberately designed to work well in shallow coastal waters, where ships are believed most likely to encounter subs. Until 1991, when the Cold War ended and the Russian nuclear sub fleet disappeared, the emphasis was on fighting subs on the high seas.
There are several upgrades available for the Mk 54. For example, to make the Mk 54 more effective on patrol aircraft, the U.S. Navy developed glide kits. Putting wings on torpedoes is all about concern at the growing use of anti-aircraft missiles by submarines. To deal with that problem, the navy sought to equip some Mk 54 torpedoes (that are normally dropped into the water at a low altitude by P-3 patrol aircraft) with an add-on glide kit. These systems consist of wings, control flaps, a flight control computer, battery, and GPS for navigation. The kit allows a torpedo to be released at 6,300 meters (20,000 feet), which is outside the range of submarine launched anti-aircraft missiles, and glide for 10-15 kilometers. When down to about 100 meters (300 feet) altitude, the glide kit is jettisoned and the torpedo enters the water to seek out the sub. Normally, aircraft have to descend to under 330 meters (a thousand feet) to launch the torpedo. This takes time and puts stress on the aircraft.
Many subs have sensors that are sensitive enough to detect low flying helicopters (the main target for the subs anti-aircraft missiles) and aircraft. Patrol aircraft are more effective if it can stay at high altitude all the time. Moreover, the glide kit is easy to build, since it can use items already used for smart bombs (JDAM) and earlier glide kits.
The Mk 54 lightweight torpedo entered production in 2004. Costing about a million dollars each, the Mk 54 is a cheaper and somewhat less capable replacement for the Cold War era high tech Mk 50 and the old reliable Mk 46. The Mk 54 is a more cost effective alternative to the three million dollar Mk 50, which was in development for over two decades. The Mk 50 was difficult to build because it was meant to be a “smart” torpedo that was light enough to be carried by helicopters but could go deep to kill Russian nuclear subs. Alas, when the Mk 50 finally became available in the late 90s, the high-seas Russian nuclear subs were gone and the typical target was now a quieter diesel-electric sub in shallow coastal waters. So the Mk 54 was developed, using cheaper, off-the-shelf, electronic components, some technology from the Mk 50 and larger Mk 48, as well as the simpler, but not deep diving, frame and propulsion systems of the older Mk 46 lightweight torpedo. Thus the 3.25 meter (ten foot) long Mk 54 is a bit of a hybrid, created to save money and also be more capable against quieter subs operating in shallower water. The Mk 54 has a range of about 10 kilometers and a top speed of about 72 kilometers an hour. It has built in sonar that can search for the target sub, as well as acoustic sensors (listening devices to pick up any sounds a sub might make). The Mk 54 also has an onboard computer and a data file of underwater noises and search tactics, which are used as it tries to find its target and keep after it until it can hit the sub and destroy it with the explosives in the warhead. Source strategypage.com
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Weight | 608 lb (276 kg)[2] |
| Length | 106.9 in (2.72 m)[2] |
| Diameter | 12.75 in (324 mm)[2] |
|
|
|
| Warhead | PBXN-103 |
| Warhead weight | 96.8 lb (43.9 kg)[2] |
| Blast yield | 238lb TNT |
|
|
|
| Engine | reciprocating external combustion |
| Propellant | Otto II (liquid) |
| Speed | >40 kn (74.1 km/h; 46.0 mph) |
|
Guidance
system |
Active or passive/active Acoustic homing |
|
Launch
platform |
Mark 32 Surface Vessel Torpedo Tubes, ASW Aircraft, RUM-139 VL-ASROC |
Source wikiwand.com
Sensors, radars and aircraft carrying capabilities of the guided-missile frigates
 HTMS Taksin (422) – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
HTMS Taksin (422) – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
Naresuan Class is equipped with Saab Sea Giraffe AMD 3D surveillance radar, Thales LW-08 long range air search radar, Thales STIR fire control radar and DE-1160 hull mounted sonar. (Thales STIR fire control radar replaced with Ceros 200 fire control director and DE-1160 hull mounted sonar replaced with Atlas Elektronik DSQS-24D hull-mounted sonar )
Saab Sea Giraffe AMD 3D surveillance radar
 Main mast with the new sensors – Image: www.air-defense.net
Main mast with the new sensors – Image: www.air-defense.net
SEA GIRAFFE AMB radar surveillance equipment designed to be capable of detecting both on the coast and in the air precisely. Designed to connect directly combat 9LV (CMS)
The radar is able to detect the angle of 0-70 degrees to 360 degrees, covering a 180 kilometer surveillance can detect targets with high accuracy. And detect even the target object invisible. Small as well as the 3D GIRAFFE AMB radar is versatile with the ability to cover all the needs. Featured in Add the time to meet and make decisions. Low radar footprint Can observe the motion of the target by land, sea and air radar highlights three critical limit.
- Investigator in the air and can interfere with the radar track of the enemy.
- Can observe and track the motion of the enemy on the side.
- Be alert gunshot detection and neck where the bullet was fired.
- Can distinguish between different types of goals Even the up and down motion of the helicopter.
- Can pointing to fight missile defense land. Naval and air precisely.
- To support gunnery ship.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
| Radar type | Stacked beam 3D radar |
| Antenna type | 3D phased array, digital beam forming |
| Frequency | C (G/H)-band |
| Elevation coverage | > 70 degrees |
| Rotation rate | 60 RPM |
| Instrumented range | 180 km |
Source Saab
Thales LW-08 long range air search radar
 Thales LW08 radar of Naresuan – Image navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Thales LW08 radar of Naresuan – Image navalanalyses.blogspot.com
The LW08 is a radar system for long-range surveillance, providing target indication to weapon control systems. It meets all vital requirements for any naval surveillance system: LW08 presents a clear picture of the environment; it does so, reliably, under any circumstances; and it does it without adding great weight to the superstructure of the ship. The aspect which distinguishes LW08 from its competitors is its wide range and superb accuracy. The system has proven its worth time and time again, operating in various configurations. LW08 performs with great frequency agility over a wide band, due to its synthesizer-driven TWT transmitter.
Excellent performance under various clutter conditions is ensured by the wide dynamic range receiver with application of digital video processing, supported by circular polarization. Moreover, due to its lightweight construction and hydraulically controlled stabilization platform, this antenna can be installed at a high mast position, thereby improving performance.
Main characteristics
- Long-range detection, with very short minimum range
- Fully coherent system
- Frequency agility over a wide band
- Pulse compression
- Linear and circular polarization
- Digital video processor, using MTI
- Hydraulic roll and pitch stabilization
Performance Data
Detection range
- Small missile : 100 km
- Fighter aircraft : 230 km
- Target speed : up to Mach 4
- Surface targets : radar horizon
- Minimum range : 2 km
- Instrumented range : 135/270 km
- Tracking capacity : 400
Technical Data
Antenna parameters
- Type : horn-fed parabolic reflector
- Beamwidth
– horizontal : 2.2º
– vertical : cosec2 up to 40º
- Polarization : linear/circular
- Rotation speeds : 7.5 and 15 rpm
Transmitter parameters
- Type : TWT
- Frequency : D-band
- Frequency modes : fixed frequency and frequency agility
- Transmission modes : full scan and sector transmission
- Average power : 5.2 kW
Receiver parameters
- Receiver channels
– air surveillance : MTI and LIN
– surface surveillance : LIN or LOG
- Video processing : MTI: digital canceller and
video correlator
Digital ISU and LOG with
PLD
- Compressed pulse length : 0.6 µs
Source thales7seas.com
Saab CEROS 200 fire control director
 Naresuan – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
Naresuan – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
The CEROS 200 comprises multiple sensors, including EO, IR, TV and Laser. In addition, it has an advanced video tracker to enable simultaneous TV and IR tracking. The radar director pedestal is of twoaxis, elevation over azimuth type, and incorporates direct-drive hydraulic motors with built-in hydrostatic bearings. The freedom of motion in azimuth is unlimited and all electrical signals are transferred via slip rings. In elevation the motion is controlled both by electrical and mechanical end stops. For stabilisation against ship motion and angular rate measurements of the pedestal, a two-axis measurement gyro is used. The gyro features high performance and reliability. At turn-off, the director is automatically slewed to parking position and secured with hydraulic locking pins. A key feature is its high ability when tracking with low angular speed. The CEROS 200 has a hydraulically-driven pedestal with a much higher Mean Time Between Failure compared with alternative approaches such as electro-driven systems.
KEY STRENGTHS:
- Extremely high accuracy
- Fast reaction
- Extremely high availability
- Patented CHASE algorithm
- Proven performance
- Unique capabilities
- Long range
- Extremely wide bandwidth (2 GHz)
- Low weight
- Low lifecycle cost
- Inherent growth potential
Source Saab
| General data: | |
|---|---|
| Type: Radar | Altitude Max: 30480 m |
| Range Max: 74.1 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0.2 km | Generation: Early 2000s |
| Properties: Moving Target Indicator (MTI), Pulse Doppler Radar (Full LDSD Capability), Continuous Wave Illumination |
| Sensors / EW: |
|---|
| CEROS 200 Tracker [9LV Mk4 ESSM] – Radar Role: Radar, FCR, Surface-to-Air & Surface-to-Surface, Short-Range Max Range: 74.1 km |
Source cmano-db.com
Among other equipment, the ships, after the upgrade have received the Atlas Elektronik DSQS-24D hull-mounted sonar that replaced the DE-1160, the Selex Communications SIT422 CI and M425 NGIFF, two Saab Bridge Pointer Target Designation Sights (TDS, INMARSAT-M, Saab Link E Link G (TIDLS), Saab Link 11 (TADIL-B) etc. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Atlas Elektronik DSQS-24D hull-mounted sonar

 Taksin (422) – Image: thaimilitary.blogspot.com
Taksin (422) – Image: thaimilitary.blogspot.com
| General data: | |
|---|---|
| Type: Hull Sonar, Active/Passive | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 44.4 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Early 1990s |
| Sensors / EW: |
|---|
| DSQS-24C [CSU 90] – Hull Sonar, Active/Passive Role: Hull Sonar, Active/Passive Search & Track Max Range: 44.4 km |
Source cmano-db.com
2 Kelvin Hughes SharpEye I-Band and E/F-Band (X & S-Band) radars
 Image: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Image: navalanalyses.blogspot.com
The ships are also equipped with one Furuno navigation radar (replaced Raytheon AN/SPS-64) and two Kelvin Hughes SharpEye I-Band and E/F-Band (X & S-Band) radars that replaced other Chinese-built radars in the class. SharpEye transmits a low power patented pulse sequence, which enables short, medium and long range radar returns to be detected simultaneously, allowing the radar operator to maintain situational awareness regardless of the range scale setting of the radar display. Other users of the radar can select their own radar display range scale. A low peak transmission power (less than 300W) equivalent to a 25kW magnetron reduces the probability of intercept by ESM systems. Doppler processing of radar returns provides coherent information concerning a target’s velocity (radial) and enable the detection of very small and slow moving objects and targets with a low RCS (Radar Cross Section) and through a series of electronic filters is able to distinguish between the targets of interest and sea, rain and land clutter. SharpEye I-Band (X-Band) transmitters are the first in their class to employ Gallium Nitride GaN power transistor technology. The significant performance benefits of GaN transistors have been harnessed to directly improve the performance of the radar. Other differentiating technologies include Moving Target Detection (MTD) providing enhanced clutter suppression at the Doppler processing stage and pulse compression of the return signal, enabling a low transmit power, providing efficient use of the radar and reducing the probability of detection by ESM equipment. SharpEye is a truly multipurpose naval radar transceiver and is/can be used for navigation, surface search and helicopter control and recovery. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
The frigate has an aft helicopter deck to allow the operations of a single helicopter, such as a Bell212 ASW or Super Lynx helicopter. There is also a hangar.
H145M landing on HTMS Taksin (422)
RTN H145M: Details
RTN Super Lynx
MARITIME
Countermeasure
 HTMS Taksin (422) – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
HTMS Taksin (422) – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
Terma SKWS (Soft Kill Weapon System) C-Guard
 Image: Terma
Image: Terma
Terma SKWS (Soft Kill Weapon System) C-Guard is the decoy launching system of the ships that replaced the obsolete Chinese ones. The system is integrated with the Combat Managment System, that can fire all existing 130 mm decoys – also known as SeaGnat decoys, made to defeat stream attack with multiple missiles and torpedoes from multiple directions. The system is based on two Terma DL-12T launchers (12 firing tubes each) on each side of the ship and four Terma Mk137 SRBOC launchers (6 firing tubes each) atop the bridge. The total number of decoy launchers is 48 (!), which is the maximum system configuration supporting the 48 launchers, three Control Units and uses two Launcher Interface Units providing a dual network. This configuration and the dual voltage power supply in each LIU secure a high MTBCF and graceful degradation in case of any malfunction. Source navalanalyses.blogspot.com
Terma DL-12T launchers
 Terma DL-12T launchers (12 firing tubes each) Naresuan – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
Terma DL-12T launchers (12 firing tubes each) Naresuan – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
Terma Mk137 SRBOC launchers
 Terma Mk137 SRBOC launchers on Naresuan – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
Terma Mk137 SRBOC launchers on Naresuan – Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
Image: defense-studies.blogspot.gr
ES-3601S – Tactical Radar ESM and Surveillance System
 Image: harris.com
Image: harris.com
The ES-3601S is a cost effective high-capability radar Electronic Support Measures system for surface naval applications. The ES-3601S uses an innovative monopulse direction-finding system for accurate bearing measurements, and has been integrated into a variety of combat system environments. The ES-3601 is currently operational on platforms from Europe to Asia.
Tactical Radar ESM and Surveillance Capabilities
- 100% Probability of Intercept
- Instantaneous DF over 360°
- Accurate 2 x 4 element monopulse DF
- Long range detection, DF and tracking
- Measures all radars simultaneously
Source harris.com
Naresuan Class propulsion and speed
Naresuan Class is powered by combined diesel or gas (CODOG) propulsion system. It includes two General Electric LM2500 gas turbine and two MTU 20V1163 TB83 diesel engines, driving two controllable pitch propellers through twin shafts. The propulsion system provides a maximum speed of 32kt and a range of 4,000nmi at 18kt speed.
2 x General Electric LM2500 gas turbine

The General Electric LM2500 is an industrial and marine gas turbine produced by GE Aviation. The LM2500 is a derivative of the General Electric CF6 aircraft engine.
The LM2500 is available in 3 different versions:
- The LM2500 delivers 33,600 shaft horsepower (shp) (25,060 kW) with a thermal efficiency of 37 percent at ISO conditions. When coupled with an electric generator, it delivers 24 MW of electricity at 60 Hz with a thermal efficiency of 36 percent at ISO conditions.
- The improved, 3rd generation, LM2500+ version of the turbine delivers 40,500 shp (30,200 kW) with a thermal efficiency of 39 percent at ISO conditions. When coupled with an electric generator, it delivers 29 MW of electricity at 60 Hz with a thermal efficiency of 38 percent at ISO conditions.
- The latest, 4th generation, LM2500+G4 version was introduced in November 2005 and delivers 47,370 shp (35,320 kW) with a thermal efficiency of 39.3 percent at ISO conditions.
LM2500 installations place the engine inside a metal container for sound and heat isolation from the rest of the machinery spaces. This container is very near the size of a standard 40-foot (12 m) intermodal shipping container – but not the same, the engine size very slightly exceeds those dimensions. The air intake ducting may be designed and shaped appropriately for easy removal of the LM2500 from their ships. Source wikiwand.com
2 x MTU 20V1163 TB83 diesel engines
| Series 1163 | |||||
| No. of cylinders | |||||
| 12V | 16V | 20V | |||
| Cylinder configuration | |||||
| 60°V | 60°V | 60°V | |||
| Bore/Stroke mm | |||||
| 230/280 | 230/280 | 230/280 | |||
| Rated power max. kW | |||||
| 4440 | 5920 | 7400 | |||
| Speed max. 1/min. | |||||
| 1300 | 1300 | 1300 | |||
Source mtu-online.com
| General characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Type: | Frigate |
| Displacement: | 2,985 tons full load |
| Length: | 120.5 m |
| Beam: | 13.7 m |
| Draught: | 6 m |
| Propulsion: | 1 × General Electric LM2500+gas turbine and 2 × MTU20V1163 TB83 diesel engines, driving two shafts with controllable pitch propellersin CODOG configuration. |
| Speed: | 32 knots (59 km/h) max |
| Range: | 4000 nmi(7408 km) at 18 kn |
| Complement: | 150 |
| Sensors and processing systems: |
|
| Electronic warfare & decoys: |
|
| Armament: |
|
| Aircraft carried: | 1 x Super Lynx 300 |
Source wikiwand.com
Main material source naval-technology.com
Images are from public domain unless otherwise stated
Updated May 16, 2017














Pingback: april 2019 – alfredtetzlaff
Pingback: alfredtetzlaff