MilSim Asia: Thailand relies on M109 simulators
11th January 2017 – 12:00 by Sompong Nondhasa in Bangkok
 Image: shephardmedia.com
Image: shephardmedia.com
The Royal Thai Army (RTA) is an ardent user of Howitzer Crew Trainers (HCT) for its M109 crews, with their software upgraded to the latest version in 2015.
Delivered to the army’s Artillery Centre on 29 January 2003, Thailand acquired the HCTs from Van Halteren Defence in the Netherlands for a price of $2 million.
The HCT is an indoor simulator for the M109A5 155mm self-propelled howitzer, providing a realistic environment to train crews.
The HCT has three main parts. The first is the instructor station, a control section used to set training situations, and to correct, record and evaluate the results of each training session for debriefings.
The second part is the training station, a transparent compartment allowing instructors to view crews and training situations. It is arranged to mimic the interior of an M109A5 turret, and it features all the equipment needed by gunners.
The final part is the training ammunitions system, it features all ammunition types that are the same size and weight as real ammunition rounds. Gunners can select and use them in their training.
The HCTs offer the RTA artillery corps low-cost training for crews in a controllable and safe environment. It avoids the cost of live-fire training and commitment of all associated resources, plus it can be used any time.
Currently the RTA has 18 M109A5s in its inventory, these have been in service since 1994.
Original post: shephardmedia.com
****-END-****
M109A5 155mm self-propelled howitzer
The M109 was, is and will be probably for years still, the most prolific self-propelled howitzer outside Soviet Union. Although its first drawings and specifications dates back from 1959, it was upgraded to such extent that it is still today in service, upgraded time and again and integrating the best technologies each era had to offer. It was sold to about 40 countries worldwide, including several NATO’s members. Its best equivalent in popularity was the soviet 2S1-2S3 family. It also left a durable imprint on the genre, a standard upon which other SPHs were compared in the Western bloc. A veteran of Vietnam, it saw action in the Yom Kippur War, Iran-Iraq war, the gulf war and invasion of Iraq until 2014.
Protection and crew
Armour is made of reinforced Rolled 5083 aluminium alloy (like the M113) assembled by Welding. Its thickness varies from 1.25″/75° (32 mm) on the upper and lower front, but also sides, rear, top and floor of the hull and same on the turret (angled 22° front and sides). The crew of six comprised the section chief, driver, gunner, assistant gunner and two ammunition handlers. In operation, the gunner aims the cannon traverse only while the assistant gunner aims the elevation (quadrant). This crew was reduced to only four on the M109A5 due to some automation which only the gunner and ammunition loader. NBC protection was individual up to the M109A4 variant where it became collective with sealed hatches and overpressure. Air climatisers were also introduced early on.
Armament
The main gun is a M126 155 mm howitzer L/39 caliber with breech interrupted screw and separate loading, bagged charge. It is fitted with both a double-baffled muzzle brake and gas chamber bore evacuator (which changed in type and performance over time) to reduce recoil. Maximal elevation for the gun is a good 75° (later improved). It goes down to a -3° depression with an hydraulic and manual backup system. Maximum fire rate is 6 rpm and Sustained 3 rpm (that too was improved with the M109A5). Max traverse speed was 11°/sec. and max elevation speed was 7°/sec.
M109A5 (1985?)
The A5 is the last cold war version of the M109, with a new M182 mount and 155 mm M284 39 cal. cannon for an effective max range of of 23,5 km in standard, but 30 km with Rocket Assisted Projectiles (RAP Rounds). The main engine was also upgraded to a Detroit 440hp diesel. The A5+ was introduced in the 1990s with a wide range of improvements, notably electronics and more modern FCS (by BAE Systems), aimed at export. This was also proposed as a conversion for regular M109A5.
Source tanks-encyclopedia.com
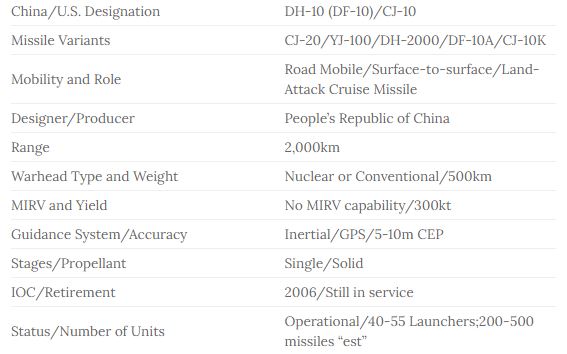
| Country of origin | United States |
| Entered service | 1963 |
| Crew | 6 men |
| Dimensions and weight | |
| Weight | 24.07 t |
| Length (gun forward) | 9.12 m |
| Hull length | 6.19 m |
| Width | 3.15 m |
| Height | 3.28 m |
| Armament | |
| Main gun | 155 mm |
| Barrel length | 23 calibers |
| Machine guns | 1 x 12.7 mm |
| Projectile weight | 43.54 kg |
| Maximum firing range | 14.6 km |
| Maximum rate of fire | 4 rpm |
| Sustained rate of fire | 2 rpm |
| Elevation range | – 3 to + 75 degrees |
| Traverse range | 360 degrees |
| Ammunition load | |
| Main gun | 28 rounds |
| Machine guns | 500 rounds |
| Mobility | |
| Engine | Detroit Diesel 8V71T diesel |
| Engine power | 450 hp |
| Maximum road speed | 65 km/h |
| Range | 390 km |
| Maneuverability | |
| Gradient | 60% |
| Side slope | 30% |
| Vertical step | 0.53 m |
| Trench | 1.83 m |
| Fording | 1.07 m |
Technical M109 data military-today.com