The Mil Mi-26 is a twin-engine heavy transport helicopter designed and manufactured by Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant, Russia, for both military and civilian roles. It is the second largest and powerful helicopter in the world, and entered into service in 1985.
The helicopter’s maiden flight took place in December 1977. About 276 Mi-26 helicopters are currently in service worldwide.
Mi-26 helicopter variants
The Mi-26 has 13 variants, which include Mi-26A, Mi-26M, Mi-26MS, Mi-26NEF-M, Mi-26P, Mi-26PP, Mi-26PK, Mi-26S, Mi-26T, Mi-26TP, Mi-26TS, Mi-26TZ and Mi-27.
The Mi-26A is an advanced version of the Mi-26 and completed its flight test in 1985. It is upgraded with a structured PNK-90 flight navigation system for automated approach and decline.
Another variant, the Mi-26M is an upgraded version of Mi-26. It is incorporated with a flight navigation system, D-127 turboshaft engines, an electronic flight instrumentation system and aerodynamic rotor blades for better performance.
The Mi-26T is a commercial cargo or freight transport version. It was first showcased in the 1997 Moscow Air Show. The helicopter was later displayed at Farnborough Air Show held in 2002 after installing advanced avionics by Rostvertol.
Mi-26T
 Mi-26T – russianhelicopters.aero
Mi-26T – russianhelicopters.aero
Mi-26T, the world’s best line production helicopter in terms of load capacity, is unrivaled in cost-performance parameters. This type helicopters are intensively used for all sorts of operations: transportation, evacuation, fire fighting etc. Mi-26T is capable of carrying up to 20 tons of cargo inside fuselage or on the external sling.
Mi-26T cockpit
 Mi-26T – T24
Mi-26T – T24 Mi-26T – T-24
Mi-26T – T-24 Mi-26T – T24
Mi-26T – T24 Mi-26T – T24
Mi-26T – T24 Mi-26T – T24
Mi-26T – T24 Mi-26T – T24
Mi-26T – T24
Characteristic
|
Performance |
|
|---|---|
|
Max. speed
|
295 km/h
|
|
Cruise speed
|
255 km/h
|
|
Max. flight range with main fuel tanks
|
800 km
|
|
Operational ceiling
|
4,600 m
|
|
Hover ceiling (OGE)
|
1,520 m
|
|
Weight Parameters |
|
|
Max. take-off weight
|
56,000 kg
|
|
With underslung load
|
56,000 kg
|
|
Max. Payload, kg |
|
|
in transport cabin
|
20,000 kg
|
|
on external sling
|
20,000 kg
|
|
Engine 2 х D-136 (2 х 11 400 h. p.) |
|
|
Take-off power
|
h. p.
|
|
Contingency power
|
h. p.
|
|
Cabin Dimensions |
|
|
Length
|
12.1 m
|
|
Width
|
3.29 m
|
|
Height
|
3.17 m
|
|
Volume
|
m3
|
|
Capacity: |
|
|
Aircrew
|
5–6
|
|
Passengers
|
82
|
Mi-26T specification russianhelicopters.aero
The Mi-26MS is an upgraded model of the Mi-26T. The variant is a medical evacuation helicopter and comprises intensive care section for four casualties and two medics, ambulance section for five stretcher patients, three seated casualties and two attendants, and a laboratory.
The Mi-26NEF-M is another variant of Mi-26 fitted with a search radar below the nose radome. It is an anti-submarine warfare version, which boasts heat exchangers and towed MAD housing fitted on a ramp.
The Mi-26P is a passenger transport version, which can carry 70 to 100 passengers. The variant features airline-type seating, with a centre aisle, bathroom, kitchen and cloakroom near the flight deck.
Another variant, the Mi-26PP, is a radio relayed version with its first flight test completed in 1986. The Mi-26PK is derived from the Mi-26P. It is a flying crane helicopter introduced in 1997. The Mi-26S is a disaster relief version incorporated with a discharging liquid tank and underbelly spraying apparatus.
The Mi-26TP is a fire-fighting helicopter, which can distribute 17,260l of water from a squat VSU-15 bucket. It was first introduced in 1994.
Another variant, the Mi-26TS, is an export version of the Mi-26T supplied to Samsung Aerospace Industries, South Korea.
The Mi-26TZ is a fuel tanker version, while the Mi-27 is airborne command post variant.
Mi-26TZ fuel tanker version
 The Mi-26TZ is a specially adapted for transporting and filling fuel in the field – Документальные Фильмы
The Mi-26TZ is a specially adapted for transporting and filling fuel in the field – Документальные Фильмы
Type : special modification of the heavy-duty helicopter typeMi-26 ( Halo A ),serving as the role of a ground filling station
Determination : Fuel transmission to helicopters and front-combat combat airplanes and ground fighting techniques
Differences from the Mi-26 helicopter (Halo A) :
– installation of three removable modules, two with fuel tanks with a total capacity of 14,000 liters, a fuel pump and a control panel and one with four air fuel hoses, ten hoses on diesel and a fuel gauge inside the cargo compartment
 Refueling hoses – Документальные Фильмы
Refueling hoses – Документальные Фильмы
Manufactured : at least six serial machines
Users : Kazakhstan and Russia
Crew: two pilots, navigator and on-board mechanic
Drive: two turbo-shaft engines of the Progress D-136 type with a maximum power of 11,400 kp
Radar: weather station type 8A313 Groza , installed inside the hull spike
Equipment: SRO-1P identification system Parol-2D, warning system RL type SPO-15 (L006) Berjoza and six whirlpools of 32 misleading IR / RL targets of the ASO-2V type (three- installed on the sides of the central part of the fuselage, in the area above the main bogie)
Capacity: Tank with 14,000 liters of fuel and canisters 1,040 l of lubricants transported inside the cargo cabin with dimensions 12,08 mx 3,25 mx 2,91 m
Source ruslet.webnode.cz
Characteristic
Time necessary for conversion from refueling equipment version………….1h.25 min
From transport version to refueling equipment version………………………… 1h. 25 min
| Performance | |
|
Performance with refuel equipment of Mi-26 T in conformity with performance of standard Mi-26T |
|
| Capacity of transported fuel | 14.040 lt |
| Transported fuel aviation kerosene | T-2, TS-1, RT |
| Diesel | DL, DZ, DA grades |
| Transported lubricants (52 tanks of 20 liters each) | 1.040 lt |
| Fuel distribution rate with pressure from pump (3,8-4,0 kgf/cm2) on each hose | |
| With 4 hoses of aviation fuel | Up to 300 lt/min |
| With 10 hoses of diesel fuel | 50 ..150 lt/min |
| Fineness of filtration of distributed fuel | |
| Aviation | 5 μm |
| Diesel | 12 16 μm |
| Time of deployment for distribution to consumers | |
| Aviation fuel | 10 min |
| Diesel fuel | 15 min |
| Time for stowage | |
| Aviation fuel refueling equipment | 15 min |
| Diesel fuel refueling equipment | 25 min |
Source redstar.gr
Mi-26 helicopter upgrades for Defense Ministry
Holding “Helicopters of Russia” prepared a project for the modernization of the Mi-26 helicopter for Russian military aircraft. At present, the Rostvertol plant is already working on the creation of a prototype of the new Mi-26T2V with the subsequent implementation of a complex of flight tests.
As the general director of the holding “Russian Helicopters” Andrey Boginsky said, the machine will embody the latest technical solutions taking into account the use in combat operations. “I want to note that we are talking about the modernization of the military version of the Mi-26 rather than the Mi-26T2 helicopter, which is exported,” he said.
The modernized Mi-26T2V is a heavy wide-body transport helicopter with a carrying capacity of 20 tons. The number of crew members of the updated version remained the same – 5 people.
The new machine will be able to provide flights in the conditions of any region, including, with complex physico-geographical and unfavorable climatic conditions. Also, the helicopter will be able to be operated in conditions of unequipped trails and along routes outside the trails, over unoriented terrain, in conditions of fire and information counteraction of the enemy.
The machine is equipped with a modern integrated complex of on-board radio electronic equipment NPK90-2, which provides helicopter piloting day and night with automatic flight along the route, exit to a predetermined point and approach, as well as pre-landing maneuvering and return to the main or alternate aerodrome. The air defense system of the helicopter provides helicopter protection against missile damage with radio and opto-electronic guidance. Source rostec.ru DD 20 OCTOBER 2017
Mil Mi-26T2V
 Mi-26T2V – Rostvertol
Mi-26T2V – Rostvertol
Differences from the Mi-26 helicopter :
– installation of an automated flight-navigation complex type NPK-90-2 instead of the original navigation equipment (this reduced the number of crew members from four persons to two) – Pictures below of Mi-26T2V shows 4 crew stations
Mi-26T2V cockpit
– installation of modified interconnection equipment
– installation of new instrumentation inside the cockpit
– installing new impact-resistant seats inside the crew’s cabin
– installing new external lighting to allow the use of night vision glasses
 Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
– installation of the L370E26L Vitebsk Defense Complex, consisting of a L370-2-01 Warnetting Anti-Missile System (L370-2-01), a L370-5L directional intruder and 28 dummy targets. All of the components of the Vitebsk-type complex are located within two pairs of tandem-shaped conformal containers that are attached to the sides of the central part of the hull. While the front is just behind the front side entry door, the rear pair of Vitebsk-type complex containers is located directly above the main chassis. While the front containers contain a L370-5L type lane and one L370-2-01 (one for the front and rear half-sphere), two 14-meter dumbbells are built into the hind legs of each of the rear containers. Source ruslet.webnode.cz
L370E26L Vitebsk Defense Complex
 Mi-26T2V – Russian Helicopters
Mi-26T2V – Russian Helicopters
It is designed to protect aircraft from anti-aircraft missiles with infrared, radar or combined homing heads. “Vitebsk” is able to track the launch of missiles within a radius of several hundred kilometers from the aircraft and “take away” the missile from the target.
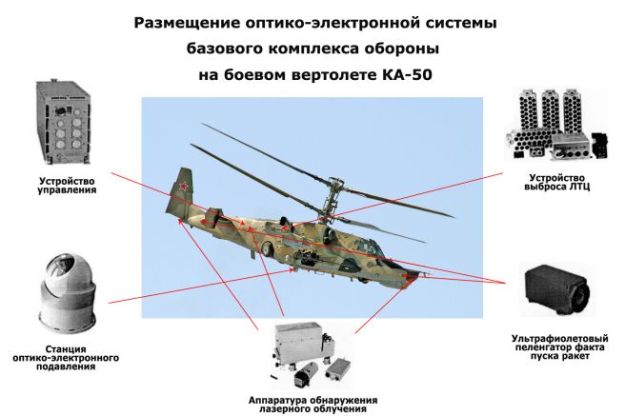
Structurally, the complex L-370 “Vitebsk” is made in the form of blocks that can be located inside the fuselage and on the outer hinges of the aircraft or helicopter. The main elements of the complex are laser radiation detection equipment, ultraviolet rocket launching direction finder, control system, opto-electronic suppression station and false thermal targets (LTC) devices. The known modifications of BKO-L-370B52 (for Ka-52), L-370E8 (for MI-8MT), L-370E26L (for MI-26), L-370E50 (for Ka-50).
 Vitebsk Defense Complex – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Vitebsk Defense Complex – Женя Вертолет YouTube
The main element of Vitebsk is the digital station for active interference (LSS) L-370-3S. It exceeds the Sorbtsiya (Su-27), Omul (Su-25), Gardenia (MiG-29) and suppresses the enemy radar in a wider frequency range. The complex includes a system of protection against missiles with a thermal homing head (TGSN), which blinds enemy missiles with a laser spotlight. Translated by google – ource arms-expo.ru
 L-370-3S
L-370-3S
Characteristic
| TTD: | |
| Ø carrier rotor: | 32,00 m |
| Ø tail rotor: | 7.61 m |
| Total length: | 40,03 m |
| Length of hull: | 33.73 m |
| Height: | 8.15 m |
| Empty weight: | ? |
| Max. takeoff weight: | 56 000 kg |
| Max. speed: | 295 km / h |
| Practical access: | 4 600 m |
| Max. range without / with 4 PTB: | 800/1 920 km |
Source ruslet.webnode.cz
Mi-26T2
 Mi-26T2 – Airguardian
Mi-26T2 – Airguardian
The Mi-26T2 is a modernisation of the Mi-26T heavy-lift transport helicopter designed by Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant, a division of Russian Helicopters.
The modernised helicopter is designed to transport heavy cargo and equipment. It can be used to quickly transport up to 82 troops and their equipment, as well as a wide range of heavy-weight combat vehicles.
 Телеканал Звезда
Телеканал Звезда
Preliminary flight tests were carried out in 2014 and serial production of the Mi-26T2 helicopter began in May 2015.
Rostvertol, which is part of Russian Helicopters, built the helicopter at its Rostov-on-Don factory.
 Mi-26 factory – T-24
Mi-26 factory – T-24
Avionics for the Mi-26T2 helicopter were developed by OJSC Ramenskoe Instrument Design Bureau (RKPB), a subsidiary of KRET.
The ambulance / emergency response variant of the Mi-26T2 helicopter can carry up to 60 wounded people. It can be configured to perform various other operations, including fire-fighting, fuel delivery, construction and installation works.
The helicopter can also provide self-contained refuelling to ground-based vehicles.
Mi-26T2 demonstration and orders
The helicopter was exhibited at the International Aviation and Space show MAKS 2011, HeliRussia 2011, and Dubai Airshow 2013. It entered the first stage of flight trials in 2011. It was demonstrated to the Algerian Armed Force in July 2012 and offered for the Indian Air Force in November 2012.
Russian Helicopters received an order to deliver six Mi-26T2s for the Algerian Air Force under a $2.7bn contract in March 2014. The first helicopter performed its maiden flight in December 2014.
 Mi-26T2 Algerian Air Force – Algeria Today
Mi-26T2 Algerian Air Force – Algeria Today
On June 26, 2013, the Algerian Air Force ordered a total of 6 Mi-26T2 helicopters. The first one (SL-21) was also the first serial specimen of the Mi-26T2 helicopter, and it was first released in the cloud on December 25, 2014. On February 11, 2015, the second series Mi-26T2 (SL-22 ). Upon completion of the tests, both of these Mi-26T2 helicopter specimens were used to train the flight and ground personnel of the customer. It was only then, on 8 July 2015, that they embarked on a trip from Rostov to Don to Algeria, respectively. at the base of Bild. The day arrived at the destination. But this was preceded by a stopover on one of the Greek islands. The other two Mi-26T2 series (SL-32 and SL-34) were flown in June and July 2015. Their handover was made before the end of the same year. Translated by google – source ruslet.webnode.cz
 Mi-26T2 Algerian Air Force – Algeria Today
Mi-26T2 Algerian Air Force – Algeria Today
Algeria ordered a second batch of eight Mi-26T2 helicopters in August 2015.
King Abdullah Design and Development Bureau placed an order with Russian Helicopters to deliver four Mi-26T2s for the Royal Jordanian Air Force, in April 2016. The first helicopter was delivered in January 2018.
Mi-26T2 transport helicopter design and features
The Mi-26T2 heavy-lift transport helicopter features new digital avionics suite and an upgraded engine. It is capable of executing missions during both day and night under all weather conditions.
 Mi-26T2 main landing gear – Телеканал Звезда
Mi-26T2 main landing gear – Телеканал Звезда
Attached to the helicopter is double-wheeled landing gear in a tricycle arrangement. Its main rotor system consists of eight blades, while the tail rotor system consists of five blades.
 Тамаз Мухашаврия YouTube
Тамаз Мухашаврия YouTube
The base variant is 12.1m long, 3.29m wide and 3.17m high. The helicopter has a cargo lifting capacity of 20t and accommodates the maximum weight of the cargo inside the cargo cabin or from an external sling, which is operated by a flight engineer.
Two members of crew operate the helicopter. A door on each side of the cabin facilitates easy entry and exit for the crew. It is fitted with a new air conditioning and cargo compartment heating systems.
 Первый канал
Первый канал Первый канал
Первый канал
Mi-26T2 cockpit
 Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
The Mi-26T2 heavy-lift transport helicopter features a glass cockpit fitted with an electronic display system of five liquid-crystal displays (LCDs), control panels, airborne computer, as well as standard and infrared (IR) lighting equipment.
 Mi-26T2 cockpit – wikipedia.org
Mi-26T2 cockpit – wikipedia.org
Additionally, a Tranzas TSL-1600 light can be installed to visually control external loads in night conditions. The cockpit can be optionally fitted with night vision goggles (NVG) based on the customer requirements.
 Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
Avionics suite onboard the Mi-26T2
The Mi-26T2 features a BREO-26 digital avionics suite to improve stability and control in all flight modes over unfamiliar terrains. The onboard avionics include NPK 90-2 flight and navigation system along with NAVSTAR / GLONASS, modern communications system, airborne flight recorder system, backup device system, and an on-board control system.
 Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
A round-the-clock gyro stabilised optoelectronic system is also fitted to provide increased surveillance capabilities.
The Mi-26T2 prototype has already been tested with the L370E26L Vitebsk self-protection suite, borrowed from the Ka-52 Alligator. The costly system integrates L370-2-01 Reagent missile approach warning sensors and directional IR jammer; the jamming effect is also being enhanced by pumping out IR flares from chaff/flare dispensers scabbed onto the fuselage sides.
 Mi-26T2 with Vitebsk self-protection – Тамаз Мухашаврия YouTube
Mi-26T2 with Vitebsk self-protection – Тамаз Мухашаврия YouTube
The Mi-26T2, in its baseline configuration, comes equipped with the all-new Russian-made BREO-26 digital avionics package, built around the KRET NPK90-2 flight-navigation avionics suite with a LINS-100RS laser inertial navigation system and an A737-1 satellite navigation receiver as well as the PKV-26D digital autopilot.
NPK-90-2 navigation equipment

The complex of on-board radio-electronic equipment NPK90-2 provides:
- round-the-clock piloting in simple and difficult weather conditions;
- automatic flight along the route with the provision of possible operational change of the flight route manually and by commands from ground control points of air traffic;
- continuous automatic determination of the position and motion of the helicopter;
- automatic determination of polar coordinates relative to radio beacons and their indication;
- exit to a predetermined point from a given direction, issuing information about the time of arrival at the intermediate (final) point of the route
- approach and pre-landing maneuvering in accordance with the landing scheme introduced for the aerodrome, including a repeated approach;
- return to the main and alternate aerodromes, as well as to landing areas for the shortest distance;
- providing information on flight parameters, operation of helicopter units and systems, tactical situation;
- display of an electronic map of the locality;
- information on the remaining path, traveled track, ground speed, instrument speed, track actual speed, and altitude flight barometric.
Source airwar.ru
LINS-100RS inertial system

LINS-100RS – has been designed according to Western and Russian standards.
LINS-100RS is a strapdown inertial-navigation system on base of ring laser gyros (RLG) and pendulous accelerometers.
LINS-100RS includes a SNS receiver installed into a monoblock (antenna assembly is included). The system has a mounting frame for providing accurate tie to coordinate system of aircraft. A monoblock case is a dust-moisture-proof design.
The system provides definition and output of flight/navigation para-meters, and is designed for new and upgraded aircraft and helicopters. Source inertech.ru
 Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
PKV-26D digital autopilot

An integrated navigation flight planning and communication system is also included in the package, as well as a precise auto hover system, digital map display, five MFI-10-7V multifunctional displays replacing a number of conventional ‘stem-gauge’ instruments.
 Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
Mi-26T2 – Первый канал
The other new avionics components are represented by the KS-26T2 communications suite, a 7A-813C weather radar and a GOES-series day/night observation turret (with gyro-stabilised infrared and TV-cameras).
Type 7A813C weather radar

It also features customer-selectable options such as night vision goggle-compatible interior and exterior lighting, a TSL-1600 searchlight, a Vitebsk self-protection suite and a SKY899 traffic collision avoidance system. Source airsoc.com
TSL-1600 searchlight
 TSL-1600 searchlight – connectingindustry.com
TSL-1600 searchlight – connectingindustry.com
TSL-1600 has high light characteristics, which makes it possible to effectively conduct search and rescue, rescue operations, patrol, investigative-search, security measures. The floodlight can also be used for nighttime photo and video shooting.
Functionality
The projector is designed for visually concealed and unconcealed aviation operations for various purposes, used in various climatic and meteorological conditions and in various areas above the earth’s and water surfaces (mountainous terrain, urban and rural areas, forests, water bodies). Search and lighting projector can be installed on a helicopter of any type with sufficient power of the generator and search and rescue aircraft. The TSL-1600 does not have its own controls and displays.For these purposes either a control panel or a set of switching and indicating elements on the aircraft or a combination thereof is used.
Another advantage of the TSL-1600 is that it can work in automated control mode, receiving commands from external controls (multi-function indicator TDS-84, FLIR, etc.). This function allows to keep or accompany the object of observation, regardless of the spatial position and speed of the aircraft.
Tactical and technical indicators
| Source of visible light | |
| Lamp Type | gas discharge xenon |
| Power | 1600 W |
| The power of light | 30 000 000 cd |
| Life time | up to 1000 hours |
| IR mode | |
| The spectral range | (800 ÷ 1200) nm |
| Beam divergence in narrow beam mode | 4 |
| Beam divergence in wide beam mode | 20 |
| Power Cardan Suspension | |
| Angle of rotation in azimuth | 350 ° (± 175 °) |
| Angle of rotation by elevation angle | + 10 ° (up) ÷ – 110 ° (downwards) |
| Angular velocity in azimuth | 0-40 ° per second |
| Angular velocity in slope | 0-40 ° per second |
| Searchlight as a whole | |
| Radiation spectrum | visible and infrared |
| Readiness time | 1 sec – for lighting the lamp |
| Input voltage | 27 V (24,0 ÷ 32,0) direct current |
| Input current | 65 A (nom.); 75 A (max.) |
| Dimensions: (L x W x H) | 418 mm x 425 mm x 427 mm |
| Total installation weight | 29 kg |
Source arms-expo.ru
SKY899 traffic collision avoidance system

- Self-calibrating antenna constantly maintains the bearing accuracy of tracked targets and offers the most precise traffic positioning information
- Verbal Intruder Positioning (VIP) announces range, bearing and relative altitude of intruder aircraft through the cockpit’s audio system
- Unmatched 5-Year Warranty
- “Look Up/Look Down” altitude display modes highlight specific layers of relative altitude range — useful during climbs, descents and takeoff
- Optional bottom mount antenna installation, useful for helicopter applications
- Integrates with Stormscope Lightning Detection Systems
- Economically fulfills TCAS I requirements for most aircraft
- 35-mile surveillance & display range
- Additional ARINC 429 EFIS output
- The preferred choice of OEM’s worldwide
Source sarasotaavionics.com
Mi-26T2 engine
 T24
T24
The Mi-26T2 heavy-lift transport helicopter is powered by two modernised, electronically controlled D-136-2 turbo-shaft gas turbine engines designed by Ivchenko-Progress and produced by Motor Sich.
The engine is equipped with full authority automatic control system of FADEC controls and generates 12,500hp of emergency power, while the maximum power rating is 11,650hp. Its engine delivers improved performance, even in hot climatic conditions.
 T24
T24
The helicopter has an operating range of approximately 800km and a maximum range 1,905km when fitted with auxiliary fuel tanks.
 T24
T24
2 x D-136-2 turbo-shaft gas turbine engines (Mi-26T2)

Source ivchenko-progress.com
 T24
T24 T-24
T-24 T24
T24
APU
 APU inlet Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
APU inlet Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube APU on Mi-26T – T24
APU on Mi-26T – T24 APU exhaust Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
APU exhaust Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube Plug for external APU source Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Plug for external APU source Mi-26T2V – Женя Вертолет YouTube
Characteristic Mi-26T2
| Modification | Mi-26T2 |
| Main screw diameter, m | 32.00 |
| Diameter of tail rotor, m | 7.61 |
| Length, m | 40. 03 |
| Height, m | 8.145 |
| Width, m | 3120 |
| Weight, kg | |
| empty | 28000 |
| normal take-off | 49600 |
| maximum take-off | 56,000 |
| engine’s type | 2 GTD ZMKB Progress D-136-2 |
| Power, hp | 2 x 11650 |
| Maximum speed, km / h | 290 |
| Cruising speed, km / h | 255 |
| Practical range, km | 2000 |
| Range of action, km | |
| with refueling of main fuel tanks | 800 |
| with refueling basic and add. fuel tanks | 1905 |
| Practical ceiling, m | 4600 |
| Static ceiling, m | 1 500 |
| Crew, people | 2 + 1 |
| Payload: | up to 120 passengers or 20000 kg of cargo in the cabin or on the suspension |
Source airwar.ru
Main material source airforce-technology.com
Images are from public domain unless otherwise stated
Main image Russian Helicopters
Updated Nov 11, 2020








Mil should look for increasing the Mi-26’s ceiling: it still flies into several ManPADS profiles while is not really fit for high mountains operations (Himalayas, Alps) where it could be really useful, it’s even a reason why India purchased CH-47 rather than more Mi-26
LikeLike