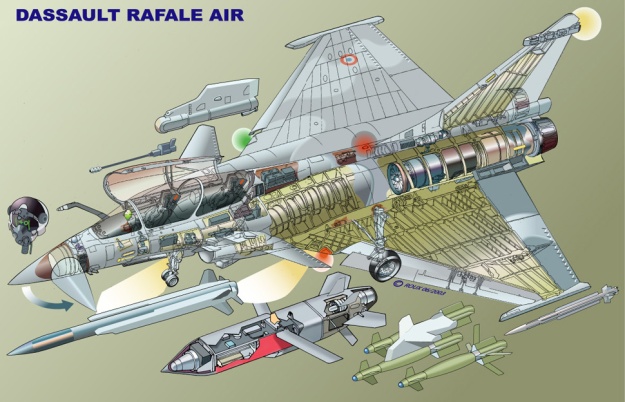
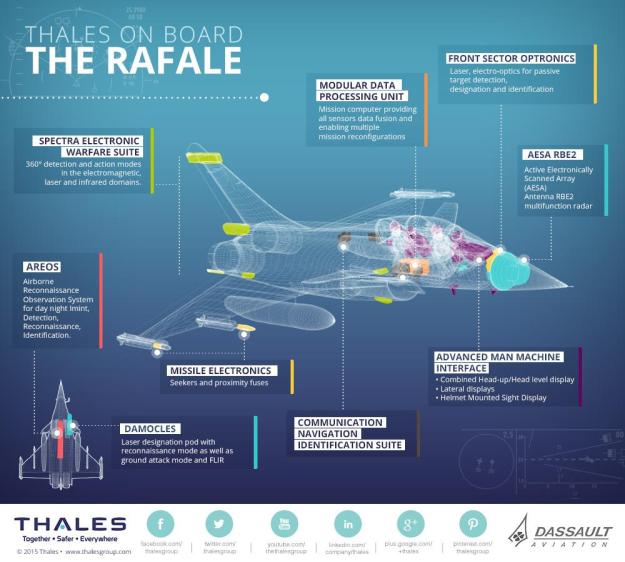
Rafale is a twin-jet combat aircraft capable of carrying out a wide range of short and long-range missions, including ground and sea attacks, reconnaissance, high-accuracy strikes and nuclear strike deterrence.
The aircraft were developed for the French Air Force and Navy. France’s Air Force and Navy ordered 180 (132 for the air force and 48 for the navy), 100 aircraft had been delivered by the end of 2010.
The Rafale entered service with the French Navy in 2004 and with the French Air Force in 2006. Ten aircraft are operational on the Charles de Gaulle aircraft carrier.
The State of Qatar signed a contract with Dassault Aviation to acquire 24 Rafale fighters in May 2015. The order value is estimated to be $7bn.

Rafale fighter aircraft development
Rafale B and C entered service with the French Air Force in June 2006, when the first squadron was established. The second air force squadron was set up in 2008. A €3.1bn ($3.89bn) contract to develop the fully capable F3 standard aircraft was awarded to Dassault Aviation (€1.5bn), Snecma (€600m), Thales (€500m) and other French contractors by the French Ministry of Defence in February 2004.
An order for 59 F3 aircraft, 47 for the air force (11 two-seat and 36 single-seat) and 12 (single-seat) for the navy, was placed in December 2004. The Rafale F3 was certified in July 2008. The contract also includes upgrades of the Rafale F2 aircraft.
The first Rafale F3 was delivered to the French Air Force in 2008. In March 2007, three French Air Force and three navy Rafale fighters were deployed in Tajikistan in support of the Nato International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in Afghanistan.
The French Government ordered 60 additional Rafale aircraft in November 2009. Brazil’s Government awarded a $4bn contract to Dassault Aviation in January 2010 to supply 36 Rafale multirole aircraft.

The UAE was expected to acquire the Rafale under a $10bn contract to replace its 60 ageing Mirage fighters. In November 2011, however, the deal came to a standstill when the UAE termed Dassault’s price and terms as “uncompetitive”. The country is also considering Eurofighter’s Typhoon to replace its ageing Mirage fighters.
In February 2012, the Indian Ministry of Defence selected Rafale for the Indian Air Force’s MMRCA (medium multirole combat aircraft) programme. The contract is worth approximately $20bn.
Rafale emerged as the preferred aircraft from among various contenders for what is being called the biggest military aviation contract in the world. Its closest contender was Eurofighter’s Typhoon.
Under the contract, Dassault will supply 126 Rafale fighters. The first 18 fighters will be supplied by 2015 and the rest will be manufactured in India under a technology transfer to Hindustan Aeronautics (HAL). This contract will be the first international supply for Rafale.
The Indian Government finalised a contract in April 2015 for the acquisition of 36 Rafale aircraft. Dassault Aviation signed a sales contract with the Arab Republic of Egypt in February 2015 for the supply of 24 Rafale fighter aircraft.
French MoD approves development of Rafale F4 standard: Here
RAFALE: TOWARDS STANDARD F4
Saint-Cloud, 22 March 2017 – On 20 March 2017, the French Minister for Defense, Mr. Jean-Yves Le Drian, authorized the start of development of the new RAFALE F4 standard.
Dassault Aviation and the 500 French companies associated with the RAFALE program wish to thank the French Ministry of Defense, the Defense procurement agency (DGA), the French Air Force and the Navy for their confidence.
The policy underpinning the RAFALE program is continuous development to adapt the aircraft to changing needs, through a succession of standards. As early as 2023, a first version of the F4 standard will follow the F3-R standard, scheduled for qualification in 2018.
“I am delighted by the Minister for Defense’s decision. The F4 standard will incorporate operational experience feedback and enable continuous improvement of the RAFALE to be maintained. It will reinforce the national skills and technological capabilities essential for preparing the development of the next generation of combat aircraft”, stated Eric Trappier, Chairman and CEO of Dassault Aviation. “I am also delighted that the Defense Ministry underlines the need to continue with acquisition of the RAFALE, beyond the 4th tranche currently in production, in order primarily to meet the needs of the French Air Force. Finally, this robust national foundation will constitute a launch pad for our aircraft in future export markets.” Source dassault-aviation.com
Qatari First Rafale Flight Testing: Here

Rafale’s F3R update on target after latest tests: Here

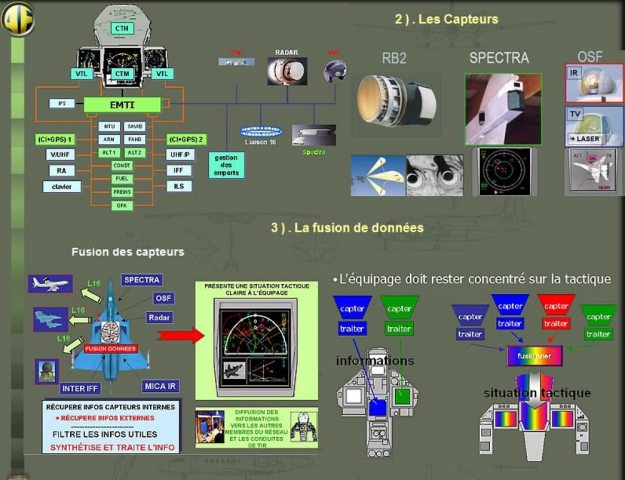
Data Fusion
The Rafale F3 not only integrates the largest and most modern range of sensors, it increases their efficiency through multi-sensor data fusion, allowing the aircraft to become a key element of a wider Network Centric Warfare system.
In this regard, Rafale crews, along with French Army Sperwer tactical UAV crews, this past winter developed a series of new procedures for launching the AASM rocket-bomb. The bomb is programmed in flight at the last moment from real-time reconnaissance coordinates of ground targets spotted by the Sperwer UAV flying at low altitude forward of a Rafale strike party.
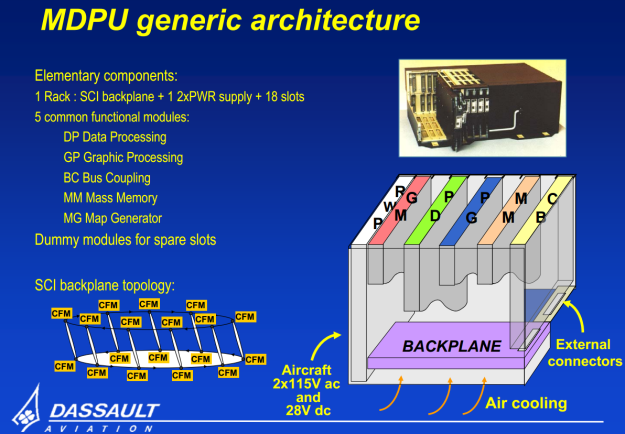
The data fusion process between all onboard sensors is the essential difference of the Rafale. The core of the enhanced capabilities lies in the Thales Modular Data Processing Unit (MDPU). According to Dassault Aviation, it has a processing power 50 times higher than that of the 2084 XRI-type computer fitted on the early versions of Mirage 2000-5. The MDPU is the cornerstone of the avionics/weapon upgradeability of the Rafale. Source aviationtoday.com
Thales Modular Data Processing Unit (MDPU)
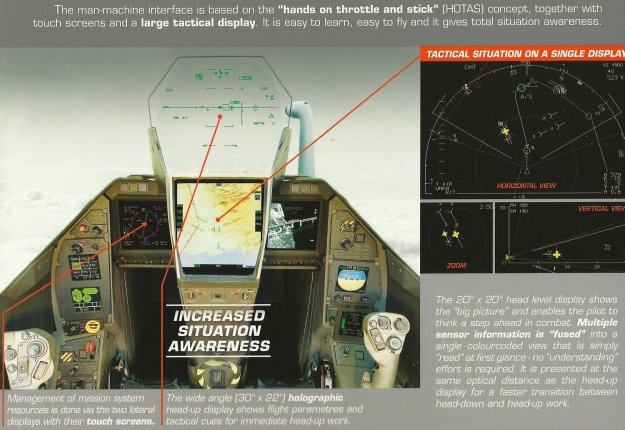
Cockpit of Dassault’s Rafale
The cockpit has hands-on throttle and stick control (HOTAS). The cockpit is equipped with a heads-up, wide-angle holographic display from Thales Avionique, which provides aircraft control data, mission data and firing cues.
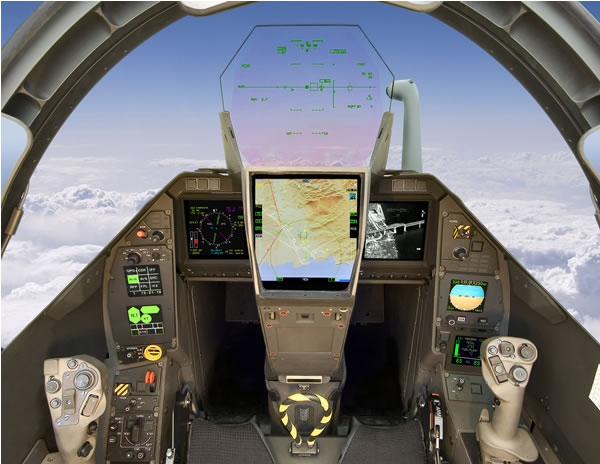

A collimated, multi-image head-level display presents tactical situation and sensor data, while two touch-screen lateral displays show the aircraft system parameters and mission data.
VEH 3022 (Viseur Electronique Holographique – Holographic Head-up Display)
 Image: thalesgroup.com
Image: thalesgroup.com
TMC 2020, head-level LCD display
 Image: thalesgroup.com
Image: thalesgroup.com
VEH 3022 HUD & TMC 2020 LCD display
 Image: rafalefan.e-monsite.com
Image: rafalefan.e-monsite.com
VTL55 display
 Image: thalesgroup.com
Image: thalesgroup.com
Display systems for Rafale
 Image: rafalefan.e-monsite.com
Image: rafalefan.e-monsite.com



The pilot also has a helmet-mounted sight and display. A CCD camera and on-board recorder records the image of the head-up display throughout the mission.
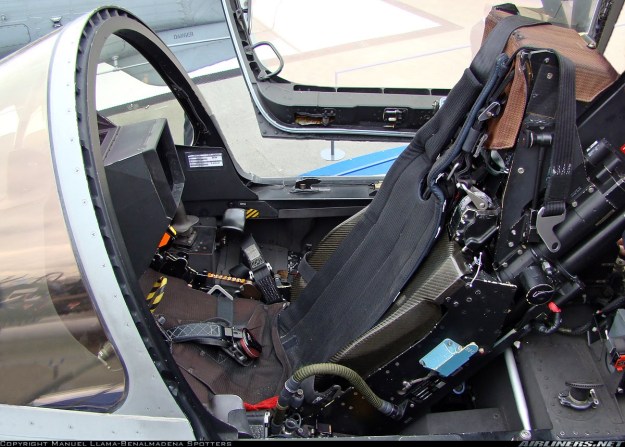

Martin-Baker Mark 16F “zero-zero” ejection seat
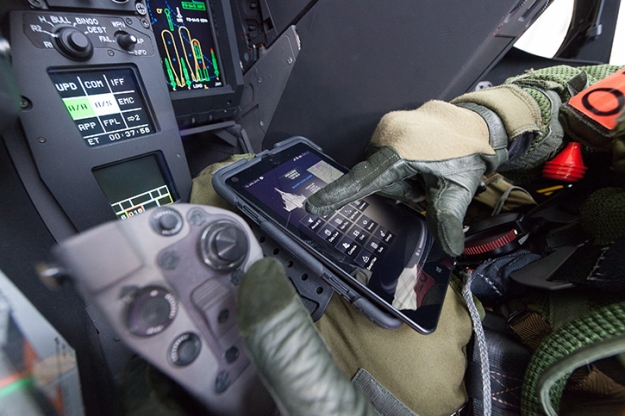
Fighter Sphere tablet
Rafale Pilot using the Fighter Sphere tablet. Sphere is an integrated Electronic Flight Bag (EFB) that greatly reduces pilot workload dealing with important but non-critical tasks during pre-flight and in flight. Photo: Dassault Aviation by P. Sagnes.
AN/AVS-9 Night Vision Goggles
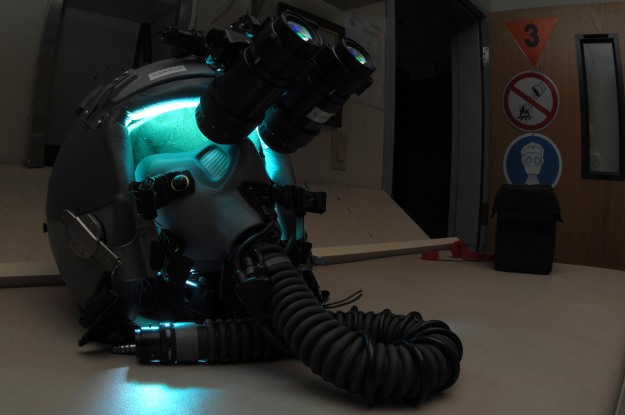

| General data: | |
| Type: Visual | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 27.8 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: LLTV, 2nd Generation (1980s/1990s) |
| Properties: Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) [Side Info], Classification [Class Info] / Brilliant Weapon [Automatic Target Aquisition], Continous Tracking Capability [Visual], LLTV / NVG / CCD (Night-Capable) / Searchlight [Visual Night-Capable] |
| Sensors / EW: |
| AN/AVS-9 Night Vision Goggles – Visual Role: LLTV, Night Vision Goggles (NVG) Max Range: 27.8 km |
Source cmano-db.com
JHMCS II –Targo HMD (Qatar Emiri Air Force (QEAF) )
- More Intelligent
- More Capable
- More Affordable
Both Digital JHMCS and JHMCS II share common design attributes that are new and improved over classic JHMCS. Both include new features and benefits that reinforce our market leadership standing.
 NOW WITH COLOR SYMBOLOGY
NOW WITH COLOR SYMBOLOGY
First
JHMCS was first in the market, first in combat. And now, the JHMCS II product line is the worlds first high definition HMD using smart-visor technology that operates in both day and night mode.
 NIGHT VISION SCENE WITH COLOR SYMBOLOGY
NIGHT VISION SCENE WITH COLOR SYMBOLOGY
Affordable
- The JHMCS II product line (both Digital JHMCS and JHMCS II) is based on the combat proven JHMCS and is now more affordable
- Both are priced to meet a broad range of market needs including reduced budget upgrades and new starts
Improved
- JHMCS II product line takes advantage of pioneering technology
- Digital image source replaces JHMCS Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
- No high voltage requirements
- Reduced routine maintenance
- Improved center of gravity provides greater pilot comfort, especially with NVGs
- No visor trimming
- Helmet borne electronics
- Virtual HUD option
- Embedded virtual training compatible
- Pilot Health Monitoring including hypoxia and G-LOC detection and warning
- Early pilot warning and aircraft recovery option
 DIGITAL JHMCS AND JHMCS II HMD
DIGITAL JHMCS AND JHMCS II HMD
Color
- Both versions in our product line utilize conformal color symbology to improve situational awareness
- Full color video imagery, FLIR and Picture-in-Picture
- Color de-brief camera
Advantage JHMCS
- More flight crews fly JHMCS around the world
- More crews have used JHMCS HMDs during combat operations
 EASY ATTACH, NIGHT VISION ADAPTOR
EASY ATTACH, NIGHT VISION ADAPTOR
Additional features and benefits
- The developers of JHMCS II have worked extensively with warfighters to create a system that improves situational awareness, provides improved comfort, better balance and easy day to night mode interchange.
- With nearly 6,000 systems sold and 15 years of experience, JHMCS based products have a heritage of superior safety achievement, testing, and qualification certifications.
- JHMCS II is fully interchangeable, retrofits perfectly with all components of JHMCS and is adaptable to any aircraft architecture.
- Improvements include Flat Panel Display, Video, No High Voltage, Higher Reliability, Better Balance and higher accuracy with the new Forward Fit Opto-Inertial Tracker.
- JHMCS II Can Be Pre-ordered Now.
- JHMCS II Has The Best Warranty And Service Support In The Industry.
Source jhmcsii.com
 © Swingwing / Defens’Aero – Visible ici en poste arrière, le viseur de casque vient d’effectuer ses premières heures de vol à bord du Rafale DQ01
© Swingwing / Defens’Aero – Visible ici en poste arrière, le viseur de casque vient d’effectuer ses premières heures de vol à bord du Rafale DQ01
Rafale F3 Avionics Suite
Today’s Rafale F3 features a fully integrated digital avionics suite with a modular core architecture. The modular data processing unit (MDPU), a mission computer comprising 18 processor modules, hosts software for most of the aircraft’s systems and forms the heart of the avionics suite.
Avionics integration is assured by linking the various systems via four to six Mil-Std-1553B databuses and one optical STANAG 3910 databus. Communication between the aircraft’s onboard systems and its weapons is enabled by a pair of Mil-Std-1760 databuses.
The Rafale’s navigation suite includes two Sagem SIGMA 95 laser gyro inertial navigation system (LINS) platforms with embedded hybrid NSS-100 GPS units. The LINS allows flight plans with up to 600 waypoints to be programmed and stored. Source aviationtoday.com

Sigma 95N Inertial Navigation System
Sigma 95N is a high-performance navigation system designed for most demanding aeronautic applications that require high navigation and guidance accuracy.
The Sigma 95N INS is based upon three highly accurate digital laser gyroscopes. It is equipped with a GPS or GPS/Glonass receiver and makes use of a powerful multimode Kalman filter to optimize performance by hybridizing inertial and satellite data. It can also integrate NATO’s new Selective Availability/Anti-Spoofing Module (SAASM) and in the close future, the Europe’s upcoming Gallileo system. Its open design and versatile interfaces multi-standard (Mil-Std-1553B, Arinc, Gost, etc.) allow easy integration in all types of avionic configurations and platforms.
Technical specifications
Overall features
- Dimensions: 209 x 200 x 385mm (8.2“ x 7.9“ x 15“)
- Weight < 15kg
- Power supply: 28 VDC, consumption < 45W (115 VAC / 400 Hz optional)
- MTBF >5,000 hours
Interfaces
- MIL-STD-1553 bus
- ARINC 429
- RS 422
- Analog and synchro (optional)
Performance
Pure inertial mode:
– Position: < 0.5 Nm/h
– Velocity: < 0.7 m/s
– Roll, pitch: < 0.03 °
– Heading: < 0.05 °
Hybrid mode:
– Position accuracy (SEP) < 10m
Source safran-electronics-defense.com

Additional navigation equipment includes the NC-12E TACAN radio navigation system, the TLS-2020 multimode receiver, which includes VOR and ILS/MLS functions, a digital map generator (DMG), a digital terrain reference navigation system, and the digital AHV 2930 radar altimeter, operational to 10,000 feet and optimized for discretion and high performance at very low altitudes. Source aviationtoday.com
NC-12E TACAN radio navigation system

NC 12 Airborne TACAN Interrogator
- Full package available with antennas, control box and DVT indicator
- Aft or fore connector configurations
- RF peak power: 500 W
- Power consumption: 28 VDC, < 25 W
- MTBF > 15,000 hours
- 3 MCU format
- Weight: 5 kg
- Air/Air range and bearing mode
Source thalesgroup.com
TLS-2020 multimode receiver
AHV 2930 radar altimeter
AHV 2930 for Fighters
- Range: 0 – 15,000 feet
- Accuracy: Sup (3 ft, 3 %)
- Interface: MIL-BUS-1553B
- Power supply: 28 VDC, 35 W
- Dimensions: 89x160x191 mm
- Weight < 2.8 kg
- Large beamwidth antennas
Source thalesgroup.com

Communications equipment comprises EAS TRA 2020 V/UHF radios for civil communication and secured TRA 6032 radios for tactical military communications. The aircraft additionally features the MIDS-LVT/Link 16 bi-directional data link terminal for secure and jam resistant near real-time communication and data exchange. The high-rate data link provides tactical data in combined air operations with other friendly assets, such as other aircraft in the formation, airborne and surface command and control centers and forward air controllers. NATO Link 16 as well as non-NATO solutions can be provided at the customer’s option. Source aviationtoday.com
TRA 2020 V/UHF radio for civil communication
TRA 2020 Airborne V/UHF AM Radio
- Output power selectable up to 15 W VHF/10 W UHF
- 118-156 MHz/225-400 MHz
- Size: 57.2x194x391 mm (2MCU/1/4 ATR)
- Weight: 4.7 kg
- COMSEC interface (KY58/KY100)
- Remote Control: 1553/ARINC 429
- Remote Control Unit (RCU)
- Guard receiver
- Fully digital design
Source thalesgroup.com
TRA 6032 radios for tactical military communications
TRA 6030-N Multi-purpose Airborne Terminal
- Full SDR architecture
- 15 W AM – 20 W FM; 30 – 600 MHz
- EPM high data rate 250 kbps (Growth > 750 kbps)
- Voice and data (L11, LY, L22, LX, LX16…)
- Optional PR4G F@stnet VHF EPM
- Synthetized guard receiver
- Embedded programmable COMSEC
- Size: 90.4x194x320.5 mm (3MCU)
- Weight =< 7.5 kg
- Remote Control: 1553/ARINC 429
- Remote Control Unit (RCU)
Source thalesgroup.com
Data Link Solutions for F-16 Tactical Communications

Link 16 is a standardized communications link for the transmission and exchange of real time tactical data among network participants (also known as TADIL J) and uses Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) to provide multiple, simultaneous communication paths through different nets.
Link 16 is the standard by which other systems are measured for airborne situational awareness. In fact, Link 16 has been credited by the U.S. Air Force as being a significant factor in saving lives in Afghanistan due to increased situational awareness provided by the system.
Compared to other communications link waveforms, Link 16:
- improves security
- improves jam resistance
- improves situational awareness
- increases data throughput
- increases capacity of information exchanged
- provides secure voice capability, relative navigation capability, and precise participant location and identification
Link 16 operates over-the-air in the L band portion (969 – 1206 MHz) of the UHF spectrum (excluding the 1030/1090 frequencies as these are used for IFF).
DLS has provided Link 16 terminals for 40 different platforms in 30 different countries plus various NATO organizations with product offerings that include:
- Multi-functional Information Distribution System (MIDS)
- Joint Tactical Information Distribution System (JTIDS) Class 2 family
- URC-138 Link 16 terminal
- Ancillary equipment
- Global Service and Support
DLS is also a leader in migrating MIDS technology to the Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS).
Source datalinksolutions.net
 Image: globalmilitarycommunications.com
Image: globalmilitarycommunications.com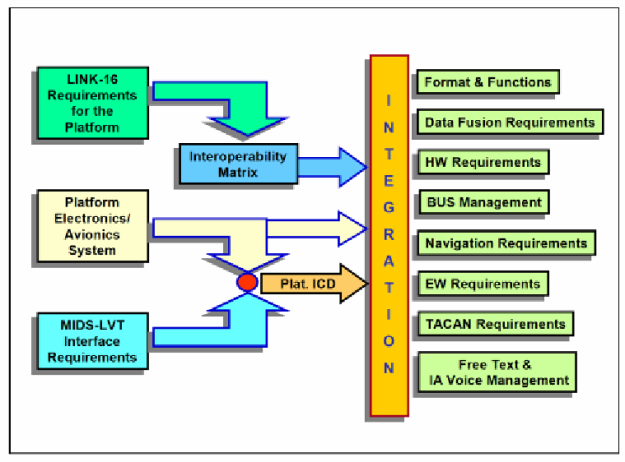 Image: researchgate.net
Image: researchgate.net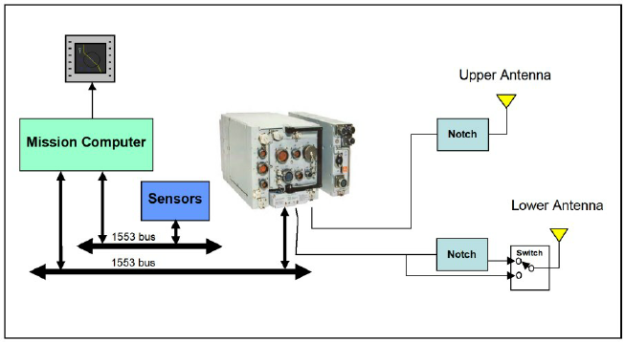 Image: researchgate.net
Image: researchgate.net
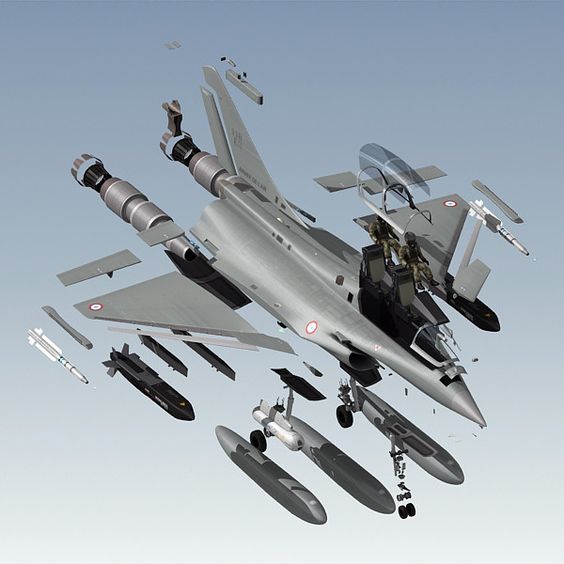
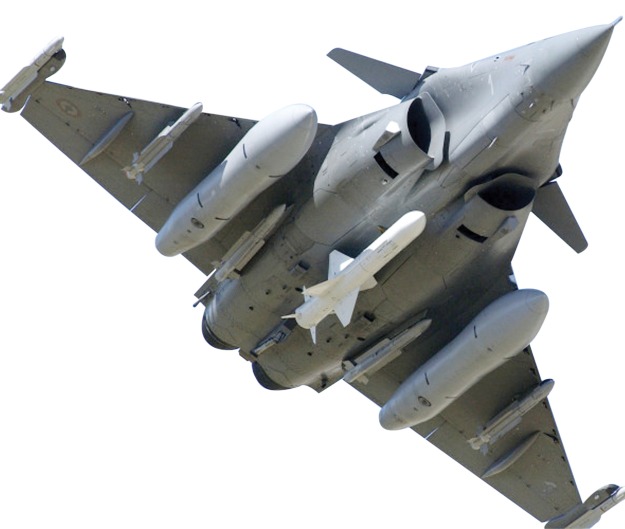
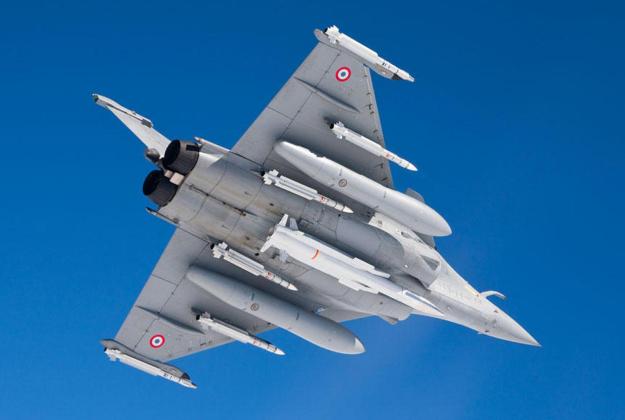
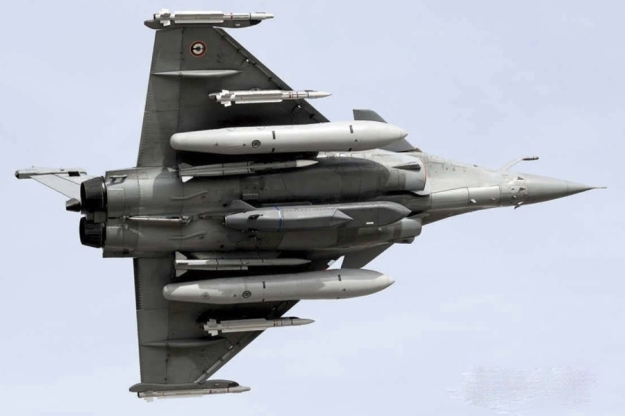
Rafale fighter weapons
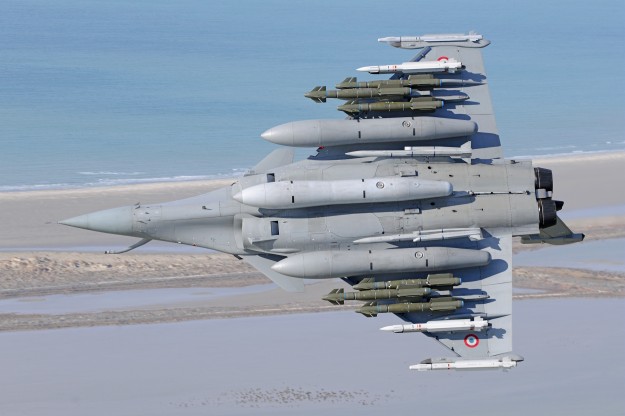

Rafale can carry payloads of more than 9t on 14 hardpoints for the air force version, with 13 for the naval version. The range of weapons includes: Mica, Magic, Sidewinder, ASRAAM and AMRAAM air-to-air missiles; Apache, AS30L, ALARM, HARM, Maverick and PGM100 air-to-ground missiles and Exocet / AM39, Penguin 3 and Harpoon anti-ship missiles.
MICA missile
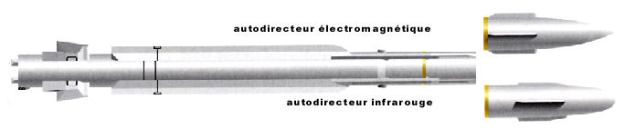
MICA is the multi-mission air-to-air missile system for the Rafale and the latest versions of Mirage 2000-5 combat aircraft. It has a high level of tactical flexibility in order to meet the most demanding operational requirements:
- Beyond Visual Range (BVR) multi-target / multi-shoot
- Enhanced Short Range (SR) performance
- Maximum flexibility for multi-role / swing-role aircraft
MICA has a totally dual role. It is able to cope with both BVR and SR combat situations and exhibits very high performance in both situations. The weapon covers Beyond Visual Range situations and in addition offers 2 guidance systems with its 2 interoperable seekers:
- RF MICA with radar seeker providing all weather shoot-up / shoot down capability
- IR MICA with dual waveband imaging infrared seeker surpassing latest generation AAM missiles.
MICA outperforms other BVR missiles with its unique stealthy interception capability provided by its silent seeker. Source mbda-systems.com
MICA EM

| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: Guided Weapon | Weight: 112 kg |
| Length: 3.1 m | Span: 0.56 m |
| Diameter: 0.17 | Generation: None |
| Properties: Home On Jam (HOJ), Anti-Air Dogfight (High Off-Boresight), Capable vs Seaskimmer, Level Cruise Flight |
| Targets: Aircraft, Missile |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| Active Radar Seeker – (AAM MR, MICA EM) Radar Weapon Seeker, Active Radar Max Range: 9.3 km |
| WEAPONS: |
|---|
| MICA EM – (2000) Guided Weapon Air Max: 83.3 km. |
Source cmano-db.com
MICA IR
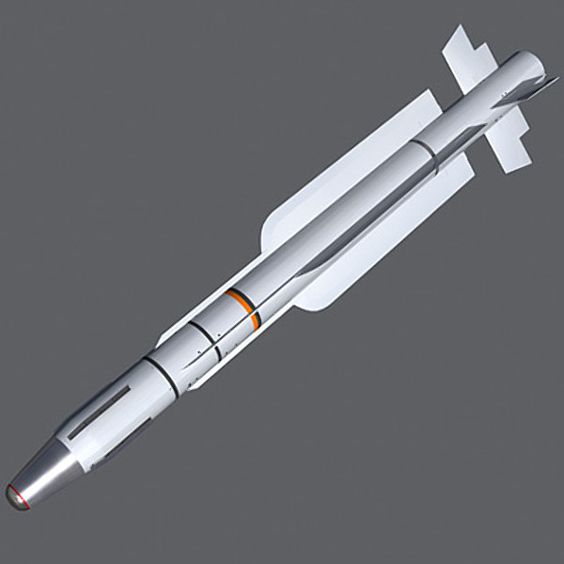

| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: Guided Weapon | Weight: 112 kg |
| Length: 3.1 m | Span: 0.56 m |
| Diameter: 0.17 | Generation: None |
| Properties: Anti-Air Dogfight (High Off-Boresight), Capable vs Seaskimmer |
| Targets: Aircraft, Missile |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| IR Seeker – (MICA) Infrared Weapon Seeker, Infrared, Dual Spectral IR Max Range: 18.5 km |
| WEAPONS: |
|---|
| MICA IR – Guided Weapon Air Max: 83.3 km. |
Source cmano-db.com
Magic 2 (R.550 Mk2)
 Image: kovy.free.fr
Image: kovy.free.fr
R.550 Mk2
- Manufacturer: Matra
- Release Date :1986
- Type : air-to-air short-range missiles
History
Second version, greatly improved.
Characteristics
- Length : 2750 mm (108 in)
- Diameter : 157 mm (6 in)
- Wingspan : 660 mm (26 in)
- Weight : 90 kg (198 lbs)
- Engine : fuel rocket engine solid SNPE Richard
- Maximum range : 10 km (6 mi 5 nm)
- Initial speed : Mach 2
- Guidance : Passive Infrared
- Load weight 12.5 kg (27.558 lbs)
- Payload : HE fragmentation
Source aviationsmilitaires.net
AIM-9 Sidewinder AAM
The F-16’s most characteristic weapon is the AIM-9 Sidewinder AAM, usually carried on the wingtip launch rails. Most US machines traditionally carried the AIM-9L/M all-aspect variants, but some foreign users have had to settle for the slightly less sophisticated AIM-9P-4 variant.
 Sidewinder AIM-9L/M
Sidewinder AIM-9L/M
Along with the Sidewinder, F-16 have also carried the medium-range AIM-7M Sparrow, though only a few nations acquired this weapon for the F-16, as well as the Sparrow’s follow-on, the AIM-120 AMRAAM. A few nations have qualified AAMs from other nations, such as the Israeli Rafael Python or French Matra Magic series of heatseeking AAMs, both in the same class as the Sidewinder.
The F-16 increasingly carries the AIM-9X AAM, and sometimes the comparable British “Advanced Short Range AAM (ASRAAM)”. Both of these are “off-boresight” AAMs, meaning they don’t have to be pointed directly at the target before launch. They are instead “cued” to the target by the pilot’s helmet-mounted sight. There are rumors that some foreign F-16s have been qualified for the new medium-range Matra MICA AAM. Source airvectors.net
ASRAAM air-to-air missile

The Advanced Short Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM) is a state of the art, highly manoeuvrable and combat effective weapon. Many combat aircraft are currently equipped with radar-guided AIM-120 AMRAAM for long range engagements and the AIM-9 Sidewinder for close combat. The two missiles are an ill-matched pair, since nearly four decades separates their origins. construction. While AMRAAM is highly effective at ranges between 5-50 kilometers, its usefulness diminishes rapidly at a shorter ranges.
A rival to the American-built AIM-9X Sidewinder, ASRAAM is equipped with a Raytheon-Hughes infrared seeker which is the baseline for the company’s AIM-9X seeker. The company developed an infrared seeker featuring a unique sapphire dome as part of an engineering-manufacturing-development and production effort valued at $215 million. This ASRAAM seeker played a part the company’s competitive win of the AIM-9X missile contract that could lead to some $5 billion in business over the next 20 years.

Manafacturer British Aerospace
Date Deployed 1998 ?
Range 8 nm ( 300 m to 15 km )
Speed Mach 3+
Propulsion One dual-thrust solid-propellant rocket motor
Guidance strapdown inertial and Imaging Infrared
Warhead 22.05 lb ( 10 kg ) blast/fragmentation
Launch Weight 220.5 lb ( 100 kg )
Length 8 ft, 11.5 in ( 2.73 m )
Diameter 6.6 in ( 0.168 m )
Fin Span 17.7 inches ( 45 cm )
Source fas.org
AIM-120C AMRAAM
 Raytheon AMRAAM AIM-120C missile
Raytheon AMRAAM AIM-120C missile
Apache Guided Weapon
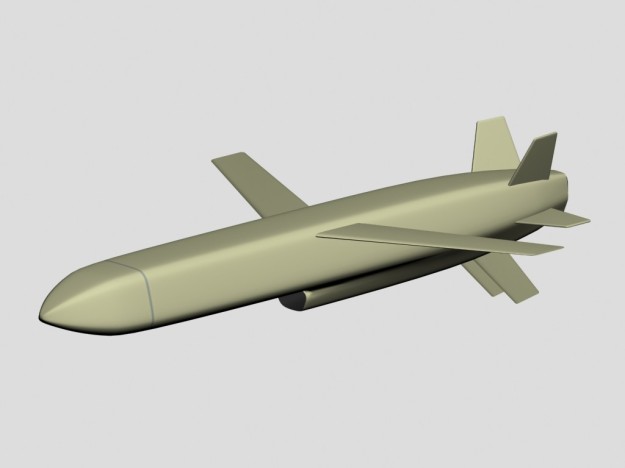

| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: Guided Weapon | Weight: 1230 kg |
| Length: 5.1 m | Span: 2.84 m |
| Diameter: 0.63 | Generation: None |
| Properties: Terrain Following, Weapon – INS w/ GPS Navigation, Weapon – Pre-Briefed Target Only, Level Cruise Flight |
| Targets: Runway |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| IIR Seeker – (Apache, Fixed Only) Infrared Weapon Seeker, Imaging IR Max Range: 18.5 km |
| WEAPONS: |
|---|
| Apache [10 x KRISS Runway Penetrators] – Guided Weapon Land Max: 138.9 km. |
Source cmano-db.com
MBDA AS30L

The AS-30L is a French short-to-medium range air-to-ground missile which employs laser homing guidance. The AS-30L is employed for attacking targets which require a high degree of precision to engage effectively, but are also potentially dangerous enough to necessitate a longer-distance “stand off” attack profile to reduce the danger to the aircraft and pilot to ground based anti-aircraft defences. The missile has a range of 3 to 11 kilometers, carries a 240 kilogram warhead, and claims a 1-meter CEP with either airborne or ground-based laser designators.
| SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| WEIGHT | 520 kg (1,146 lb) |
| LENGTH | 3.7 m (12 ft 1 in) |
| DIAMETER | 340mm (13 in) |
| WARHEAD | 240 kg (529 lb) impact-fuzed SAPHE (Semi-Armor-Piercing High-Explosive) |
|
DETONATION
MECHANISM |
Delayed AP impact fuse (2 m ferroconcrete) |
|
|
|
| ENGINE | Two-stage solid propellant rocket motors, composite booster, double-based sustainer |
| WINGSPAN | 1 m (3.2 ft) |
|
OPERATIONAL
RANGE |
Minimum range: 3 km (1.8 mi)Maximum range: 11 km (6.8 mi) |
| FLIGHT CEILING | 10,000 m (32,800 ft) |
| SPEED | 1,700 km/h (1,056 mph) |
|
GUIDANCE
SYSTEM |
semi-active laser homing |
|
LAUNCH
PLATFORM |
Mirage 2000D, Mirage 2000-5, F-16,Jaguar, Mirage F1, upgraded Super Etendard, Rafale |
Source wikipedia.org
ALARM anti-radiation missile

The ALARM is an anti-radiation missile of UK origin. It was designed for the suppression of enemy air defences. The name ALARM stands for Air Launched Anti-Radiation Missile. The ALARM was selected over the proven American AGM-88 HARM, partly because of its unique loitering capability. Today the ALARM remains one of the most capable anti-radiation missiles available.
As an air launched missile the ALARM has a conventional design. The seeker and warhead are housed in the nose and the engine makes up the rest of the missile. The unique feature in this missile its loitering mode. Aside from a direct attack pattern it may travel up to 13 km altitude and if the target radar shuts down it slowly descends using a parachute. When the target radar lights up again the secondary rocket motor is fired.
The ALARM uses as passive radar seeker. This allows it to autonomously home in on an enemy radar. Unlike the older generation of anti-radiation missiles the ALARM has a wide spectrum passive seeker. This means that it can be used against a wide range of radar systems without the need to select a specific seeker for a specific type of threat.
The ALARM is a modern anti-radiation missile with unique loitering capability. The ALARM can be recognized by the four small fins at the front and two sets of four fins at the rear.
ALARM 1: Original production model.
ALARM 2: Upgraded sensitivity for use against wider range of radars.

| Type | Anti-radiation missile |
| Diameter | 0.23 m body, 0.73 m wingspan |
| Length | 4.24 m |
| Weight | 268 kg |
| Guidance | Inertial, wide spectrum passive radar homing seeker |
| Warhead | HE-frag warhead with laser proximity fuze |
| Propulsion | Two-stage solid propellant rocket motor |
| Speed | 2.450 km/h max |
| Range | 93 km |
| Altitude | 13 km |
| Engagement envelope | – |
| Remarks | Parachute loitering ability |
Source weaponsystems.net
HARM missile
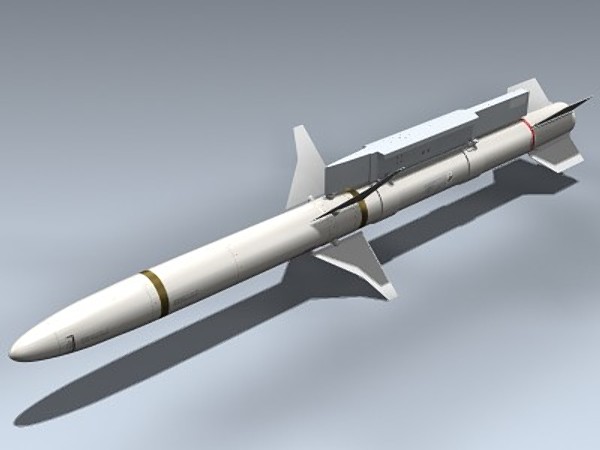 HARM missile
HARM missile
The AGM-88 HARM (high-speed antiradiation missile) is a supersonic air-to-surface tactical missile designed to seek and destroy enemy radar-equipped air defense systems. The AGM-88 can detect, attack and destroy a target with minimum aircrew input. Guidance is provided through reception of signals emitted from a ground-based threat radar. It has the capability of discriminating a single target from a number of emitters in the environment. The proportional guidance system that homes in on enemy radar emissions has a fixed antenna and seeker head in the missile nose. A smokeless, solid-propellant, dual-thrust rocket motor propels the missile. The Navy and Marine Corps F/A-18 and EA-6B have the capability to employ the AGM-88. With the retirement of the F-4, the F-16C is the only aircraft in the current Air Force inventory to use the AGM-88. The B version has an improved guidance section which incorporates an improved tactical software and electronically reprogrammable memory.
| Primary Function: | Air-to-surface anti-radiation missile |
| Mission | Defense suppression |
| Targets | Fixed soft |
| Service | Navy and Air Force |
| Contractor: | Raytheon [Texas Instruments] |
| Program status | Operational |
| Date Deployed: | 1984 |
| Power Plant: | Thiokol dual-thrust rocket motor |
| Thrust: | Dual thrust |
| Length: | 13 feet, 8 inches (4.14 meters) |
| Launch Weight: | 800 pounds (360 kilograms) |
| Diameter: | 10 inches (25.40 centimeters) |
| Wingspan: | 3 feet, 8 inches (101.60 centimeters) |
| Range: | 30 plus miles (48 plus kilometers) |
| Speed: | Max. speed: 2280 km/h |
| Guidance System: | Proportional |
| Guidance method | Homes on electronic emissions |
| Warhead | WAU-7/B, 143.51bs. Direct Fragmentation |
| Explosive (NEW) | PBXC-116 (45.2 lbs.) |
| Fuze | Pulsed Laser Proximity/Contact |
| Propulsion | Boost Sustain 64,000 lbs./sec. Low Smoke |
Source fas.org
MBDA AM39 Exocet anti-ship missile

The Exocet (French for “flying fish”) is a French anti-ship missile developed in the 1970s. While lacking in warhead size and range, this battle-tested missile is still in production.
This missile is an internally guided weapon. When it is about 12-15 kilometers from the target, it begins to utilize its active radar. The Exocet has a solid-fuel rocket motor. It can reach a top speed of Mach 0.9 (1 130 km/h).
The main advantage of the Exocet is its low flight altitude (generally 1-2 meters above the water). Due to this low altitude, this sea-skimming missile can often avoid detection until it is about 6 000 meters from the target, which leaves little time for launching surface-to-air missiles. Consequently, this missile has a good hit probability.
The Exocet is primarily useful against small warships like frigates and corvettes due to its small warhead size.
| Country of origin | France |
| Entered service | 1979 |
| Missile length | 4.7 m |
| Missile diameter | 0.35 mm |
| Wing span | 1 – 1.1 m |
| Launch weight | 670 kg |
| Warhead weight | 165 kg |
| Warhead type | Conventional |
| Range of fire | 42 – 180 km |
Source military-today.com
 Exocet on centerline
Exocet on centerline
Harpoon missile
 Boeing Harpoon
Boeing Harpoon
The Harpoon missile provides the Navy and the Air Force with a common missile for air, ship, and submarine launches. The weapon system uses mid-course guidance with a radar seeker to attack surface ships. Its low-level, sea-skimming cruise trajectory, active radar guidance and warhead design assure high survivability and effectiveness. The Harpoon missile and its launch control equipment provide the warfighter capability to interdict ships at ranges well beyond those of other aircraft.
The Harpoon missile was designed to sink warships in an open-ocean environment. Other weapons (such as the Standard and Tomahawk missiles) can be used against ships, but Harpoon and Penguin are the only missiles used by the United States military with anti-ship warfare as the primary mission. Once targeting information is obtained and sent to the Harpoon missile, it is fired. Once fired, the missile flys to the target location, turns on its seeker, locates the target and strikes it without further action from the firing platform. This allows the firing platform to engage other threats instead of concentrating on one at a time.
An appropriately configured HARPOON can be launched from an AERO-65 bomb rack, AERO-7/A bomb rack, MK 6 canister, MK 7 shock resistant canister, MK 12 thickwall canister, MK 112 ASROC launcher, MK 8 and MK 116 TARTAR launcher, or submarine torpedo tube launcher.
| Primary Function: | Air-to-surface anti-ship missile | |||
| Mission | Maritime ship attack | |||
| Targets | Maritime surface | |||
| Service | Navy and Air Force | |||
| Contractor: | Boeing [ex McDonnell Douglas] | |||
| Power Plant: | Teledyne Turbojet and solid propellant booster for surface and submarine launch | |||
| Program status | Operational | |||
| sea-launch | air-launch | SLAM | SLAM-ER | |
| First capability | 1977 | 1979 | ||
| Thrust: | 660 pounds | |||
| Length: | 15 feet (4.55 meters) |
12 feet, 7 inches (3.79 meters) |
14 feet, 8 inches (4.49 meters) |
|
| Weight: | 1,470 pounds (661.5 kilograms) |
1,145 pounds (515.25 kilograms) |
1,385 pounds (629.55 kilograms) |
|
| Diameter: | 13.5 inches (34.29 centimeters) | |||
| Wingspan: | 3 feet (91.44 centimeters) | |||
| Range: | Greater than 60 nautical miles | 150+ miles | ||
| Speed: | 855 km/h | |||
| Guidance System: | Sea-skimming cruise with mid-course guidance monitored by radar altimeter, active seeker radar terminal homing | inertial navigation system with GPS, infrared terminal guidance | ||
| Warheads: | Penetration high-explosive blast (488 pounds) | |||
| Explosive | Destex | |||
| Fuze | Contact | |||
Source fas.org
For a strategic mission the Rafale can deliver the MBDA (formerly Aerospatiale) ASMP stand-off nuclear missile. In December 2004, the MBDA Storm Shadow / Scalp EG stand-off cruise missile was qualified on the Rafale.
MBDA (formerly Aerospatiale) ASMP stand-off nuclear missile

The ASMP (Air-Sol Moyenne Portee, medium-range air-to-surface) is a ramjet powered, land attack cruise missile that carries a nuclear payload. The missile was developed from a competition between Matra’s turbojet proposal and Aerospatiale’s ramjet proposal (now MBDA). The ramjet version was chosen and full-scale development began in 1978. The goal was to replace the AN-22 nuclear bomb carried by the Mirage IV with a cruise missile that could penetrate air defenses and achieve a more credible deterrent vis-à-vis the Soviet Union. A longer range version, ASMP-A (Amelioreor Plus), has since been developed and became operational in October 2009. The ASMP is 5.38 m in length, .38 m in body diameter, and 860 kg in launch weight. The missile carries the TN-81, a 300 kT nuclear warhead with a 200 kg payload. The ASMP is an inertial-guided, air-to-surface missile guided most likely by terrain-mapping and an onboard computer which is programmed before launch. The motor assembly is comprised of a solid-propellant engine which fires after the missile has been released from the aircraft. Upon ignition, the missile accelerates to Mach 2.0 in five seconds after which the booster cartridge is ejected from the ramjet exhaust nozzle. Then, the liquid (kerosene) – powered ramjet motor takes over and accelerates to a maximum speed of Mach 3.0 depending on the altitude. The ASMP has a high altitude range of 300 km, and a low altitude range of 80 km.
The ASMP was deployed in 1986 by the French Air Force, and later in 1989 by the French Navy. A 150 missiles were reportedly scheduled for production, but reports indicate only 87 missiles were constructed.
 Rafale carrying ASMP missiles
Rafale carrying ASMP missiles
Originated From:France
Possessed By:France
Alternate Name:ASMP-A
Class:Supersonic
Basing:Air-to-surface
Length:5.38 m
Diameter:.38 m
Launch Weight:860 kg
Payload:200 kg
Warhead:TN-81, 300 kT nuclear
Propulsion:Ramjet
Range:300 km
Status:Operational
In Service:1986
Source missilethreat.com
In September 2005, the first flight of the MBDA Meteor BVRAAM beyond visual range air-to-air missile was conducted on a Rafale fighter. In December 2005, successful flight trials were carried out from the Charles de Gaulle of the range of Rafale’s weapon systems – Exocet, Scalp-EG, Mica, ASMP-A (to replace the ASMP) and Meteor missiles.
MBDA Meteor BVRAAM

Design of the Meteor missile system
The missile, being designed as a complete unit, requires no assembly and maintenance immediately before loading. This arrangement reduces its overall life logistic support cost.
Meteor can be launched as a stealth missile. It is equipped with enhanced kinematics features. It is capable of striking different types of targets simultaneously in almost any weather.
The Meteor has a length of 3.65m and diameter of 0.178m. It is designed to be compatible with AIM-120 type rail and eject launcher systems.
Meteor BVRAAM blast-fragmentation warhead
The Meteor missile is equipped with a blast-fragmentation warhead, supplied by TDW of Germany. The warhead is designed as a structural component of the missile. The missile integrates proximity and impact fuses.
Sensors on the beyond visual range air-to-air missile
The Meteor is equipped with a two way datalink, which allows the launch platform to provide updates on targets or re-targeting when the missile is in flight. The datalink is capable of transmitting information such as kinematic status. It also notifies target acquisition by the seeker.
The Meteor is installed with an active radar target seeker, offering high reliability in detection, tracking and classification of targets. The missile also integrates inertial measurement system (IMS) supplied by Litef.
Meteor missile performance
The missile has a range in excess of 100km. It is designed for a speed greater than Mach 4. The missile has a large no escape zone.

Propulsion system on the next generation missile
The Meteor missile is powered by a solid fuel variable flow ducted rocket (ramjet) supplied by Bayern-Chemie. The ramjet provides the Meteor missile with a capability to maintain consistent high speeds. This ability helps the missile to chase and destroy fast moving flexible targets.

The Meteor includes an electronics and propulsion control unit (EPCU). The EPCU adjusts the rocket’s air intake and duct covers based on the cruise speed and the target’s altitude.
The EPCU observes the distance and fuel level in the rocket and adjusts the throttle of the rocket. This feature of the EPCU helps the missile to manage its fuel system. Source airforce-technology.com

| SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| WEIGHT | 185 kg (407 lb) |
| LENGTH | 3.65 m (12 ft 0 in) |
| DIAMETER | 0.178 m (7.0 in) |
| WARHEAD | High explosive blast-fragmentation |
|
DETONATION
MECHANISM |
Proximity/impact fuse |
| ENGINE | Throttleable ducted rocket |
|
OPERATIONAL
RANGE |
100+ km(63mi, 60 km No Escape Zone)[3][4][N 1] |
| SPEED | over Mach 4 |
|
GUIDANCE
SYSTEM |
Inertial guidance, mid-course update via datalink, terminal active radar homing |
|
LAUNCH
PLATFORM |
Eurofighter Typhoon Dassault Rafale Saab JAS 39 Gripen F-35 (Pending) |
Specification wikiwand.com
MBDA Storm Shadow / SCALP

The Storm Shadow / SCALP is a long-range, air-launched, stand-off attack missile designed and developed by France-based MBDA Systems. The missile was developed primarily for the UK and French armed forces. It is derived from the MBDA Systems’ Apache anti-runway missile.
The missile is intended to strike high-valued stationary assets such as airbases, radar installations, communications hubs and port facilities. The Storm Shadow is capable of engaging the targets precisely in any weather conditions during day and night. The long range and low attitude combined with subsonic speed make the Storm Shadow a stealthy missile.
Storm Shadow guidance and navigation system
The Storm Shadow missile is designed to strike the targets with an enhanced accuracy, employing different navigation systems installed onboard.
The navigation system of the missile includes inertial navigation (INS), global positioning system (GPS) and terrain reference navigation for better control over the path and accurate target strike. The missile is fitted with a passive imaging infrared seeker.
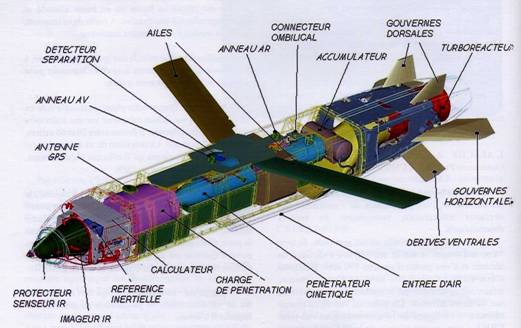 Image: tpe-rafale.e-monsite.com
Image: tpe-rafale.e-monsite.com
The Storm Shadow missile is programmed with each and every detail of the target and the path to be taken to reach the target prior to its launch. Once released from the aircraft, the missile follows a pre-programmed path at low level with the help of continuous updates from the onboard navigation system. It employs imaging infrared seeker to compare the actual target area with stored imagery repeatedly until reaching the target.
Storm Shadow warhead details
The missile is fitted with a two-stage bomb royal ordnance augmented charge (BROACH) blast/ penetrator warhead.
The first stage of the warhead makes the way for the second stage by cutting the surface of the target. The larger second stage (main) of the warhead then penetrates into the target and detonates.
Storm Shadow propulsion system
 Turbomeca Microturbo TRI 60-30 turbojet – Image: leteckemotory.cz
Turbomeca Microturbo TRI 60-30 turbojet – Image: leteckemotory.cz
The Storm Shadow missile is equipped with a Turbomeca Microturbo TRI 60-30 turbojet propulsion system, which can produce a 5.4kN of thrust. Source airforce-technology.com
Apart from extreme accuracy, the second element of Storm Shadow effectiveness is the sophisticated warhead it carries, the Bomb, Royal Ordnance, Augmenting CHarge (BROACH). BROACH uses a precursor penetrator charge followed by a follow through main charge. Combined with an advanced fuze (like Paveway IV, from Thales) it has proven to be devastatingly effective. Source thinkdefence.co.uk
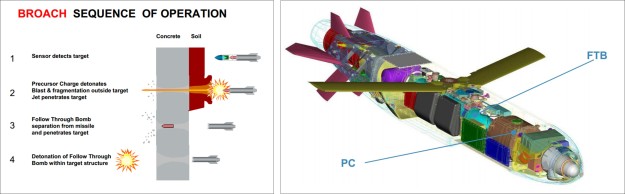 Image: thinkdefence.co.uk
Image: thinkdefence.co.uk
Technical data:
Originated From: France
Possessed By: France, United Kingdom, Italy, Greece, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Alternate Name: APACHE AP, SCALP EG, Storm Shadow, SCALP Naval, Black Shaheen
Class: Short Range Cruise Missile
Basing: air-, ship-, sub-launched
Length: 5.1 m (5.5 m for SCALP Naval)
Diameter: 630 mm
Launch Weight: 1,300 kg (1,230 kg for APACHE AP)
Warhead: 1 X 400 kg HE penetration
Propulsion: turbojet
Range: 140- 400 km
Status: Operational
In Service: 2004
| Variant | SCALP EG/Storm Shadow | |
| Range | 400 km | |
| Platform | Air-Launched | |
| Warhead | 1X400 kg HE penetration | |
| Diameter | 630 mm | |
| Launch Weight | 1,300 kg | |
| Countries Possessing Missile | France, Greece, Italy, Saudi Arabia, United Kingdom |
Technical data source missilethreat.csis.org
 Storm Shadow / SCALP on centerline, Meteor BVRAAM & MICA
Storm Shadow / SCALP on centerline, Meteor BVRAAM & MICA
BrahMos-NG project officially aims to arm the Indian Rafale
In April 2007, the Rafale carried out the first firing of the Sagem AASM precision-guided bomb, which has both GPS / inertial guidance and, optionally, imaging infrared terminal guidance. Rafale have been equipped with the AASM from 2008. Rafale can carry six AASM missiles, with each aiming to hit the target with 10m accuracy.
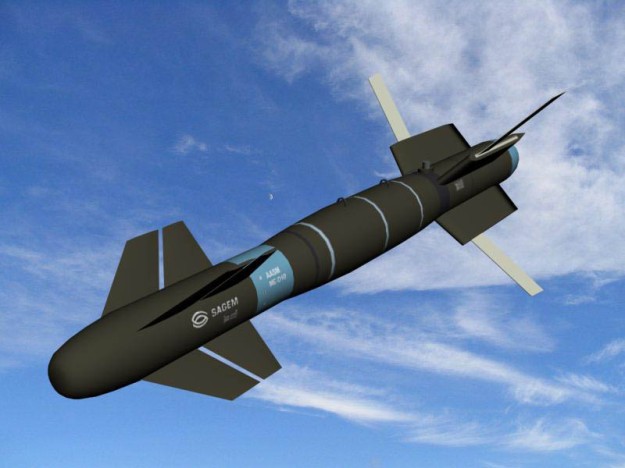
Sagem AASM precision-guided bomb (Armement Air-Sol Modulaire)
The Armement Air-Sol Modulaire (Air-to-Ground Modular Weapon) (AASM) “Hammer” is a French Precision-Guided Munition developed by Sagem Défense Sécurité. AASM comprises a frontal guidance kit and a rear-mounted range extension kit matched to a dumb bomb. The weapon is modular because it can integrate different types of guidance units and different types of bombs. The basic version features a 250-kilogram (550 lb) bomb plus hybrid inertial navigation system (INS) / Global Positioning System (GPS) guidance. Other variants add infrared homing or laser guidance to increase accuracy; there are also versions with 125-kilogram (276 lb), 500-kilogram (1,100 lb) or 1,000-kilogram (2,200 lb) bomb bodies.
 Sagem Défense Sécurité. AASM on both wing pylons
Sagem Défense Sécurité. AASM on both wing pylons
GBU-12 Paveway II

GBU-12 Paveway II laser-guided bomb Mk 82 500 lb (227 kg) bomb
GBU-22 Paveway III Mk 82
GBU-22 Paveway III Mk 82 500 lb (227 kg) laser-guided bomb
GBU-49 Paveway II laser-guided bomb BLU-133 500 lb
GBU-49 Paveway II laser-guided bomb BLU-133 500 lb (227 kg) bomb. Raytheon’s Enhanced dual-mode GPS and Laser guided version of the laser-only GBU-12
GBU-24 Paveway III – Mk 84/BLU-109
GBU-24 Paveway III – Mk 84/BLU-109 2,000 lb (907 kg) class laser-guided bomb
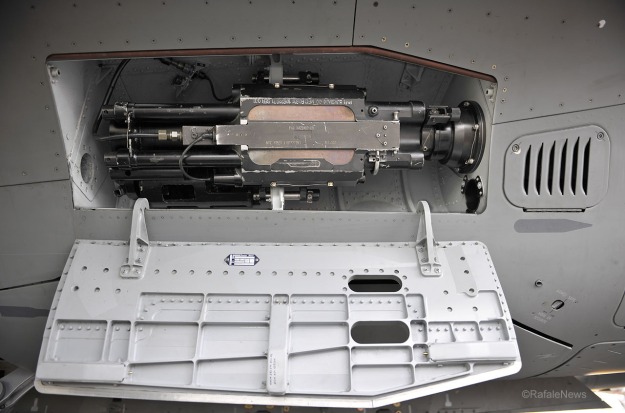
The Rafale has a twin gun pod and a Nexter (formerly Giat) 30mm DEFA 791B cannon, which can fire 2,500 rounds a minute. The Rafale is equipped with laser designation pods for laser guidance of air-to-ground missiles.
Nexter (formerly Giat) 30mm DEFA 791B cannon

The 30mm cannons model 781 and model 791 were designed to replace the models of the DEFA family, which equipped several French aircraft from the 60’s.
The family of cannons is genericamnete known as GIAT-30.
It is an electrically operated weapon.
The Model GIAT-30 M781 is designed for on-board installation of helicopters, but can also be installed on towers to equip armored vehicles.
The GIAT-30 M791 was adapted for use in fixed-wing combat aircraft. It was installed aboard the French fighter Rafale. Unlike the M781 version, it only fires in burst, although the burst speed is operator controllable and selectable between 300, 600, 1500 or 2,500 shots per minute
| Manufacturer: Giat Industries / NEXTER Main Function: Approximate air combat Caliber: 30mm |
|
| Cadence of fire: 750 rounds per min. | Surface Working Range: 0Km |
| Anti Air Reach: 0Km | Maximum elevation: 0º |
| Ammo weight: 0Kg | System weight: 65Kg |
| Number of cannons: 1 | Crew: 0 |
Translated by google – Source areamilitar.net
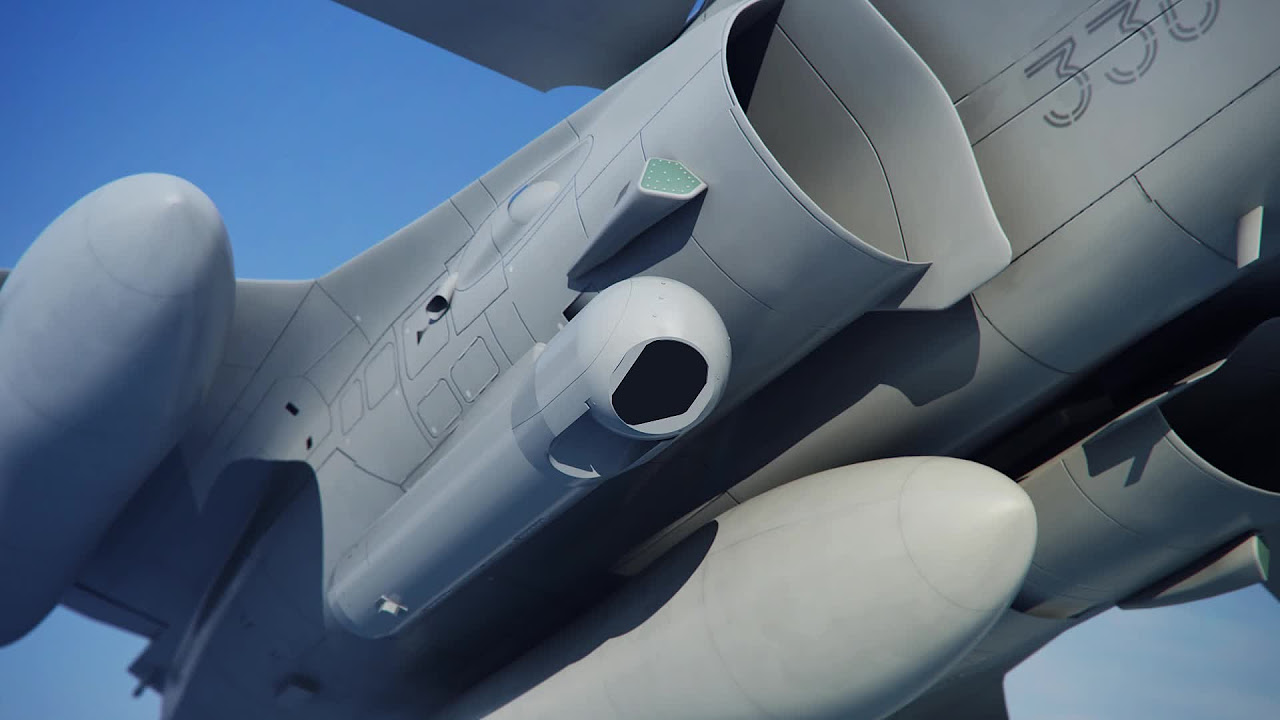
Countermeasure and sensor technology on the twin-jet combat aircraft

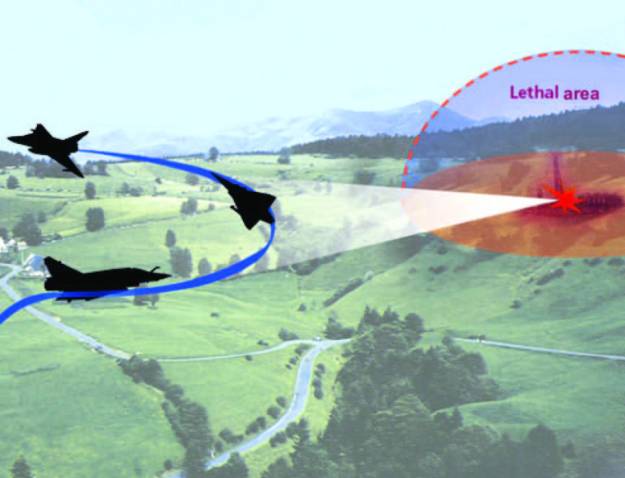
Rafale’s electronic warfare system is the Spectra from Thales. Spectra incorporates solid state transmitter technology, a DAL laser warning receiver, missile warning, detection systems and jammers.
The Rafale is equipped with an RBE2 passive electronically scanned radar developed by Thales, which has look-down and shoot-down capabilities. The radar can track up to eight targets simultaneously and provides threat identification and prioritisation.
Thales developed an active electronically scanned version of the RBE2 which equipped the Rafale in February 2011. Flight tests of the radar onboard the Rafale took place in 2008.
RUAG Aviation has been awarded a $5m contract by Thales in May 2009 to produce sub assemblies for the RBE2 radar to be equipped on the Rafale fighter jet.
Optronic systems include the Thales / SAGEM OSF infrared search and track system, installed in the nose of the aircraft. The optronic suite carries out search, target identification, telemetry and automatic target discrimination and tracking.
In January 2012, the French Ministry of Defence awarded a ten-year contract to Thales to maintain the electronic systems and warfare of the aircraft.
AESA Radar
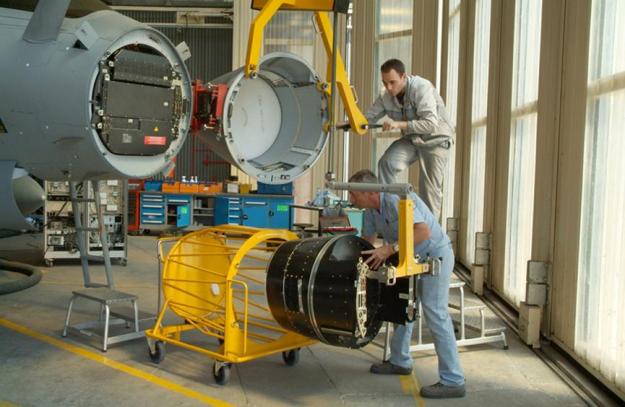
While the first 100 or so Rafales were fitted with the early Thales RBE2 radar, the most important sensor of the next generation Rafale will be the new Thales RBE2 AA active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar, which will replace the passive array of the RBE2.
Thales completed its first active phased array, comprising 1,000 gallium-arsenide Transmit/Receive modules, in 2006. In late April this year, the company said the RBE2 AA had successfully completed a new series of tests on Rafale, carried out jointly with the French DGA defense procurement agency, at the Cazaux flight-test center.
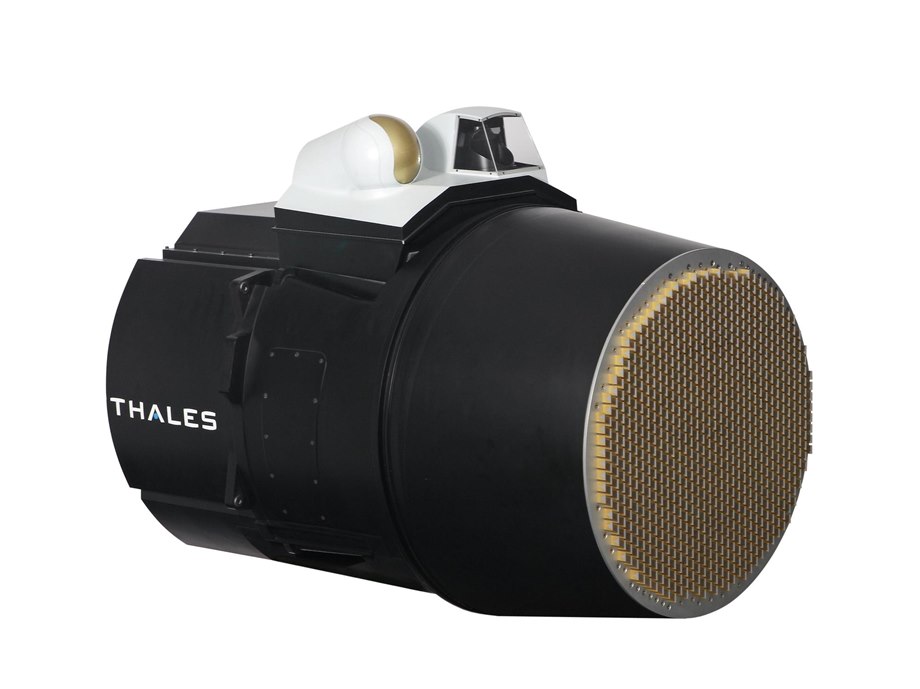
RBE2 AA active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar
 Thales RBE2 AA active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar
Thales RBE2 AA active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar
“This milestone marks the latest step toward qualifying the RBE2 AESA radars this year in readiness for delivery of the first two units to Dassault Aviation during the first quarter of 2010,” Thales stated. “The radars will be installed on the aircraft in 2011 for delivery to the French Air Force early in 2012.”
In operational terms, the RBE2 AA radar can track many targets in the radar field of view irrespective of the relative location between targets and/or the host aircraft. In addition, the radar provides a significant increase in detection range on enemy aircraft and a significant increase in reliability with respect to previous-generation radars.

Since the AESA radar antenna comprises a very large number of active modules, the failure of some of these modules has no noticeable effect on the overall performance and reliability of the system. Consequently, the active front end only requires maintenance every 10 years or more, thereby contributing to increased aircraft availability and reducing replacement part costs.
The RBE2 is a track while scan, monopulse-doppler X-band multimode fire-control radar system built around a modular concept. Air-to-air tracking and air-to-ground mapping functions can be interleaved due to the radar’s agile beam sweeping capabilities.
RBE-2AA AESA (LPI)
 Thales RBE2 AA radar
Thales RBE2 AA radar
| General data: | |
| Type: Radar | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 259.3 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0.2 km | Generation: Early 2010s |
| Properties: Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) [Side Info], Non-Coperative Target Recognition (NCTR) – Narrow Beam Interleaved Search and Track [Class Info], Continous Tracking Capability [Phased Array Radar], Track While Scan (TWS), Low Probability of Intercept (LPI), Pulse Doppler Radar (Full LDSD Capability), Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) |
| Sensors / EW: |
| RBE-2AA AESA – (LPI) Radar Role: Radar, FCR, Air-to-Air & Air-to-Surface, Medium-Range Max Range: 259.3 km |
Radar data cmano-db.com
Fitted in the aircraft’s pointed nose, the RBE2 provides +/- 60 degree azimuth and elevation coverage and includes the SB-25A MkXII compatible IFF interrogator/transponder with Mode S capability. The IFF system uses phased array antennas just like the Spectra active electronic countermeasures (ECM) antennas.
The present radar air-to-air modes include long-range search; multi target track and engagement; air combat modes; Non-Cooperative Target Recognition (NCTR); and look down/shoot down functions. In air-to-air mode, the RBE2 gives a tracking range beyond 60 nautical miles against a 30-square-foot target, with detection ranges up to 75 nautical miles. The radar can track and prioritize up to 40 targets simultaneously and engage up to eight with Mica, and soon Meteor, air-to-air missiles.
The RBE2 air-to-ground modes include: Doppler Beam Sharpening (DBS) mapping; SAR mapping; Fixed Target Track (FTT); Sea Surface Search and Track While Scan; Ground Moving Target Identification and Track (GMTI/T); target acquisition and air-to-ground ranging. Terrain following and avoidance modes can be combined to generate 3-D radar maps, thus enabling full automatic terrain following flights using the radar only.

The Rafale also can rely on several other sensors:
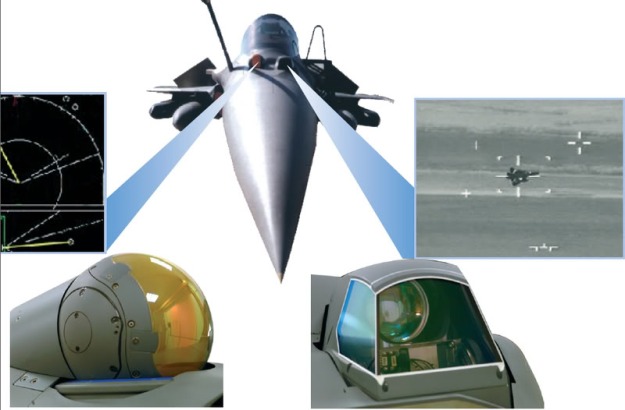
- Front-Sector Optronics (or OSF for optronique secteur frontal) system, developed by Thales (for TV) and Sagem (IR). Integrated over the aircraft’s nose in the form of a double ball, it can operate in the optronic wavelengths and provide long-distance tracking in the full passive mode. It is immune to radar jamming and provides covert long-range detection and identification, high resolution angular tracking and laser range-finding for air, sea and ground targets.
- Spectra EW system, developed by Thales and MBDA, provides a multi-spectral threat warning capability against hostile radars, missiles and lasers. According to test pilots who have flown the Rafale, the EW system provides the aircraft with the highest survivability assets against airborne and ground threats to date. It also provides passive, 360-degree tactical situation awareness.
Source aviationtoday.com
Front-Sector Optronics

Developed by Safran Electronics & Defense, the IRST (Infra Red Search and Track) are IR passive surveillance systems designed for automatic multiple target detection and tracking on combat aircraft. Unlike radars, they are totally passive, insensitive to jamming and guarantee absolute discretion for airborne missions. For example, Safran has developed the IR Search and Track channel of the Front Sector Optronics equipping the Rafale. The IR Search and Track channel uses sophisticated processing algorithms for the automatic detection and tracking of airborne threats and targets on the ground.
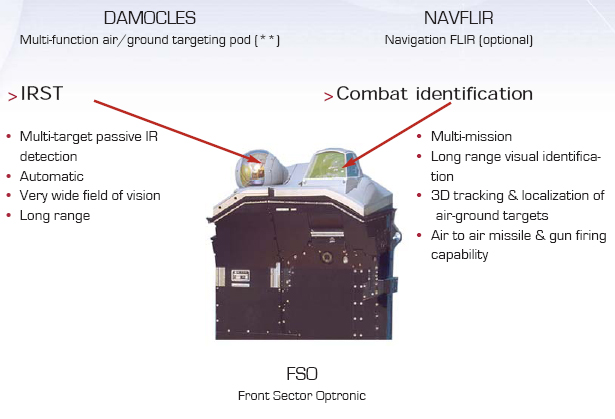
IR Search & Track systems for combat aircraft
The “front sector optronics” (FSO) system is a passive electro-optical sensor developed for the Rafale multirole fighter. Safran Electronics & Defense is responsible for the infrared search & track (IRST) and forward-looking infrared (FLIR) part of the FSO, while Thales provides the daytime video channel and laser rangefinder. Using those two optronic channels, the FSO provides day/night, long-range detection, recognition and identification of air, sea and land targets. The FSO does not emit any radiation and is insensitive to jamming. Fully integrated in the aircraft’s nav-attack system, it provides tactical information and target engagement.
Its infrared capacities are essential during night flights, in particular for long-range target recognition. Source safran-electronics-defense.com
OSF-IT [FLIR / IRST] (Rafale F3R Re-Introduction, FSO-IT)

| General data: | |
| Type: Infrared | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 185.2 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Infrared, 3rd Generation Imaging (2000s/2010s, Impr LANTIRN, Litening II/III, ATFLIR) |
| Properties: Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) [Side Info], Classification [Class Info] / Brilliant Weapon [Automatic Target Aquisition], Continous Tracking Capability [Visual] |
| Sensors / EW: |
| OSF-IT [FLIR / IRST] – (Rafale F3R Re-Introduction, FSO-IT) Infrared Role: Infrared, Navigation / Attack FLIR & Air-to-Air Tracking Max Range: 185.2 km |
OSF-IT [Laser Rangefinder]
| General data: | |
| Type: Laser Rangefinder | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 7.4 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Not Applicable (N/A) |
| Sensors / EW: |
| OSF-IT [Laser Rangefinder] – Laser Rangefinder Role: Laser Rangefinder Max Range: 7.4 km |
OSF-IT [CCD] (Rafale, FSO-IT)
| General data: | |
| Type: Visual | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 55.6 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: LLTV, 3rd Generation (2000s/2010s) |
| Properties: Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) [Side Info], Classification [Class Info] / Brilliant Weapon [Automatic Target Aquisition], Continous Tracking Capability [Visual], LLTV / NVG / CCD (Night-Capable) / Searchlight [Visual Night-Capable] |
| Sensors / EW: |
| OSF-IT [CCD] – (Rafale, FSO-IT) Visual Role: LLTV, Attack Max Range: 55.6 km |
Source cmano-db.com
Spectra EW system
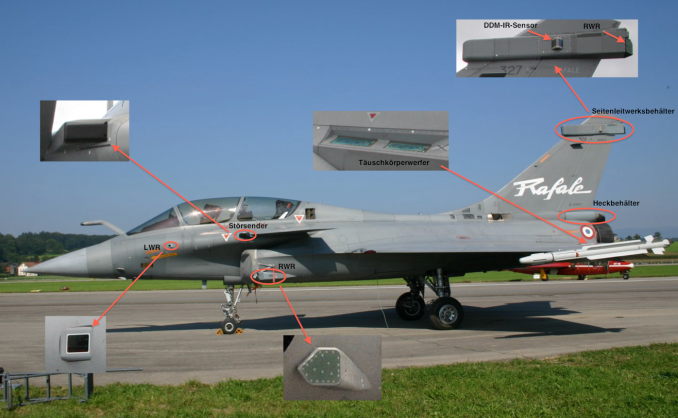 Integrated defensive-aids system named SPECTRA, which protects the aircraft against airborne and ground threats
Integrated defensive-aids system named SPECTRA, which protects the aircraft against airborne and ground threats
SPECTRA [RWR/ELINT, F3.4 Std]
| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: ESM | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 222.2 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Early 2010s |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| SPECTRA [RWR/ELINT, F3.4 Std] – ESM Role: ELINT Max Range: 222.2 km |
Source cmano-db.com
| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: Infrared | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 27.8 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Late 2000s |
| Properties: Continous Tracking Capability [Visual] |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| DDM-NG – (2013, Rafale F3) Infrared Role: MAWS, Missile Approach Warning System & Infrared Spherical Situational Awareness Max Range: 27.8 km |
Source cmano-db.com
SPECTRA [LWR, F3.4 Std]
| GENERAL DATA: | |
|---|---|
| Type: ESM | Altitude Max: 0 m |
| Range Max: 11.1 km | Altitude Min: 0 m |
| Range Min: 0 km | Generation: Early 2010s |
| SENSORS / EW: |
|---|
| SPECTRA [LWR, F3.4 Std] – ESM Role: LWR, Laser Warning Receiver Max Range: 11.1 km |
Source cmano-db.co
Additional Sensors
For conventional strike and reconnaissance, the Rafale F3 can be fitted with the Thales Damocles optronic multifunction pod or the Areos stand-off optronic reconnaissance system.
Damocles is a multi-function optronic pod comparable to American or Israeli-designed podded systems. Its laser designation function enables full day and night laser-guided weapons capability. The IR sensor of the Damocles operates in the mid-wave infrared band, allowing it to retain its effectiveness in warm and/or humid conditions. It is interoperable with all existing laser-guided weapons and provides outstanding performance for long-distance recognition.
Equipped with an embedded digital recorder, the Damocles pod provides a tactical reconnaissance capacity with post-flight images analysis. A FLIR navigation module is part of the pod. It provides an infrared image superimposed on the pilot’s display combined with the data supplied by the navigation and weapon system.
Areos, or Reco NG in French parlance, is a full imagery intelligence (IMINT) system composed of an airborne pod and a ground station.
The Rafale already is combat proven. Today, French Air Force Rafales daily fly from Kandahar, Afghanistan, in support of ISAF and Afghan National Army operations against Taliban rebels. The aircraft is being used to deliver AASM and Paveway II bombs, or to perform 30mm gun passes during missions in support of the Afghan army, French troops and NATO allies. Source aviationtoday.com
DAMOCLES – Multi-function Targeting pod
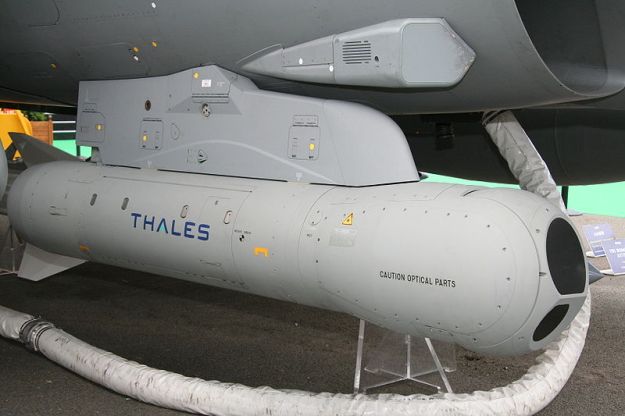

Multi-function pod with a laser designation function to provide a day/night smart weapons guidance capability as well as a full suite of sensors for navigation and airto-
air target identification roles.
Currently in service, combat proven and integrated on Mirage 2000, Mirage F1, RAFALE, SEM, SU-30, Tornado and Typhoon.
Air-to-Ground
- Compatible with laser guided weapons, INS/GPS guided missiles and imagery-guided weapons
- Attacks in autonomous or cooperative mode, using integrated laser spot tracker and laser marker
- Long range damage assessment capability
- Target recognition capability
- 3D localisation
- Integrated navigation FLIR
Reconnaissance
- Medium range day/night small targets reconnaissance Air-to-Air
- Day/night visual airborne target identification
KEY FEATURES
- Powerful laser and high resolution imagery provide the aircraft with a stand-off range and tactical ground/air defence system survivability
- Advanced technology featuring state-of-the-art staring array detector effective at long range
- Robust new generation tracking systems
- Superior image processing
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Imagery
- 3rd generation detector
- Spectral band: 3-5 μm
- Field of View:
– Wide FoV: 4° x 3°
– Narrow FoV: 1° x 0.75°
– Electronic magnification: x2
Laser range-finding
- Wavelength: 1.5 μm
- Eye-safe
Laser designation
- Wavelength: 1.06 μm
- STANAG 3733
Laser spot tracker
- Wavelength: 1.06 μm
Laser marker
- Wavelength: 0.8 μm
 DAMOCLES – Multi-function Targeting pod – Image: thalesgroup.com
DAMOCLES – Multi-function Targeting pod – Image: thalesgroup.com
TALIOS multifunction targeting pod
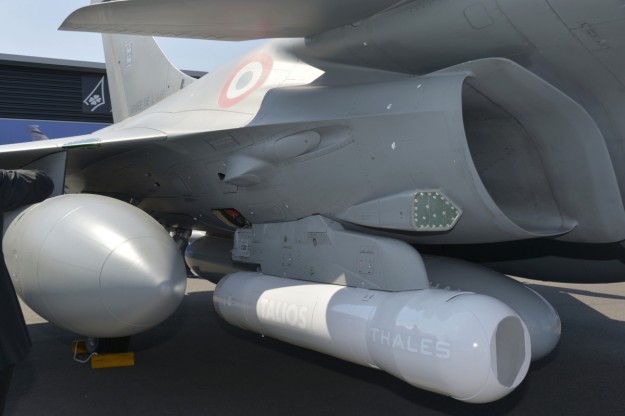

Designed entirely around operational feedback from users, TALIOS is the latest addition to the Thales family. TALIOS is the first optronic pod to cover the entire critical decision chain from intelligence gathering to weapon delivery.
Capabilities range from deep strike with long-range missiles and bombs to air-to-air target identification and close air support, and include the rapidly emerging requirement of Non-Traditional Information, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (NTISR).

Key features
- Latest generation of high-resolution sensors and high-precision line-of-sight stabilization
- Wide-angle vision providing critical contextual information and making the pod a key component of the pilot’s visual environment throughout the mission.
- Open architecture and a high level of functional integration
All functions will be standard for both French and international customers. With its open architecture, the TALIOS pod is conceived as a ‘plug & fight’ system for integration on all existing and future fighters. Source thalesgroup.com
AREOS Reco NG pod

AREOS (Airborne Recce Observation System) is a stand-off reconnaissance system designed for tactical and strategic missions. It provides a unique day/night imagery intelligence (IMINT) capability for detection, reconnaissance and identification at stand-off ranges, as well as very low altitudes and high speeds, under any weather conditions.
Composed of an airborne pod and a ground/shipboard station, AREOS combines state-of-the-art imaging technologies with high-performance datalinks. These advanced functions save precious time in the sensor-to-shooter loop to quickly meet evolving mission demands, including the new requirements of peace-keeping operations.
Combat-proven with the French Air Force and Navy on board the Rafale F3, the system is fully compliant with NATO standards for integration into large-scale C4ISR systems and coalition operations. Source thalesgroup.com
Lockheed Martin’ Sniper pod (AN/AAQ-33) (Qatar Emiri Air Force (QEAF))
 Lockheed Martin’s Sniper ATP (Advanced Targeting Pod) Picture: Lockheed Martin – Image: navyrecognition.com
Lockheed Martin’s Sniper ATP (Advanced Targeting Pod) Picture: Lockheed Martin – Image: navyrecognition.com
Mission
Sniper pods provide improved long-range target detection/identification and continuous stabilized surveillance for all missions, including close air support of ground forces. The Sniper pod enables aircrews to detect and identify weapon caches and individuals carrying armaments, all outside jet noise ranges. Superior imagery, a video datalink and J-series-weapons-quality coordinates provided by the Sniper pod enable rapid target decisions and keep aircrews out of threat ranges.
High resolution imagery for non-traditional intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (NTISR) enables the Sniper pod to play a major role in Air Force operations in theater, providing top cover for ground forces, as well as increasing the safety of civilian populations.
The Sniper pod is combat proven on U.S. Air Force and international F-15E, F-16 (all blocks), B-1, A-10C, Harrier GR7/9 and CF-18 aircraft. Lockheed Martin is also in the final stages of integrating the Sniper pod on the B-52. The pod’s plug-and-play capability facilitates moving the pod across platforms without changing software.
Features
Sniper pods include a high definition mid-wave forward looking infrared (FLIR), dual-mode laser, HDTV, laser spot tracker, laser marker, video data link, and a digital data recorder. Advanced image processing algorithms, combined with rock steady stabilization techniques, provide cutting-edge performance. The pod features automatic tracking and laser designation of tactical size targets via real-time imagery presented on cockpit displays. The Sniper pod is fully compatible with the latest J-series munitions for precision weapons delivery against multiple moving and fixed targets.
Advanced Targeting Pod – Sensor Enhancement (ATP-SE) design upgrades include enhanced sensors, advanced processors, and automated NTISR modes.
The Sniper pod’s architecture and modular design permits true two-level maintenance, eliminating costly intermediate-level support. Automated built-in test permits flightline maintainers to isolate and replace an LRU in under 20 minutes. Spares are ordered through a user-friendly website offering in-transit visibility to parts shipment.
The Sniper pod’s modular design also offers an affordable road map for modernizing and enhancing precision targeting capabilities for U.S. Air Force and coalition partner aircraft.
General characteristics
Primary function: positive identification, automatic tracking and laser designation, NTISR
Prime contractor: Lockheed Martin
Length: 98.2 inches (252 centimeters)
Diameter: 11.9 inches (30 centimeters)
Weight: 446 pounds (202 kilograms)
Aircraft: F-15E, F-16 Block 30/40/50, A-10, B-1
Sensors: high resolution FLIR and HDTV, dual mode laser designator, laser spot tracker and laser marker
Source af.mil
 © Swingwing Rafale equipped with the SNIPER Pod
© Swingwing Rafale equipped with the SNIPER Pod
Navigation and communications of Dassault Aviation’s Rafale
The communications suite on the Rafale uses the Saturn on-board V/UHF radio, which is a second-generation, anti-jam tactical UHF radio for Nato. Saturn provides voice encryption in fast-frequency hopping mode.
The aircraft is also equipped with fixed-frequency VHF / UHF radio for communications with civil air traffic control. A multifunction information distribution system (MIDS) terminal provides secure, high-data-rate tactical data exchange with Nato C2 stations, AWACS aircraft or naval ships.
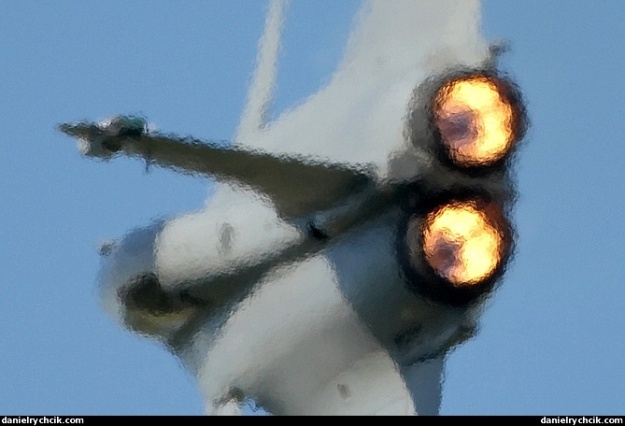
The Rafale is powered by two M88-2 engines, each providing a thrust of 75kN.
Rafale is equipped with a Thales TLS 2000 navigation receiver, which is used for the approach phase of flight. TLS 2000 integrates the instrument landing system (ILS), microwave landing system (MLS) and VHF omni-directional radio-ranger (VOR) and marker functions.
The radar altimeter is the AHV 17 altimeter from Thales, which is suitable for very low flight. The Rafale has a TACAN tactical air navigation receiver for en-route navigation and as a landing aid.
The Rafale has an SB25A combined interrogator-transponder developed by Thales. The SB25A is the first IFF using electronic scanning technology.
Rubis 3 Auxiliary Power Unit
The Rubis 3 Auxiliary Power Unit has been designed to meet the on-board power requirements of the Dassault Aviation Rafale multi-role combat aircraft, powered by Safran Aircraft Engines M88 engines.
Able to start the main engines on the ground or in flight, the Rubis 3 provides the aircraft with autonomy and increased safety.
The Rubis 3 has benefitted from continuous improvements since it came into service in order to exceed the needs of the customers in the most severe environments and conditions of use.
Providing power among the highest in the Safran Power Units range, the Rubis 3 delivers:
- the pneumatic power that is essential for quickly starting the main engines,
- the air-flow rate required to operate the air conditioning system of the cockpit and avionics,
- the electrical power over the on-board network, supplying power to a number of items of aircraft equipment.
 Rubis 3 Auxiliary Power Unit on left rear of aircraft
Rubis 3 Auxiliary Power Unit on left rear of aircraft
Rafale engines
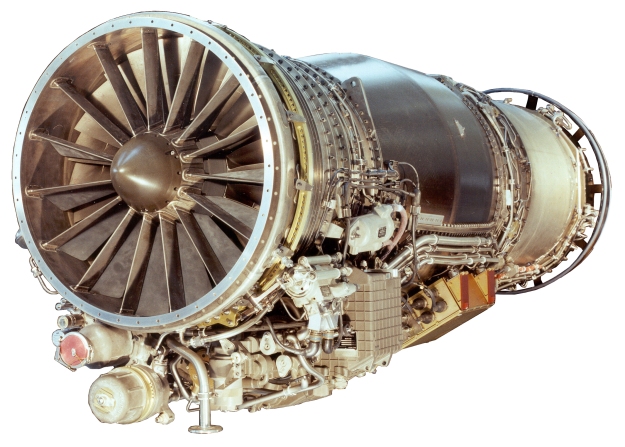
The Rafale is powered by two M88-2 engines from SNECMA, each providing a thrust of 75kN. The aircraft is equipped for buddy-buddy refuelling with a flight refuelling hose reel and drogue pack. The first M88 engine was delivered in 1996. It is a twin-shaft bypass turbofan engine principally suitable for low-altitude penetration and high-altitude interception missions.
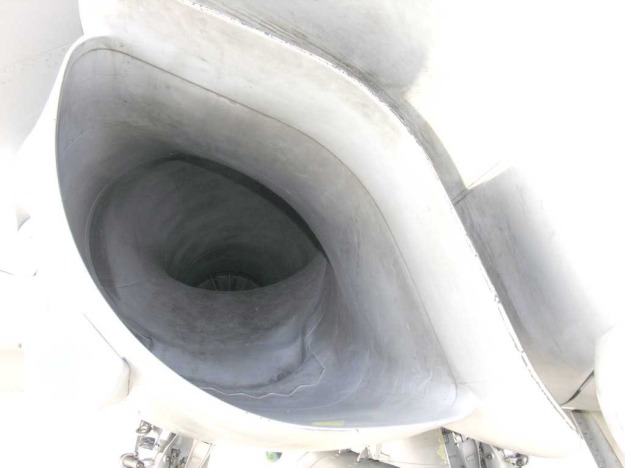 Air intakes have no moving parts
Air intakes have no moving parts
The M88 incorporates the latest technologies such as single-piece bladed compressor disks (blisks), an on-polluting combustion chamber, single-crystal high-pressure turbine blades, powder metallurgy disks, ceramic coatings and composite materials.
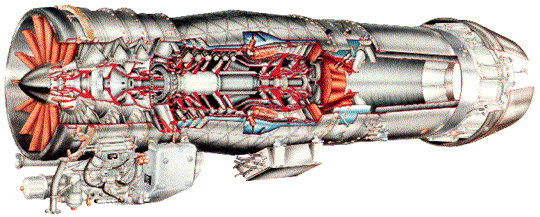 M88-2 engine – Image: ohio.edu
M88-2 engine – Image: ohio.edu
The M88 engine comprises a three-stage LP compressor with inlet guide vane, an annular combustion chamber, single-stage cooled HP turbine, single-stage cooled LP turbine, radial A/B chamber, variable-section convergent flap-type nozzle and full authority digital engine control (FADEC).
Messier-Dowty provides ‘jumper’ landing gear, designed to spring-out when the aircraft is catapulted by the nose gear strut.
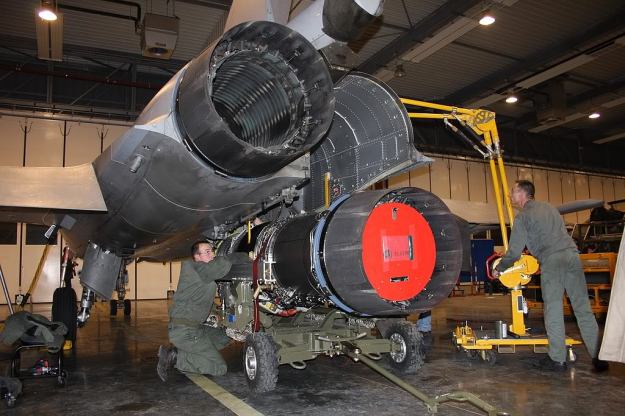

M88-4E upgrade
Keen to reduce total cost of ownership of the aircraft, DGA tapped M88 contractor Snecma to initiate the engine’s third major redesign. Known as the M88-4E, it eventually will replace the M88-2, Snecma’s second upgrade, which aimed to reduce maintenance costs by extending time between inspections of key components, such as the compressor and turbine.

Offering a low-emission combustor, single-crystal turbine blades and powder metallurgy disks, the M88-2 is designed to reduce Rafale’s electromagnetic and infrared signature. Incorporating a modular architecture, the engine can be quickly returned to service after maintenance as modules can be removed for repair or overhaul without grounding the aircraft. The M88-4E will further reduce the aircraft’s fuel consumption and augment the lifespan of critical engine parts—in particular the core and afterburner— reducing fuel burn by 2-4%.
DGA awarded Snecma a contract in January 2008 for 16 upgraded M88-2 engines, spare parts and repair services. The first ground test of the improved powerplant was performed in September 2009, with a first flight test in March 2010. The agency also invested €100 million in the project’s industrial ecosystem through Snecma. source aviationweek.com
IR signature Rafale vs F-22
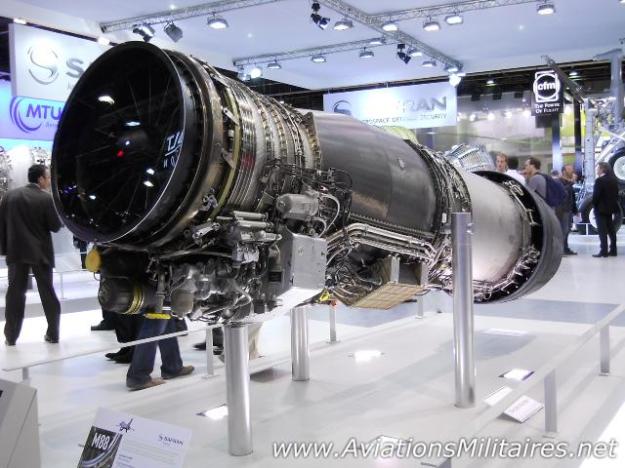
2 x SNECMA M88-2 engines
 M88-2 engines
M88-2 engines
To further improve fleet dispatch reliability, in 2012 Safran Aircraft Engines introduced a new production standard, the M88-4E, also dubbed the “TCO Package” (total cost of ownership), featuring critical parts with longer lifespans. The mean time between overhauls was increased from 2,500 to 4,000 cycles, or a 60% jump in time on wing. All modules on the M88-4E are fully interchangeable with those on the M88-2.
| Technical characteristics | |
| Thrust with afterburner (lbf) | 16,860 |
| Dry thrust (lbf) | 11,240 |
| Specific fuel consumption with afterburner [(lb/lbf.h)] | 1.66 |
| Specific fuel consumption without afterburner [(lb/lbf.h)] | 0.78 |
| Airflow rate (lb/s) | 143.30 |
| Turbine entry temperature (K) | 1,850 (2,870.6°F) |
| Pressure ratio | 24.50 |
| Bypass ratio | 0.30 |
| Length (in) | 139.29 |
| Inlet diameter (in) | 27.40 |
| Weight (lbs) | 1,977.55 |
Source safran-aircraft-engines.com

Variants
Rafale A
- Technology demonstrator, first flew in 1986.
Rafale D
- Dassault used this designation (D for discrète) in the early 1990s to emphasise the new semi-stealthy design features.
Rafale B
- Two-seater version for the French Air Force.
Rafale C
- Single-seat version for the French Air Force.
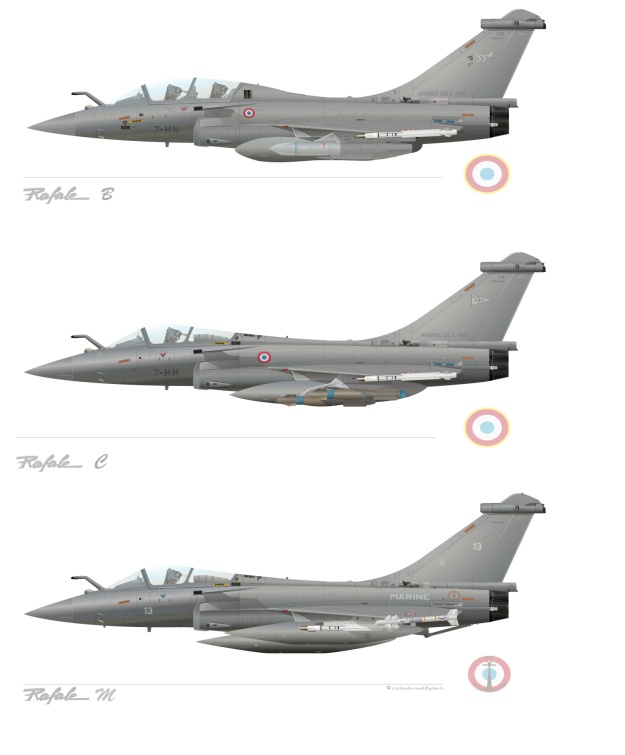 Image: wikiwand.com
Image: wikiwand.com
Rafale M
- Carrier-borne version for the French Naval Aviation, which entered service in 2001. For carrier operations, the M model has a strengthened airframe, longer nose gear leg to provide a more nose-up attitude, larger tailhook between the engines, and a built-in boarding ladder. Consequently, the Rafale M weighs about 500 kg (1,100 lb) more than the Rafale C. It is the only non-US fighter type cleared to operate from the decks of US carriers, using catapults and their arresting gear, as demonstrated in 2008 when six Rafales from Flottille 12F integrated into the USS Theodore Roosevelt Carrier Air Wing interoperability exercise.
Rafale N
- Originally called the Rafale BM, was a planned missile-only two-seater version for the Aéronavale. Budgetary and technical constraints have been cited as grounds for its cancellation.
Rafale R
- Proposed reconnaissance-oriented variant.
Rafale DM
- Two-seater version for the Egyptian Air Force.
Rafale EM
- Single-seat version for the Egyptian Air Force.
Rafale EH
- Single-seat version for the Indian Air Force.
Rafale DH
- Two-seat version for the Indian Air Force.
Operators: Here

Specifications and performance data:
| Dimensions: | |
| Wing span | 10.90 m |
| Length | 15.30 m |
| Height | 5.30 m |
| Weight: | |
| Overall empty weight | 10 t (22,000 lbs) class |
| Max. take-off weight | 24.5 t (54,000 lbs) |
| Fuel (internal) | 4.7 t (10,300 lbs) |
| Fuel (external) | up to 6.7 t (14,700 lbs) |
| External load | 9.5 t (21,000 lbs) |
| Store stations: | |
| Total | 14 |
| Heavy-wet | 5 |
| Performance: | |
| Max. thrust | 2 x 7.5 t |
| Limit load factors | -3.2 g / +9 g |
| Max. speed | M = 1.8 / 750 knots |
| Approach speed | less than 120 knots |
| Landing ground run | 450 m (1,500 ft) without drag-chute |
| Service ceiling | 50,000 ft |
Specification data dassault-aviation.com
Main material source airforce-technology.com
Revised Jun 17, 2017
Updated Jul 03, 2017


































Thank you for the information.Nice website.
LikeLike
Thanks
LikeLike